| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1402011 | Journal of Molecular Structure | 2015 | 7 Pages |
•Three new complexes involving thiophenepropionate, 1,2-bis(4-pyridyl) ethane and Cu and Zn ions.•The complexes present 2-D (Cu compound) and 3-D (Zn compounds) coordination polymers.•The Zn compound 3 present supramolecular interactions involving π-stacking.•Raman and infrared spectra confirm the geometries of coordination for the complexes.
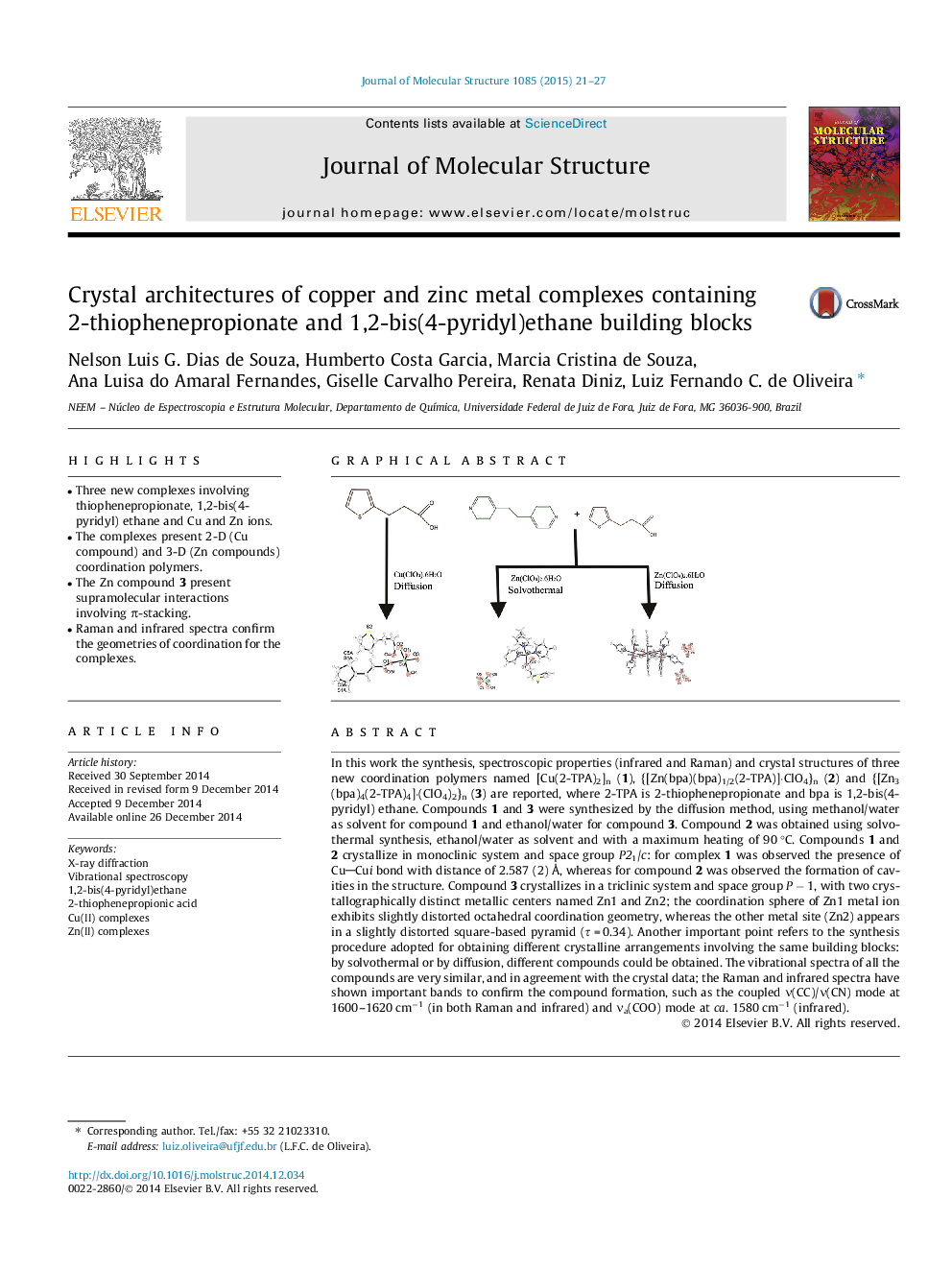
In this work the synthesis, spectroscopic properties (infrared and Raman) and crystal structures of three new coordination polymers named [Cu(2-TPA)2]n (1), {[Zn(bpa)(bpa)1/2(2-TPA)]⋅ClO4}n (2) and {[Zn3(bpa)4(2-TPA)4]⋅(ClO4)2}n (3) are reported, where 2-TPA is 2-thiophenepropionate and bpa is 1,2-bis(4-pyridyl) ethane. Compounds 1 and 3 were synthesized by the diffusion method, using methanol/water as solvent for compound 1 and ethanol/water for compound 3. Compound 2 was obtained using solvo-thermal synthesis, ethanol/water as solvent and with a maximum heating of 90 °C. Compounds 1 and 2 crystallize in monoclinic system and space group P21/c: for complex 1 was observed the presence of CuCui bond with distance of 2.587 (2) Å, whereas for compound 2 was observed the formation of cavities in the structure. Compound 3 crystallizes in a triclinic system and space group P − 1, with two crystallographically distinct metallic centers named Zn1 and Zn2; the coordination sphere of Zn1 metal ion exhibits slightly distorted octahedral coordination geometry, whereas the other metal site (Zn2) appears in a slightly distorted square-based pyramid (τ = 0.34). Another important point refers to the synthesis procedure adopted for obtaining different crystalline arrangements involving the same building blocks: by solvothermal or by diffusion, different compounds could be obtained. The vibrational spectra of all the compounds are very similar, and in agreement with the crystal data; the Raman and infrared spectra have shown important bands to confirm the compound formation, such as the coupled ν(CC)/ν(CN) mode at 1600–1620 cm−1 (in both Raman and infrared) and νa(COO) mode at ca. 1580 cm−1 (infrared).
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide