| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1402776 | Journal of Molecular Structure | 2014 | 7 Pages |
•A new succinate bridged 1D coordination polymer of cobalt(II) is isolated.•X-ray study reveals interesting 2D sheet and 3D network structures.•Variable-temperature magnetic susceptibility shows weak antiferromagnetic coupling.•Thermogravimetric analysis proves the thermal stability and decomposition pattern.
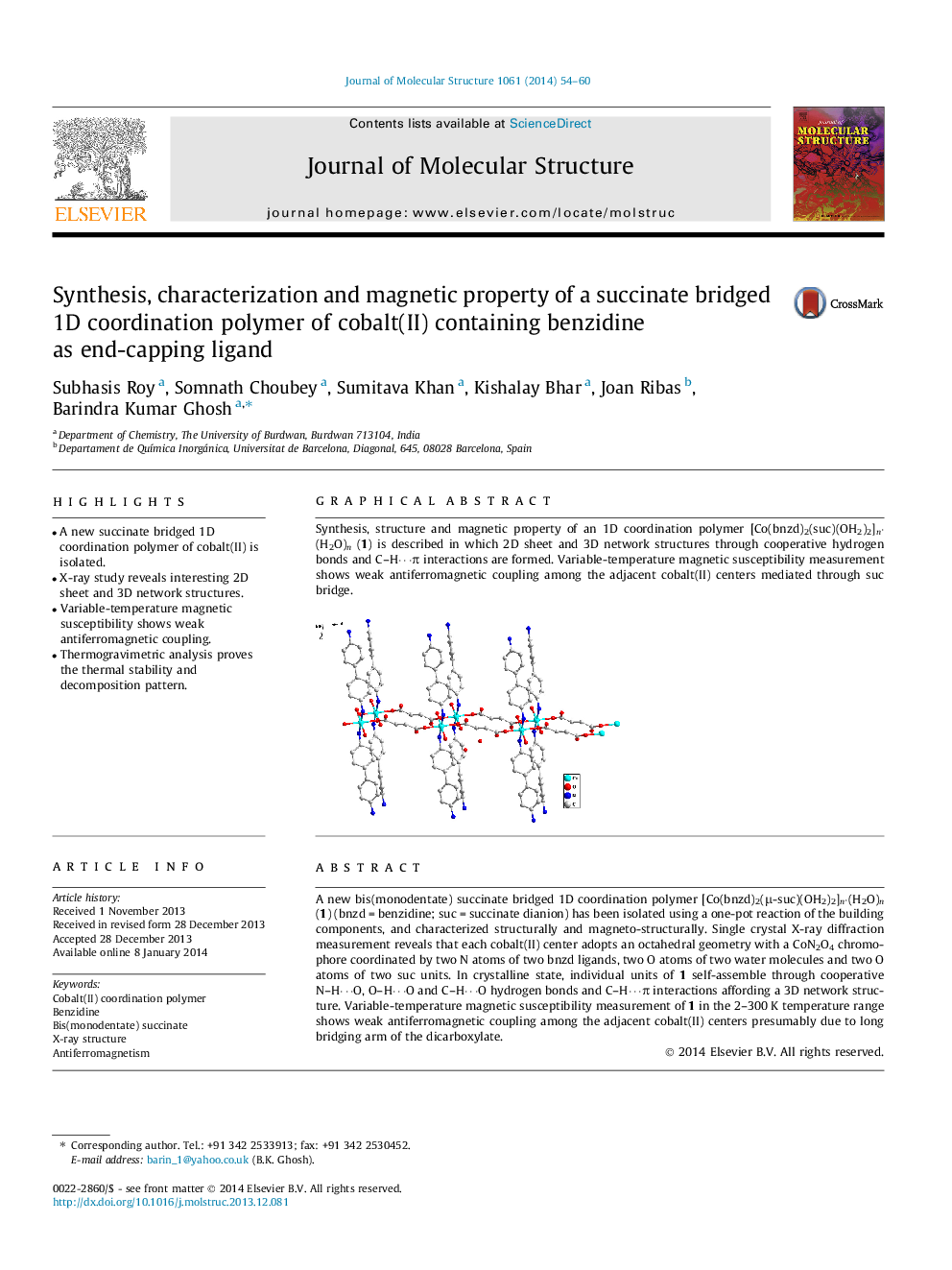
A new bis(monodentate) succinate bridged 1D coordination polymer [Co(bnzd)2(μ-suc)(OH2)2]n⋅(H2O)n (1) (bnzd = benzidine; suc = succinate dianion) has been isolated using a one-pot reaction of the building components, and characterized structurally and magneto-structurally. Single crystal X-ray diffraction measurement reveals that each cobalt(II) center adopts an octahedral geometry with a CoN2O4 chromophore coordinated by two N atoms of two bnzd ligands, two O atoms of two water molecules and two O atoms of two suc units. In crystalline state, individual units of 1 self-assemble through cooperative N–H⋯O, O–H⋯O and C–H⋯O hydrogen bonds and C–H⋯π interactions affording a 3D network structure. Variable-temperature magnetic susceptibility measurement of 1 in the 2–300 K temperature range shows weak antiferromagnetic coupling among the adjacent cobalt(II) centers presumably due to long bridging arm of the dicarboxylate.
Graphical abstractSynthesis, structure and magnetic property of an 1D coordination polymer [Co(bnzd)2(suc)(OH2)2]n·(H2O)n (1) is described in which 2D sheet and 3D network structures through cooperative hydrogen bonds and C–H⋯π interactions are formed. Variable-temperature magnetic susceptibility measurement shows weak antiferromagnetic coupling among the adjacent cobalt(II) centers mediated through suc bridge.Figure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide