| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1164929 | Analytica Chimica Acta | 2013 | 6 Pages |
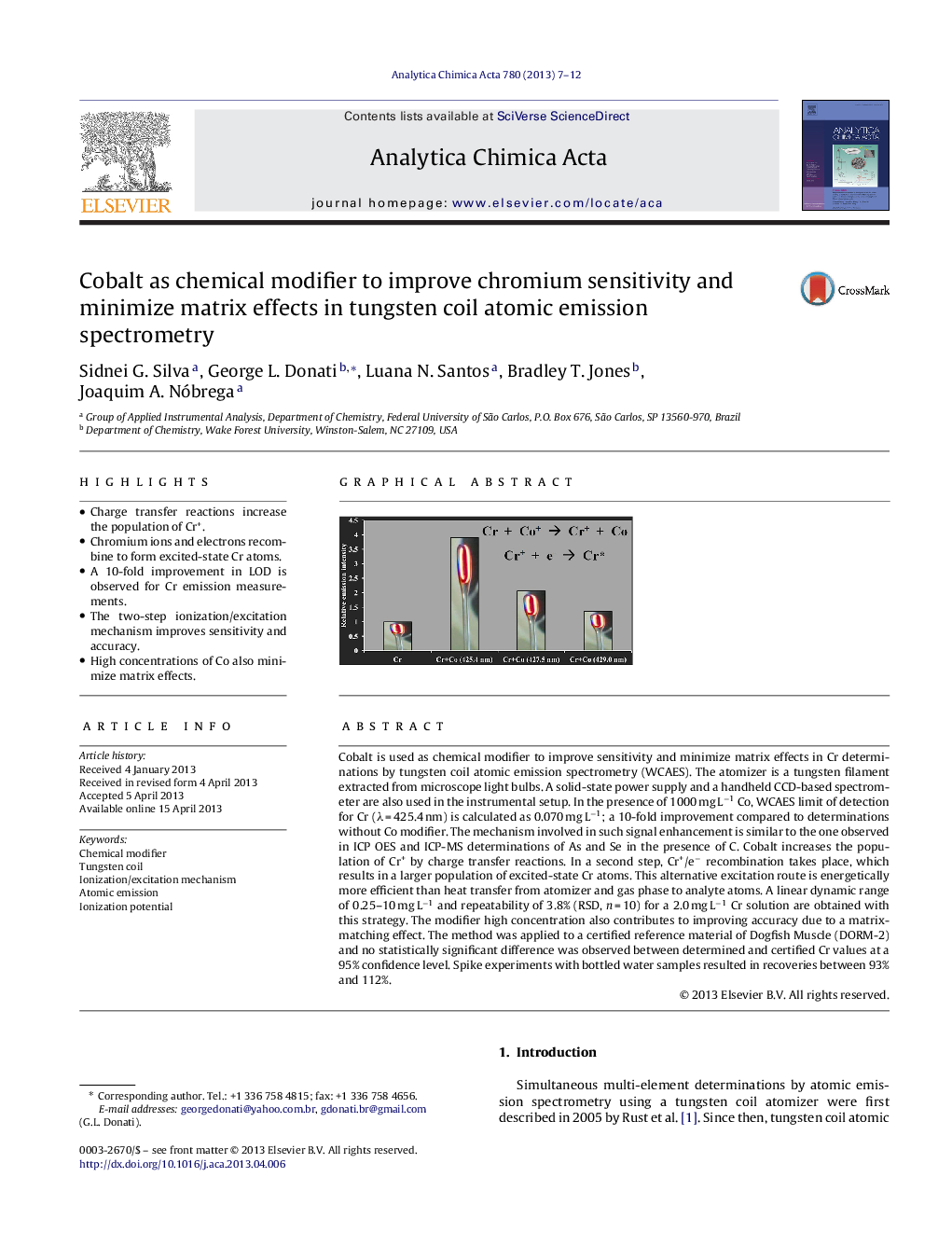
•Charge transfer reactions increase the population of Cr+.•Chromium ions and electrons recombine to form excited-state Cr atoms.•A 10-fold improvement in LOD is observed for Cr emission measurements.•The two-step ionization/excitation mechanism improves sensitivity and accuracy.•High concentrations of Co also minimize matrix effects.
Cobalt is used as chemical modifier to improve sensitivity and minimize matrix effects in Cr determinations by tungsten coil atomic emission spectrometry (WCAES). The atomizer is a tungsten filament extracted from microscope light bulbs. A solid-state power supply and a handheld CCD-based spectrometer are also used in the instrumental setup. In the presence of 1000 mg L−1 Co, WCAES limit of detection for Cr (λ = 425.4 nm) is calculated as 0.070 mg L−1; a 10-fold improvement compared to determinations without Co modifier. The mechanism involved in such signal enhancement is similar to the one observed in ICP OES and ICP-MS determinations of As and Se in the presence of C. Cobalt increases the population of Cr+ by charge transfer reactions. In a second step, Cr+/e− recombination takes place, which results in a larger population of excited-state Cr atoms. This alternative excitation route is energetically more efficient than heat transfer from atomizer and gas phase to analyte atoms. A linear dynamic range of 0.25–10 mg L−1 and repeatability of 3.8% (RSD, n = 10) for a 2.0 mg L−1 Cr solution are obtained with this strategy. The modifier high concentration also contributes to improving accuracy due to a matrix-matching effect. The method was applied to a certified reference material of Dogfish Muscle (DORM-2) and no statistically significant difference was observed between determined and certified Cr values at a 95% confidence level. Spike experiments with bottled water samples resulted in recoveries between 93% and 112%.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide