| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1402399 | Journal of Molecular Structure | 2014 | 7 Pages |
•Optical properties of Sm3+:K–Ca–Li fluorophosphate glasses have been prepared.•Characterized the structural and optical properties of the investigated glasses.•Non-exponential decay rates revealed the presence of dipole–dipole interactions.•The studied fluorophosphates glasses exhibit good thermal stability.
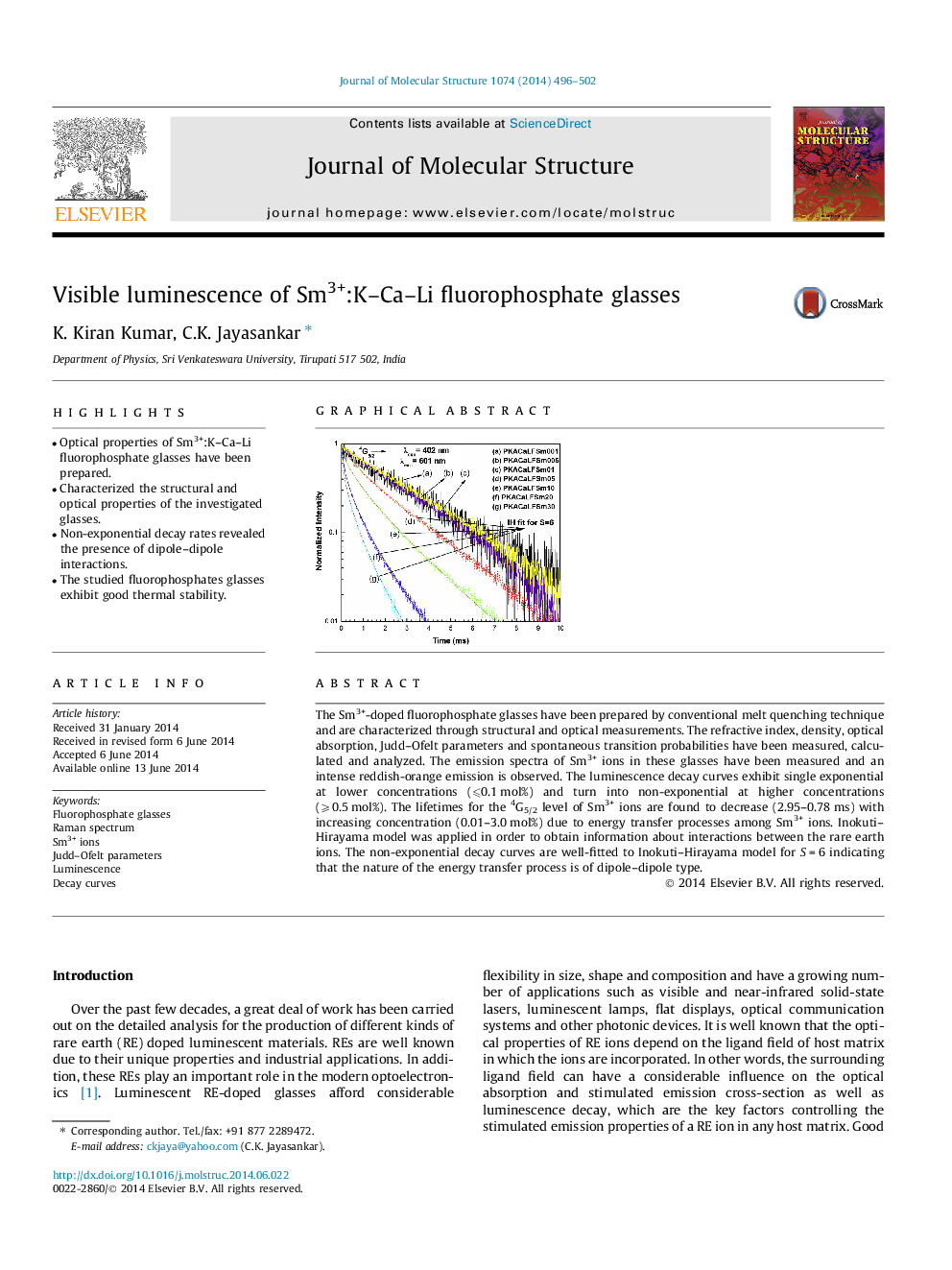
The Sm3+-doped fluorophosphate glasses have been prepared by conventional melt quenching technique and are characterized through structural and optical measurements. The refractive index, density, optical absorption, Judd–Ofelt parameters and spontaneous transition probabilities have been measured, calculated and analyzed. The emission spectra of Sm3+ ions in these glasses have been measured and an intense reddish-orange emission is observed. The luminescence decay curves exhibit single exponential at lower concentrations (⩽0.1 mol%) and turn into non-exponential at higher concentrations (⩾0.5 mol%). The lifetimes for the 4G5/2 level of Sm3+ ions are found to decrease (2.95–0.78 ms) with increasing concentration (0.01–3.0 mol%) due to energy transfer processes among Sm3+ ions. Inokuti–Hirayama model was applied in order to obtain information about interactions between the rare earth ions. The non-exponential decay curves are well-fitted to Inokuti–Hirayama model for S = 6 indicating that the nature of the energy transfer process is of dipole–dipole type.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide