| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1402135 | Journal of Molecular Structure | 2015 | 7 Pages |
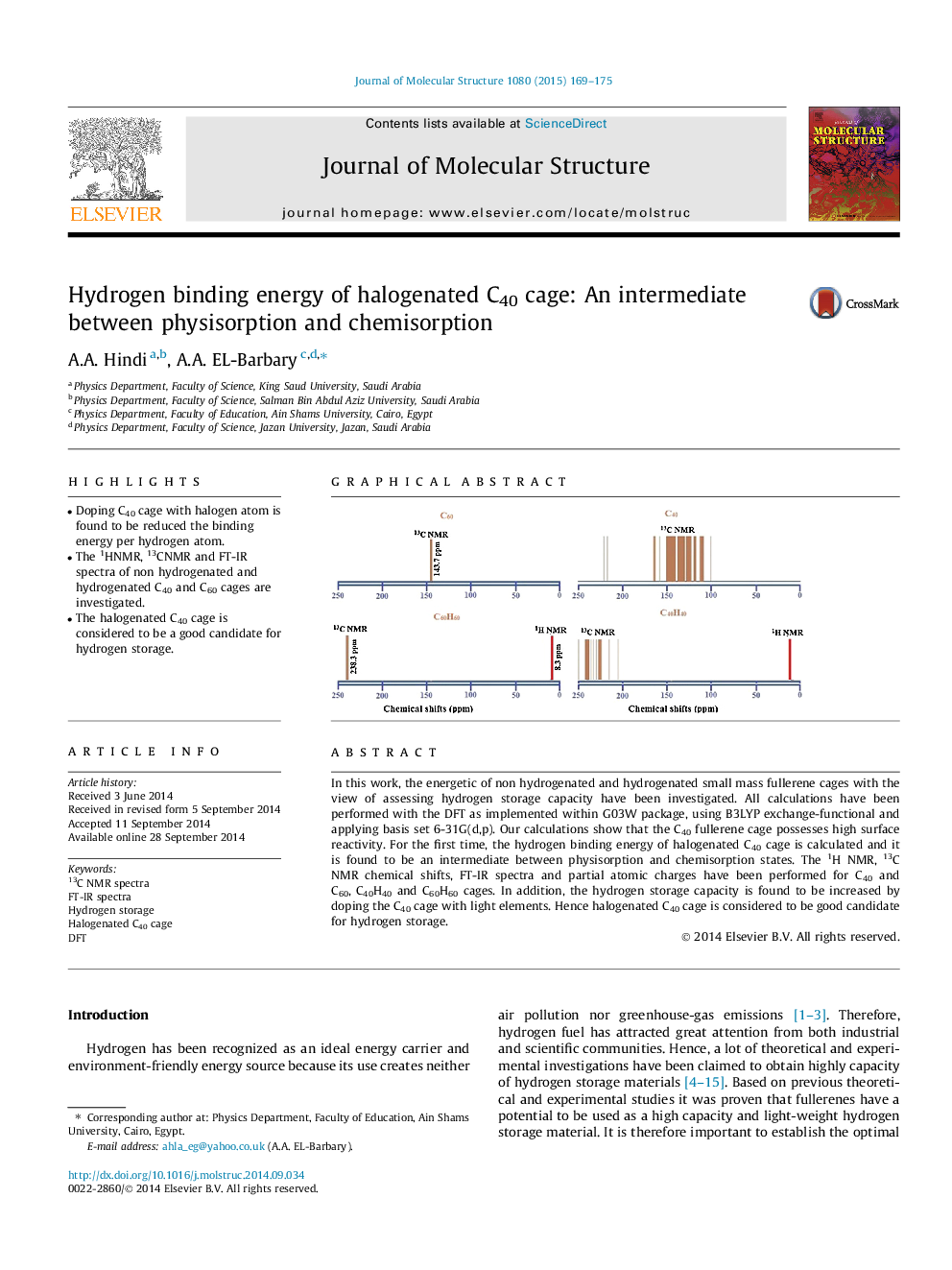
•Doping C40 cage with halogen atom is found to be reduced the binding energy per hydrogen atom.•The 1HNMR, 13CNMR and FT-IR spectra of non hydrogenated and hydrogenated C40 and C60 cages are investigated.•The halogenated C40 cage is considered to be a good candidate for hydrogen storage.
In this work, the energetic of non hydrogenated and hydrogenated small mass fullerene cages with the view of assessing hydrogen storage capacity have been investigated. All calculations have been performed with the DFT as implemented within G03W package, using B3LYP exchange-functional and applying basis set 6-31G(d,p). Our calculations show that the C40 fullerene cage possesses high surface reactivity. For the first time, the hydrogen binding energy of halogenated C40 cage is calculated and it is found to be an intermediate between physisorption and chemisorption states. The 1H NMR, 13C NMR chemical shifts, FT-IR spectra and partial atomic charges have been performed for C40 and C60, C40H40 and C60H60 cages. In addition, the hydrogen storage capacity is found to be increased by doping the C40 cage with light elements. Hence halogenated C40 cage is considered to be good candidate for hydrogen storage.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide