| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1167048 | Analytica Chimica Acta | 2011 | 7 Pages |
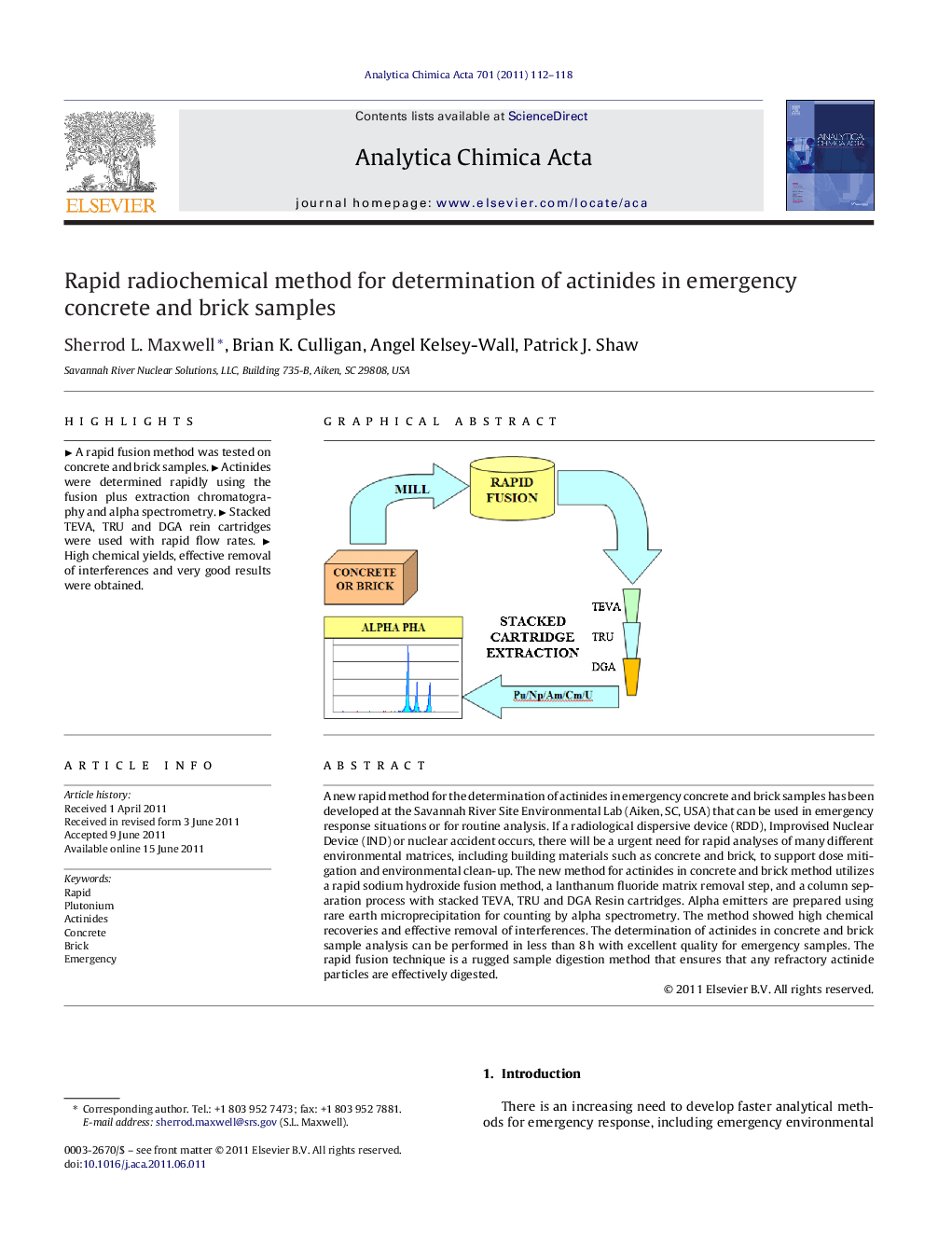
A new rapid method for the determination of actinides in emergency concrete and brick samples has been developed at the Savannah River Site Environmental Lab (Aiken, SC, USA) that can be used in emergency response situations or for routine analysis. If a radiological dispersive device (RDD), Improvised Nuclear Device (IND) or nuclear accident occurs, there will be a urgent need for rapid analyses of many different environmental matrices, including building materials such as concrete and brick, to support dose mitigation and environmental clean-up. The new method for actinides in concrete and brick method utilizes a rapid sodium hydroxide fusion method, a lanthanum fluoride matrix removal step, and a column separation process with stacked TEVA, TRU and DGA Resin cartridges. Alpha emitters are prepared using rare earth microprecipitation for counting by alpha spectrometry. The method showed high chemical recoveries and effective removal of interferences. The determination of actinides in concrete and brick sample analysis can be performed in less than 8 h with excellent quality for emergency samples. The rapid fusion technique is a rugged sample digestion method that ensures that any refractory actinide particles are effectively digested.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights► A rapid fusion method was tested on concrete and brick samples. ► Actinides were determined rapidly using the fusion plus extraction chromatography and alpha spectrometry. ► Stacked TEVA, TRU and DGA rein cartridges were used with rapid flow rates. ► High chemical yields, effective removal of interferences and very good results were obtained.