| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1164626 | Analytica Chimica Acta | 2014 | 10 Pages |
•A new modified electrochemical sensor was constructed and used.•NiFe2O4/graphene was used as the modifier.•The sensor was used for the determination of tramadol and acetaminophen in real samples.•Modification improved the sensitivity and detection limit of the method.•The oxidation of tramadol and acetaminophen at the surface of the electrode was studied.
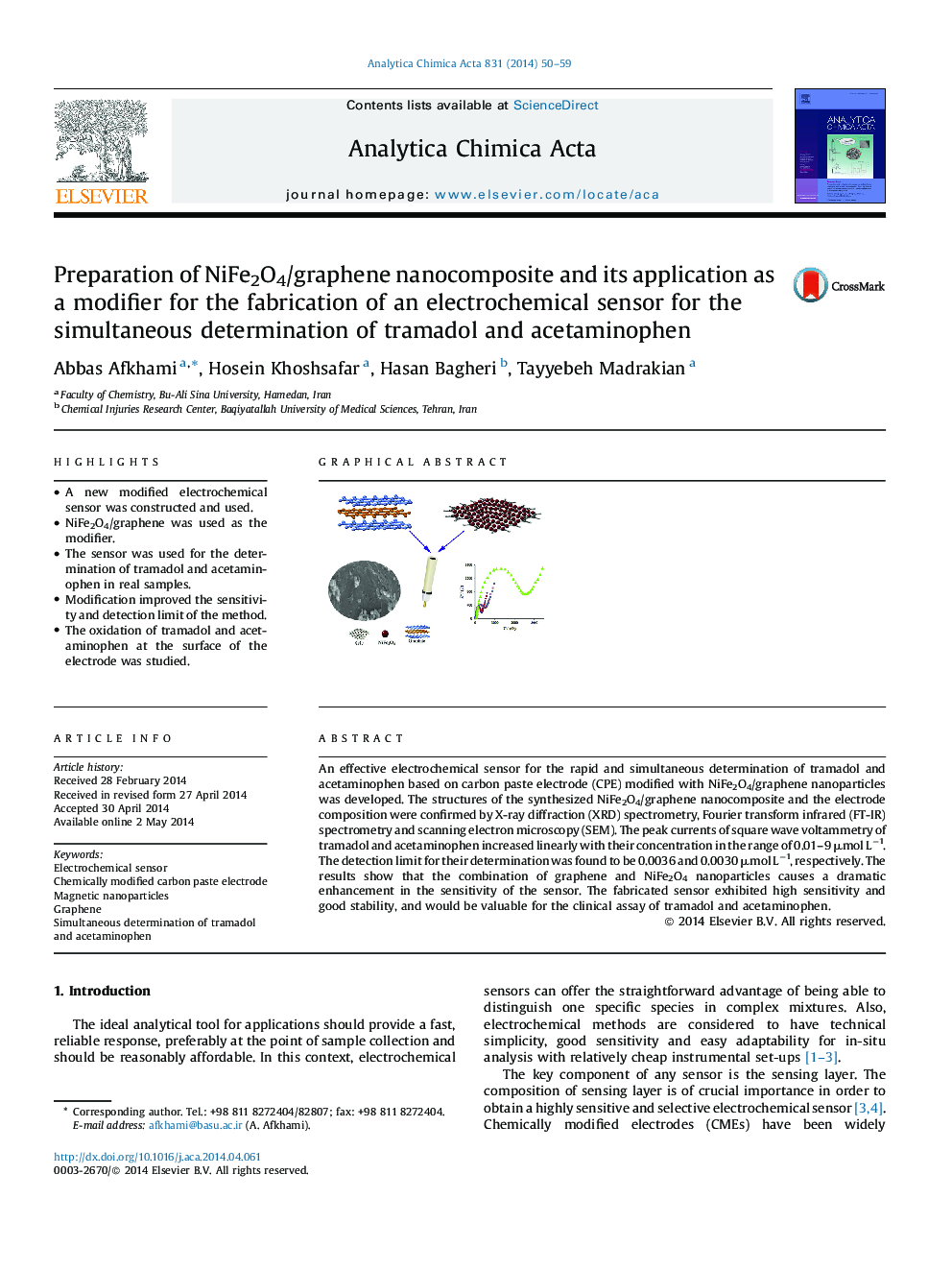
An effective electrochemical sensor for the rapid and simultaneous determination of tramadol and acetaminophen based on carbon paste electrode (CPE) modified with NiFe2O4/graphene nanoparticles was developed. The structures of the synthesized NiFe2O4/graphene nanocomposite and the electrode composition were confirmed by X-ray diffraction (XRD) spectrometry, Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectrometry and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The peak currents of square wave voltammetry of tramadol and acetaminophen increased linearly with their concentration in the range of 0.01–9 μmol L−1. The detection limit for their determination was found to be 0.0036 and 0.0030 μmol L−1, respectively. The results show that the combination of graphene and NiFe2O4 nanoparticles causes a dramatic enhancement in the sensitivity of the sensor. The fabricated sensor exhibited high sensitivity and good stability, and would be valuable for the clinical assay of tramadol and acetaminophen.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide