| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1402018 | Journal of Molecular Structure | 2015 | 6 Pages |
•We endeavored to discovery plumbagin bioisostere as herbicide targeting to AtKAPAS.•The metabolic site of plumbagin was identified.•Compound library was filtered by performing a similarity-based virtual screeening.
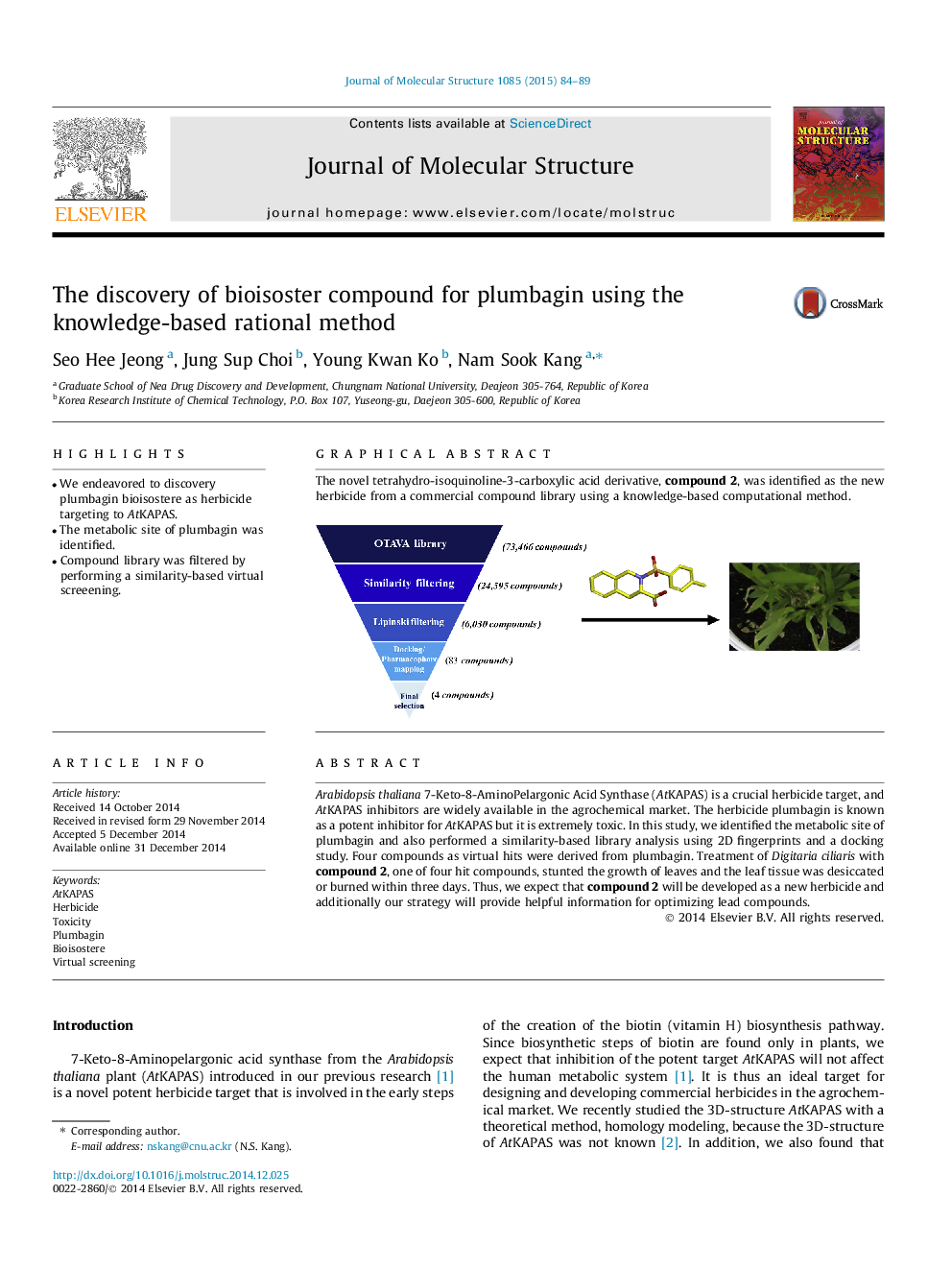
Arabidopsis thaliana 7-Keto-8-AminoPelargonic Acid Synthase (AtKAPAS) is a crucial herbicide target, and AtKAPAS inhibitors are widely available in the agrochemical market. The herbicide plumbagin is known as a potent inhibitor for AtKAPAS but it is extremely toxic. In this study, we identified the metabolic site of plumbagin and also performed a similarity-based library analysis using 2D fingerprints and a docking study. Four compounds as virtual hits were derived from plumbagin. Treatment of Digitaria ciliaris with compound 2, one of four hit compounds, stunted the growth of leaves and the leaf tissue was desiccated or burned within three days. Thus, we expect that compound 2 will be developed as a new herbicide and additionally our strategy will provide helpful information for optimizing lead compounds.
Graphical abstractThe novel tetrahydro-isoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid derivative, compound 2, was identified as the new herbicide from a commercial compound library using a knowledge-based computational method.Figure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide