| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1163736 | Analytica Chimica Acta | 2015 | 8 Pages |
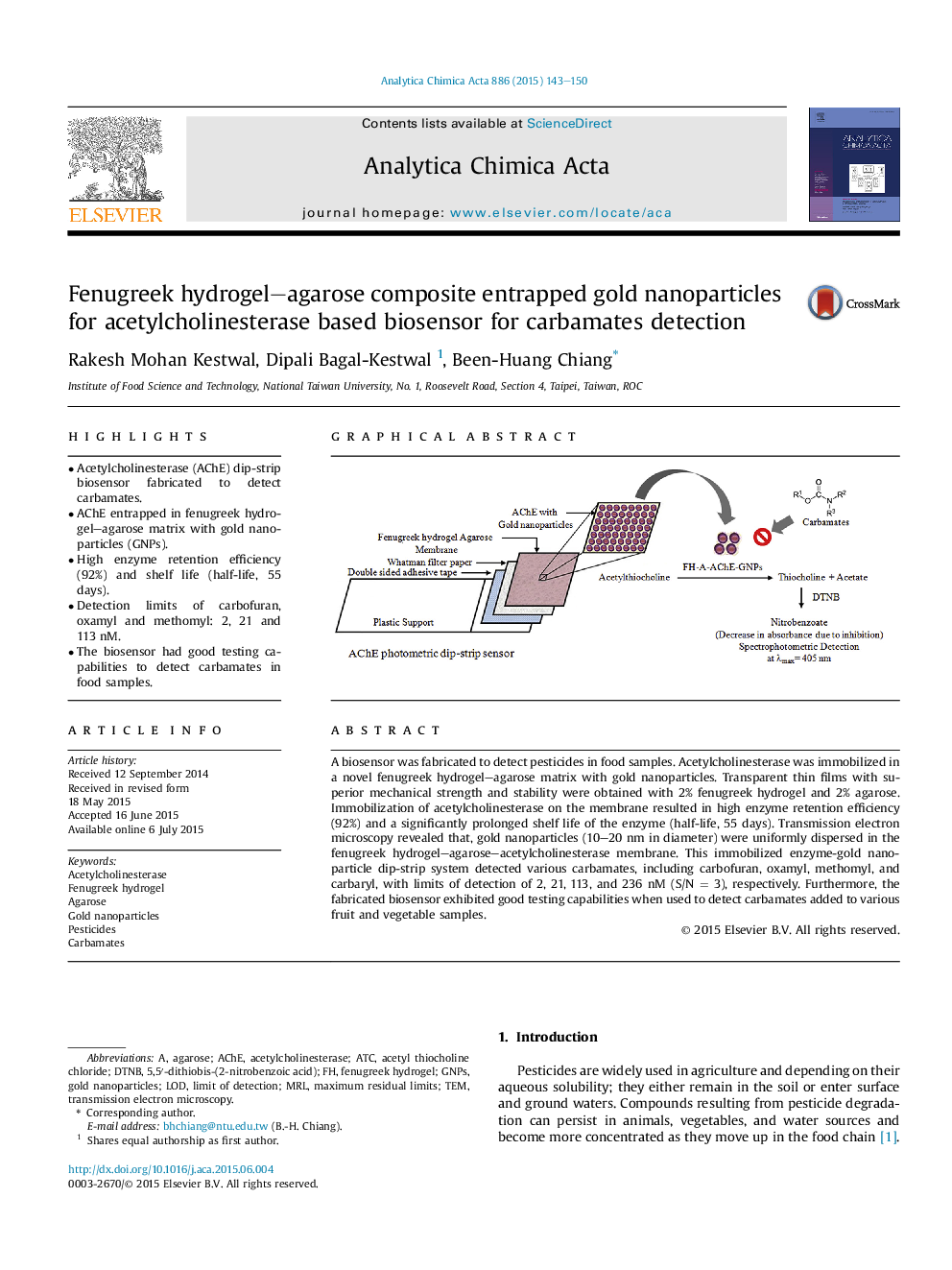
•Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) dip-strip biosensor fabricated to detect carbamates.•AChE entrapped in fenugreek hydrogel–agarose matrix with gold nanoparticles (GNPs).•High enzyme retention efficiency (92%) and shelf life (half-life, 55 days).•Detection limits of carbofuran, oxamyl and methomyl: 2, 21 and 113 nM.•The biosensor had good testing capabilities to detect carbamates in food samples.
A biosensor was fabricated to detect pesticides in food samples. Acetylcholinesterase was immobilized in a novel fenugreek hydrogel–agarose matrix with gold nanoparticles. Transparent thin films with superior mechanical strength and stability were obtained with 2% fenugreek hydrogel and 2% agarose. Immobilization of acetylcholinesterase on the membrane resulted in high enzyme retention efficiency (92%) and a significantly prolonged shelf life of the enzyme (half-life, 55 days). Transmission electron microscopy revealed that, gold nanoparticles (10–20 nm in diameter) were uniformly dispersed in the fenugreek hydrogel–agarose–acetylcholinesterase membrane. This immobilized enzyme-gold nanoparticle dip-strip system detected various carbamates, including carbofuran, oxamyl, methomyl, and carbaryl, with limits of detection of 2, 21, 113, and 236 nM (S/N = 3), respectively. Furthermore, the fabricated biosensor exhibited good testing capabilities when used to detect carbamates added to various fruit and vegetable samples.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide