| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1166095 | Analytica Chimica Acta | 2012 | 9 Pages |
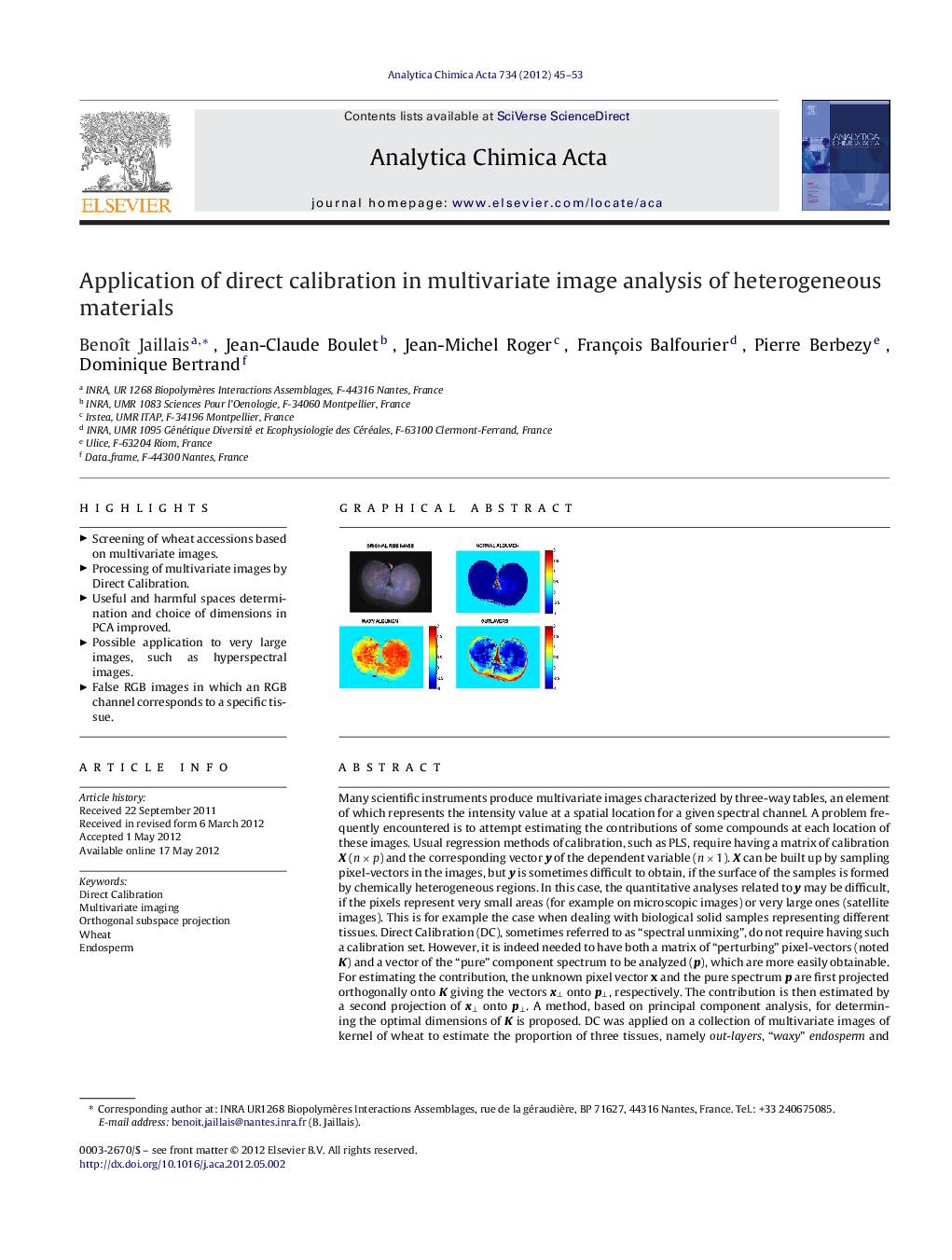
Many scientific instruments produce multivariate images characterized by three-way tables, an element of which represents the intensity value at a spatial location for a given spectral channel. A problem frequently encountered is to attempt estimating the contributions of some compounds at each location of these images. Usual regression methods of calibration, such as PLS, require having a matrix of calibration X (n × p) and the corresponding vector y of the dependent variable (n × 1). X can be built up by sampling pixel-vectors in the images, but y is sometimes difficult to obtain, if the surface of the samples is formed by chemically heterogeneous regions. In this case, the quantitative analyses related to y may be difficult, if the pixels represent very small areas (for example on microscopic images) or very large ones (satellite images). This is for example the case when dealing with biological solid samples representing different tissues. Direct Calibration (DC), sometimes referred to as “spectral unmixing”, do not require having such a calibration set. However, it is indeed needed to have both a matrix of “perturbing” pixel-vectors (noted K) and a vector of the “pure” component spectrum to be analyzed (p), which are more easily obtainable. For estimating the contribution, the unknown pixel vector x and the pure spectrum p are first projected orthogonally onto K giving the vectors x⊥ onto p⊥, respectively. The contribution is then estimated by a second projection of x⊥ onto p⊥. A method, based on principal component analysis, for determining the optimal dimensions of K is proposed. DC was applied on a collection of multivariate images of kernel of wheat to estimate the proportion of three tissues, namely out-layers, “waxy” endosperm and normal endosperm. The eventual results are presented as images of wheat kernels in false colors associated to the estimated proportions of the tissues. It is shown that DC is appropriate for estimating contributions in situations in which the more usual methods of calibration cannot be applied.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights► Screening of wheat accessions based on multivariate images. ► Processing of multivariate images by Direct Calibration. ► Useful and harmful spaces determination and choice of dimensions in PCA improved. ► Possible application to very large images, such as hyperspectral images. ► False RGB images in which an RGB channel corresponds to a specific tissue.