| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1163978 | Analytica Chimica Acta | 2015 | 9 Pages |
•Highly-controllable core–shell MIPs@SiO2–ZnS:Mn QDs were prepared.•The MIPs@SiO2–ZnS:Mn QDs integrated the advantages of molecular imprinting and QDs.•We used MIPs@SiO2–ZnS:Mn QDs as phosphorescence probes for detection of 2,4-DCP.•MIPs@SiO2–ZnS:Mn QDs were successfully applied to detect 2,4-DCP in real samples.
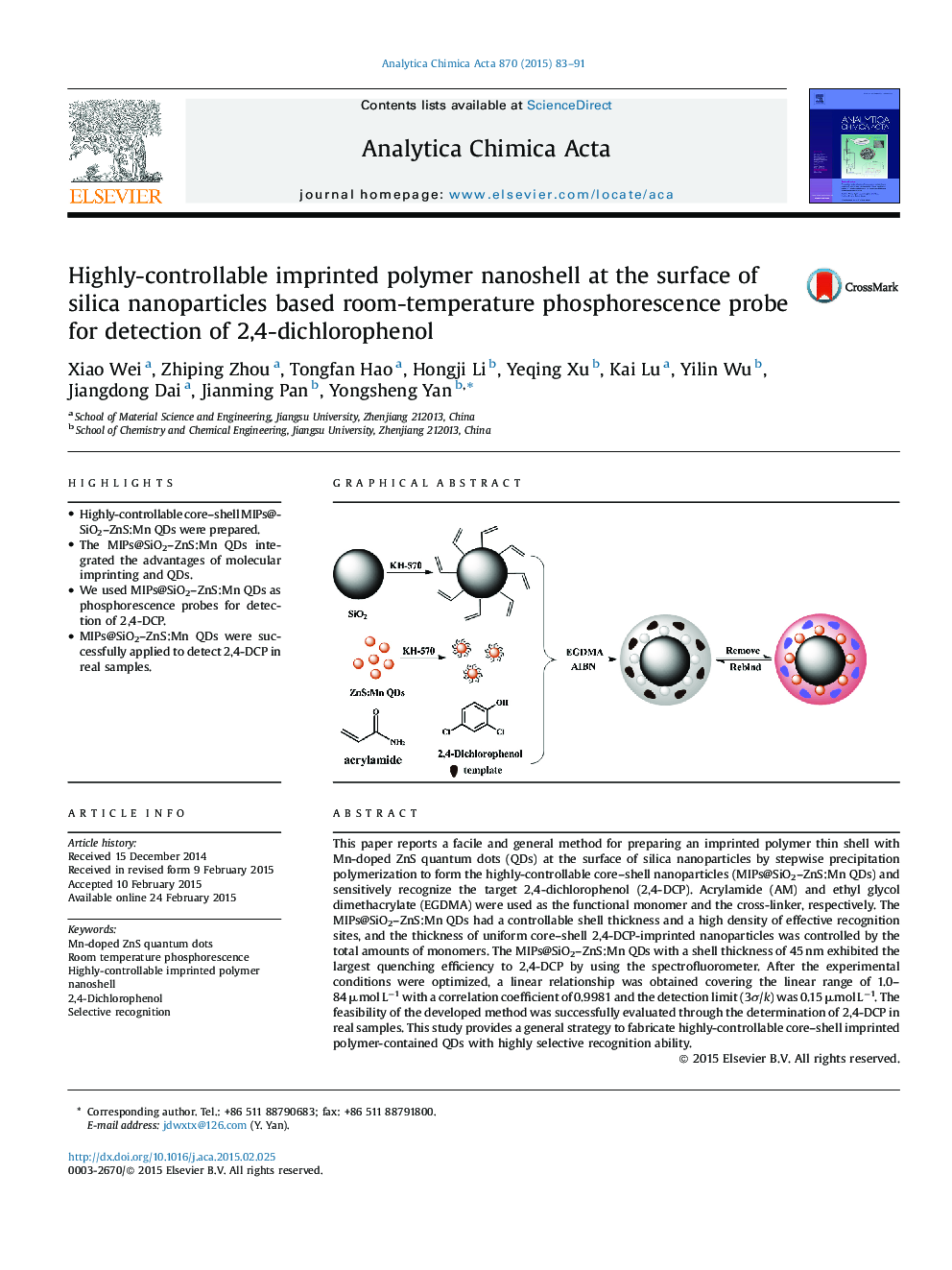
This paper reports a facile and general method for preparing an imprinted polymer thin shell with Mn-doped ZnS quantum dots (QDs) at the surface of silica nanoparticles by stepwise precipitation polymerization to form the highly-controllable core–shell nanoparticles (MIPs@SiO2–ZnS:Mn QDs) and sensitively recognize the target 2,4-dichlorophenol (2,4-DCP). Acrylamide (AM) and ethyl glycol dimethacrylate (EGDMA) were used as the functional monomer and the cross-linker, respectively. The MIPs@SiO2–ZnS:Mn QDs had a controllable shell thickness and a high density of effective recognition sites, and the thickness of uniform core–shell 2,4-DCP-imprinted nanoparticles was controlled by the total amounts of monomers. The MIPs@SiO2–ZnS:Mn QDs with a shell thickness of 45 nm exhibited the largest quenching efficiency to 2,4-DCP by using the spectrofluorometer. After the experimental conditions were optimized, a linear relationship was obtained covering the linear range of 1.0–84 μmol L−1 with a correlation coefficient of 0.9981 and the detection limit (3σ/k) was 0.15 μmol L−1. The feasibility of the developed method was successfully evaluated through the determination of 2,4-DCP in real samples. This study provides a general strategy to fabricate highly-controllable core–shell imprinted polymer-contained QDs with highly selective recognition ability.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide