| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1163909 | Analytica Chimica Acta | 2014 | 6 Pages |
•A novel electrochemical method has been established for hypoxia-inducible factor-1.•The sensitivity of the method surpasses that of current immunoassays.•The assay of placenta sample can be used to evaluate the severity of preeclampsia.
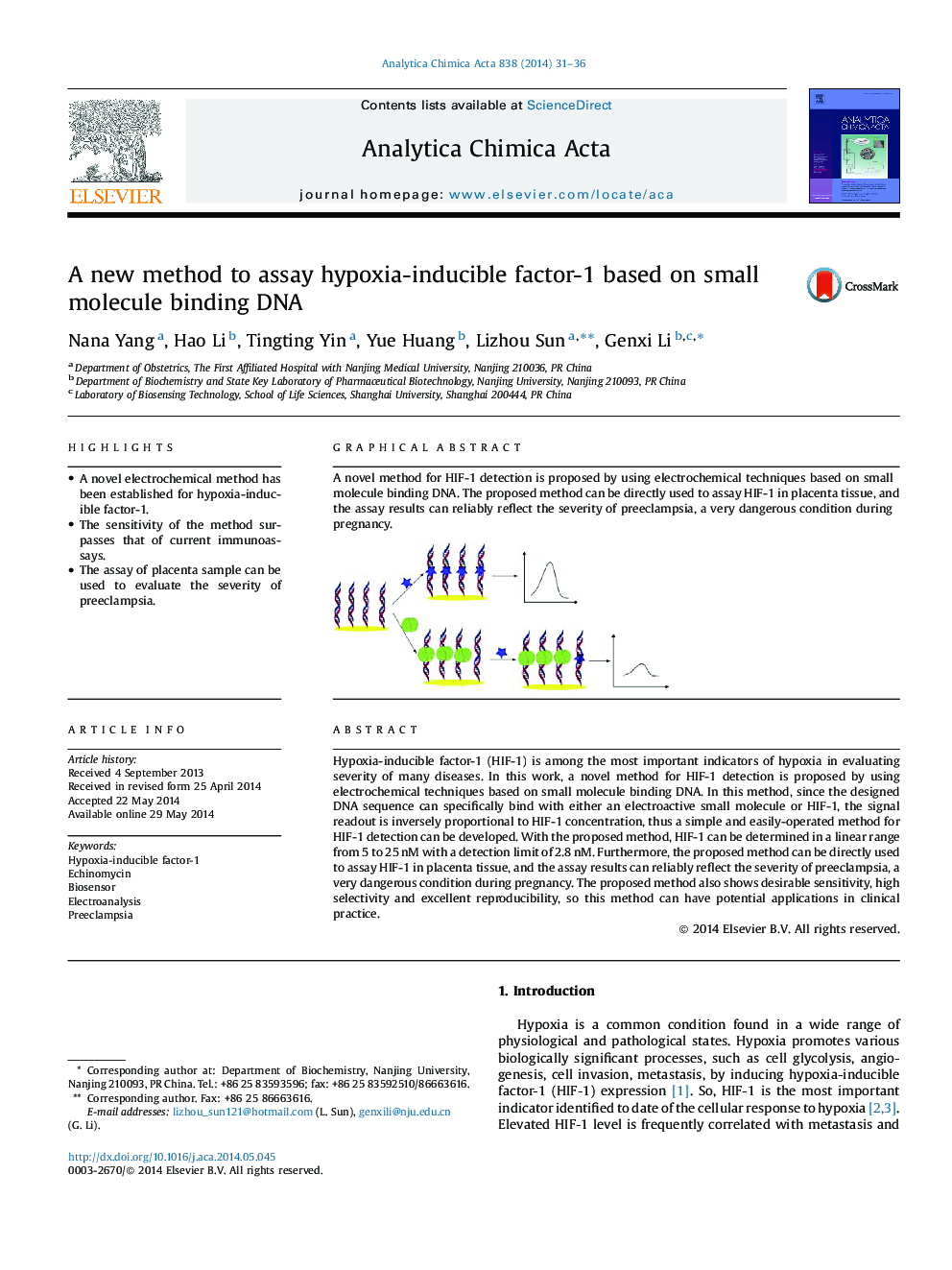
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1) is among the most important indicators of hypoxia in evaluating severity of many diseases. In this work, a novel method for HIF-1 detection is proposed by using electrochemical techniques based on small molecule binding DNA. In this method, since the designed DNA sequence can specifically bind with either an electroactive small molecule or HIF-1, the signal readout is inversely proportional to HIF-1 concentration, thus a simple and easily-operated method for HIF-1 detection can be developed. With the proposed method, HIF-1 can be determined in a linear range from 5 to 25 nM with a detection limit of 2.8 nM. Furthermore, the proposed method can be directly used to assay HIF-1 in placenta tissue, and the assay results can reliably reflect the severity of preeclampsia, a very dangerous condition during pregnancy. The proposed method also shows desirable sensitivity, high selectivity and excellent reproducibility, so this method can have potential applications in clinical practice.
Graphical abstractA novel method for HIF-1 detection is proposed by using electrochemical techniques based on small molecule binding DNA. The proposed method can be directly used to assay HIF-1 in placenta tissue, and the assay results can reliably reflect the severity of preeclampsia, a very dangerous condition during pregnancy.Figure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide