| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1165962 | Analytica Chimica Acta | 2013 | 7 Pages |
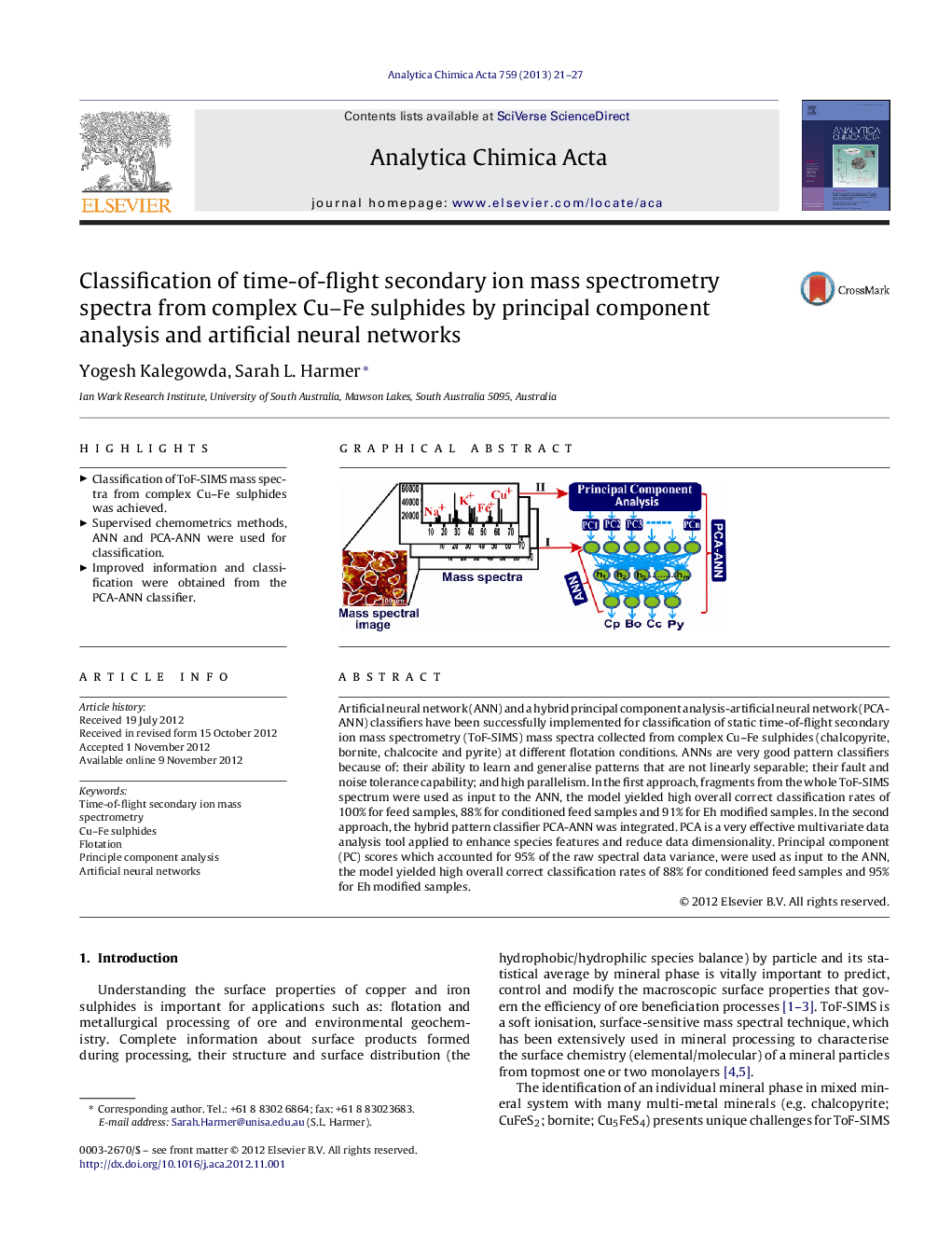
Artificial neural network (ANN) and a hybrid principal component analysis-artificial neural network (PCA-ANN) classifiers have been successfully implemented for classification of static time-of-flight secondary ion mass spectrometry (ToF-SIMS) mass spectra collected from complex Cu–Fe sulphides (chalcopyrite, bornite, chalcocite and pyrite) at different flotation conditions. ANNs are very good pattern classifiers because of: their ability to learn and generalise patterns that are not linearly separable; their fault and noise tolerance capability; and high parallelism. In the first approach, fragments from the whole ToF-SIMS spectrum were used as input to the ANN, the model yielded high overall correct classification rates of 100% for feed samples, 88% for conditioned feed samples and 91% for Eh modified samples. In the second approach, the hybrid pattern classifier PCA-ANN was integrated. PCA is a very effective multivariate data analysis tool applied to enhance species features and reduce data dimensionality. Principal component (PC) scores which accounted for 95% of the raw spectral data variance, were used as input to the ANN, the model yielded high overall correct classification rates of 88% for conditioned feed samples and 95% for Eh modified samples.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights► Classification of ToF-SIMS mass spectra from complex Cu–Fe sulphides was achieved. ► Supervised chemometrics methods, ANN and PCA-ANN were used for classification. ► Improved information and classification were obtained from the PCA-ANN classifier.