| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1165225 | Analytica Chimica Acta | 2013 | 6 Pages |
•An effective approach has been developed for T-cell epitopes prediction.•A combined feature has been provided to show significant improvement in accuracy.•Random forest provides some useful tools to select informative features and make classification simultaneously.•A freely available web server of for predicting peptide immunogenicity is established.
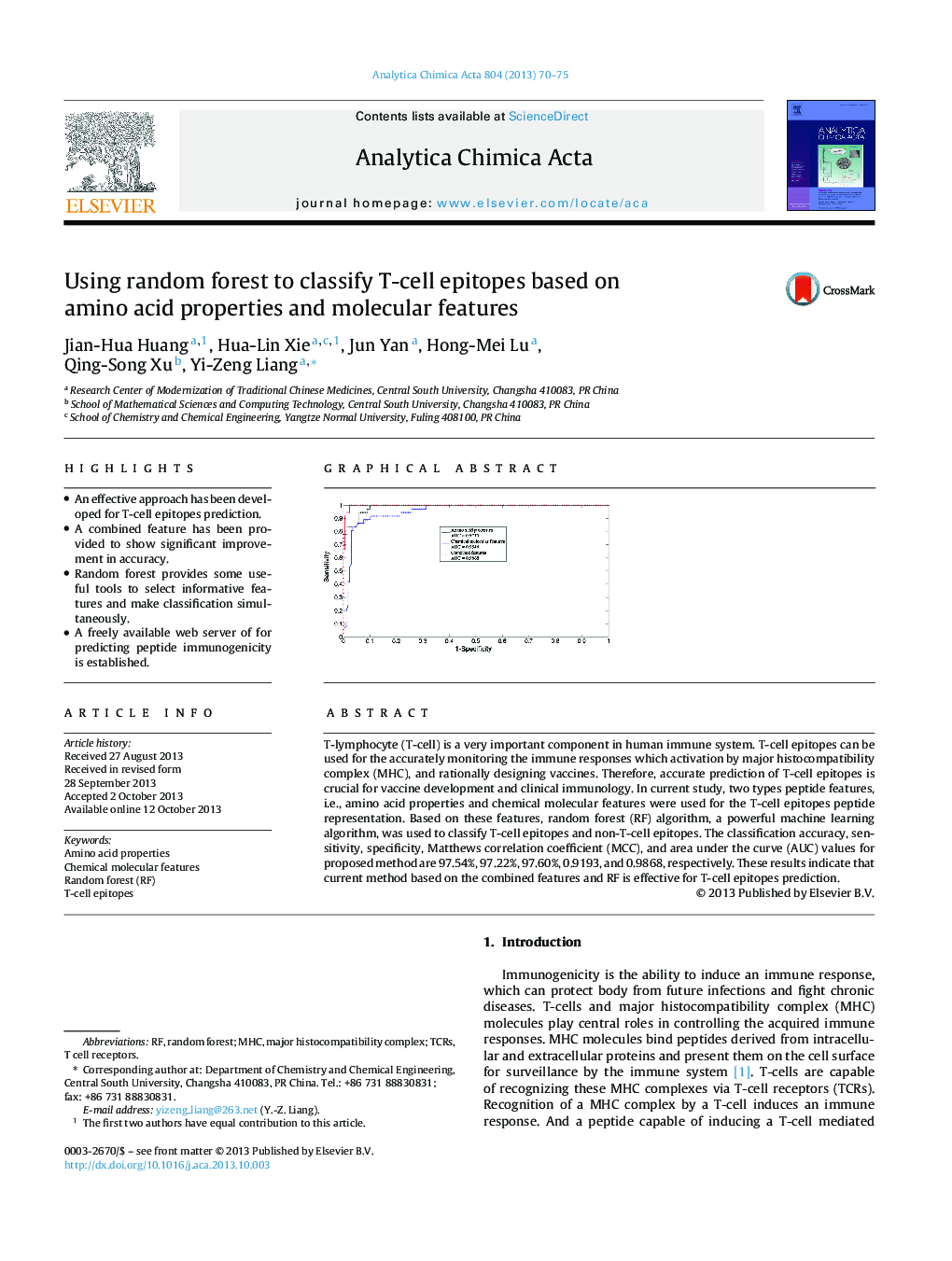
T-lymphocyte (T-cell) is a very important component in human immune system. T-cell epitopes can be used for the accurately monitoring the immune responses which activation by major histocompatibility complex (MHC), and rationally designing vaccines. Therefore, accurate prediction of T-cell epitopes is crucial for vaccine development and clinical immunology. In current study, two types peptide features, i.e., amino acid properties and chemical molecular features were used for the T-cell epitopes peptide representation. Based on these features, random forest (RF) algorithm, a powerful machine learning algorithm, was used to classify T-cell epitopes and non-T-cell epitopes. The classification accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, Matthews correlation coefficient (MCC), and area under the curve (AUC) values for proposed method are 97.54%, 97.22%, 97.60%, 0.9193, and 0.9868, respectively. These results indicate that current method based on the combined features and RF is effective for T-cell epitopes prediction.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide