| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1164767 | Analytica Chimica Acta | 2013 | 7 Pages |
•A robust referencing schema for colorimetric indicators is proposed.•Time-resolved ratiometric read-out is realized.•(Photo)chemically stable inorganic phosphors are used.•The new method enables simple and low cost read-out set-up.•Application of the schema for sensing pH or carbon dioxide is demonstrated.
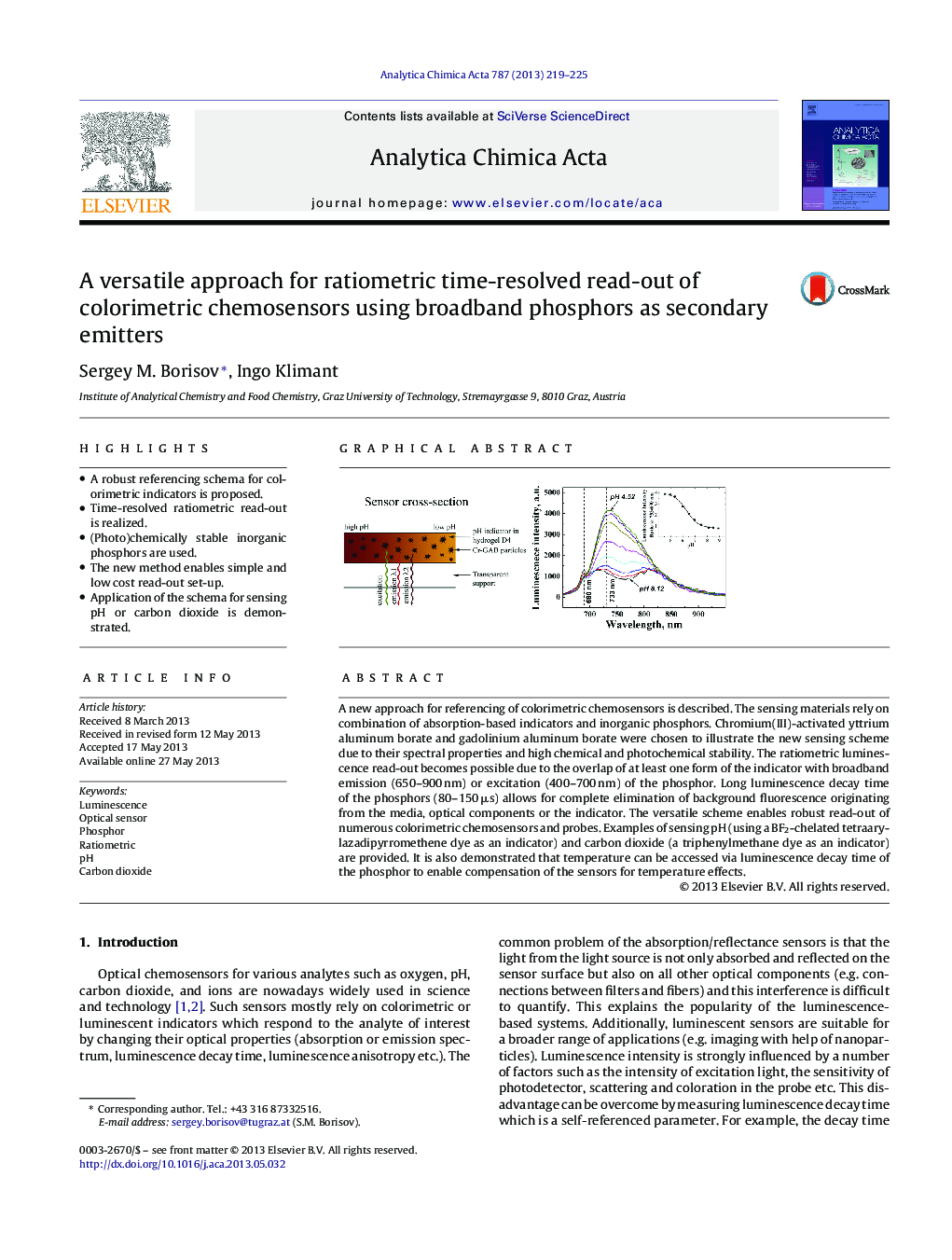
A new approach for referencing of colorimetric chemosensors is described. The sensing materials rely on combination of absorption-based indicators and inorganic phosphors. Chromium(III)-activated yttrium aluminum borate and gadolinium aluminum borate were chosen to illustrate the new sensing scheme due to their spectral properties and high chemical and photochemical stability. The ratiometric luminescence read-out becomes possible due to the overlap of at least one form of the indicator with broadband emission (650–900 nm) or excitation (400–700 nm) of the phosphor. Long luminescence decay time of the phosphors (80–150 μs) allows for complete elimination of background fluorescence originating from the media, optical components or the indicator. The versatile scheme enables robust read-out of numerous colorimetric chemosensors and probes. Examples of sensing pH (using a BF2-chelated tetraarylazadipyrromethene dye as an indicator) and carbon dioxide (a triphenylmethane dye as an indicator) are provided. It is also demonstrated that temperature can be accessed via luminescence decay time of the phosphor to enable compensation of the sensors for temperature effects.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide