| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1164209 | Analytica Chimica Acta | 2014 | 7 Pages |
•We report a novel colorimetric AuNP probe for detecting F− in environmental waters.•Most of the materials used in this method are cheap and available commercially.•The sensing of the probe rely on both hydrogen bond and specific chemical reaction.•The probe is able to accurately discriminate F− from a wide range of ions.•This study provides a new thought to develop superior AuNP probes.
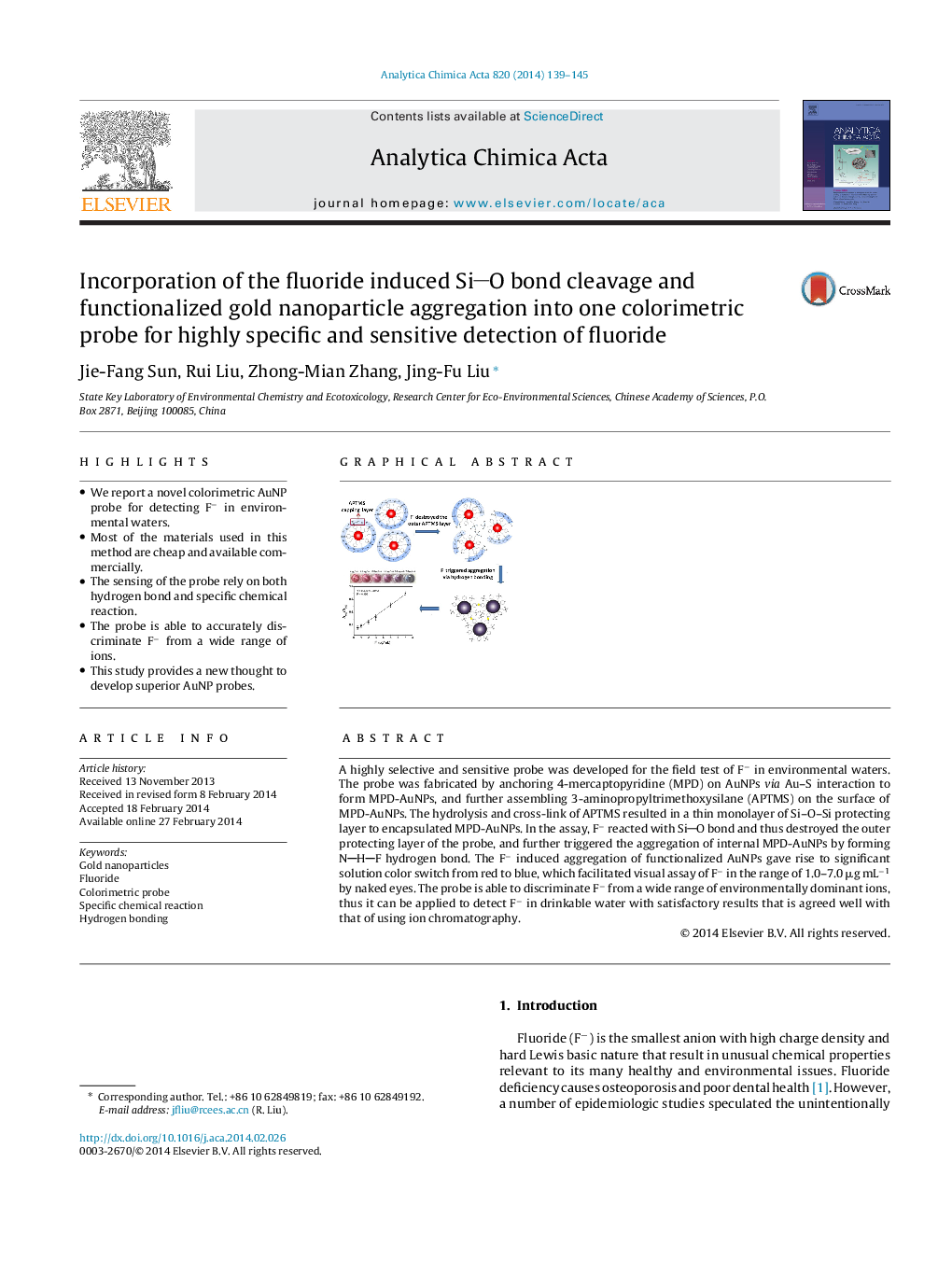
A highly selective and sensitive probe was developed for the field test of F− in environmental waters. The probe was fabricated by anchoring 4-mercaptopyridine (MPD) on AuNPs via Au–S interaction to form MPD-AuNPs, and further assembling 3-aminopropyltrimethoxysilane (APTMS) on the surface of MPD-AuNPs. The hydrolysis and cross-link of APTMS resulted in a thin monolayer of Si–O–Si protecting layer to encapsulated MPD-AuNPs. In the assay, F− reacted with SiO bond and thus destroyed the outer protecting layer of the probe, and further triggered the aggregation of internal MPD-AuNPs by forming NHF hydrogen bond. The F− induced aggregation of functionalized AuNPs gave rise to significant solution color switch from red to blue, which facilitated visual assay of F− in the range of 1.0–7.0 μg mL−1 by naked eyes. The probe is able to discriminate F− from a wide range of environmentally dominant ions, thus it can be applied to detect F− in drinkable water with satisfactory results that is agreed well with that of using ion chromatography.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide