| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1165145 | Analytica Chimica Acta | 2012 | 5 Pages |
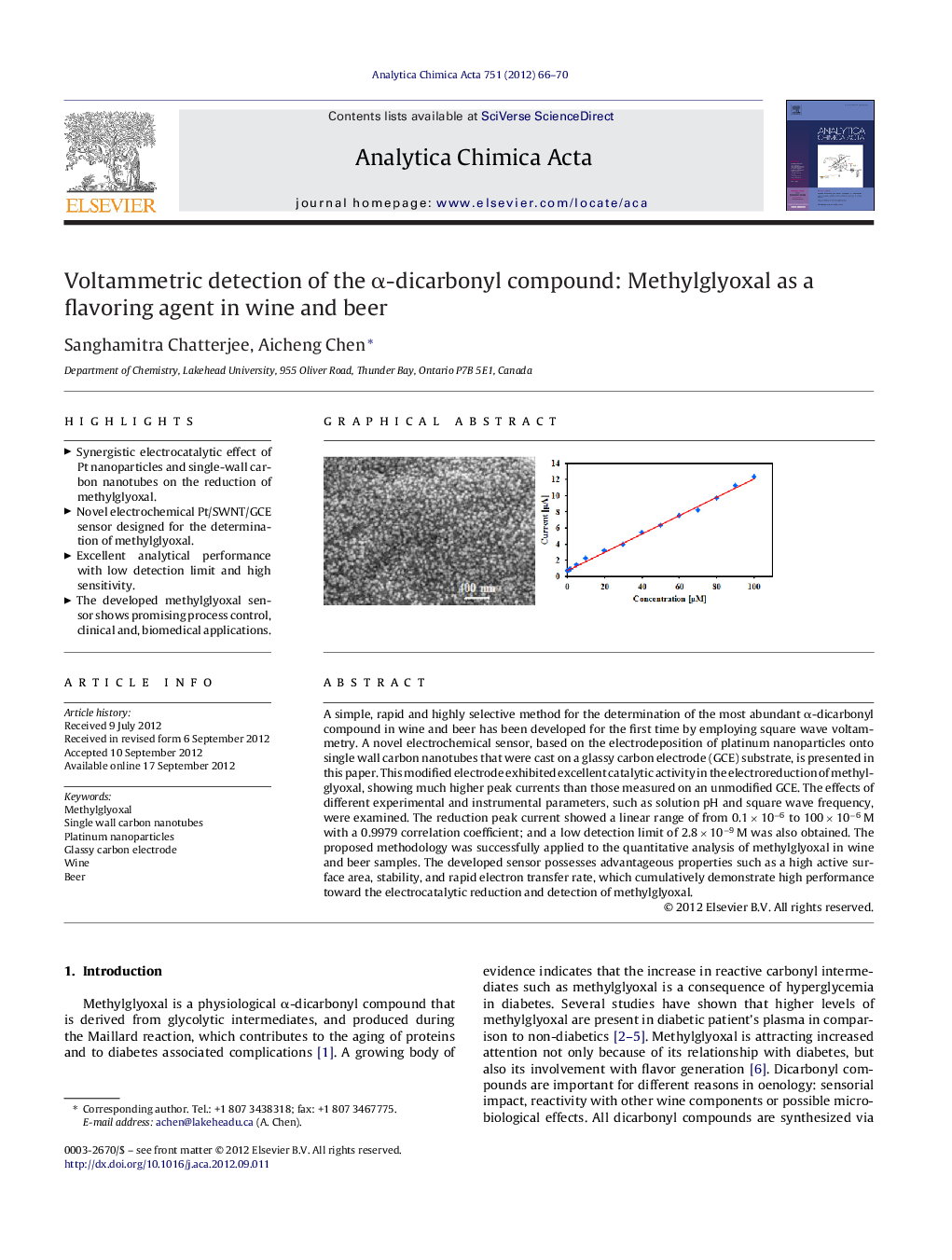
A simple, rapid and highly selective method for the determination of the most abundant α-dicarbonyl compound in wine and beer has been developed for the first time by employing square wave voltammetry. A novel electrochemical sensor, based on the electrodeposition of platinum nanoparticles onto single wall carbon nanotubes that were cast on a glassy carbon electrode (GCE) substrate, is presented in this paper. This modified electrode exhibited excellent catalytic activity in the electroreduction of methylglyoxal, showing much higher peak currents than those measured on an unmodified GCE. The effects of different experimental and instrumental parameters, such as solution pH and square wave frequency, were examined. The reduction peak current showed a linear range of from 0.1 × 10−6 to 100 × 10−6 M with a 0.9979 correlation coefficient; and a low detection limit of 2.8 × 10−9 M was also obtained. The proposed methodology was successfully applied to the quantitative analysis of methylglyoxal in wine and beer samples. The developed sensor possesses advantageous properties such as a high active surface area, stability, and rapid electron transfer rate, which cumulatively demonstrate high performance toward the electrocatalytic reduction and detection of methylglyoxal.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights► Synergistic electrocatalytic effect of Pt nanoparticles and single-wall carbon nanotubes on the reduction of methylglyoxal. ► Novel electrochemical Pt/SWNT/GCE sensor designed for the determination of methylglyoxal. ► Excellent analytical performance with low detection limit and high sensitivity. ► The developed methylglyoxal sensor shows promising process control, clinical and, biomedical applications.