| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1405408 | Journal of Molecular Structure | 2015 | 8 Pages |
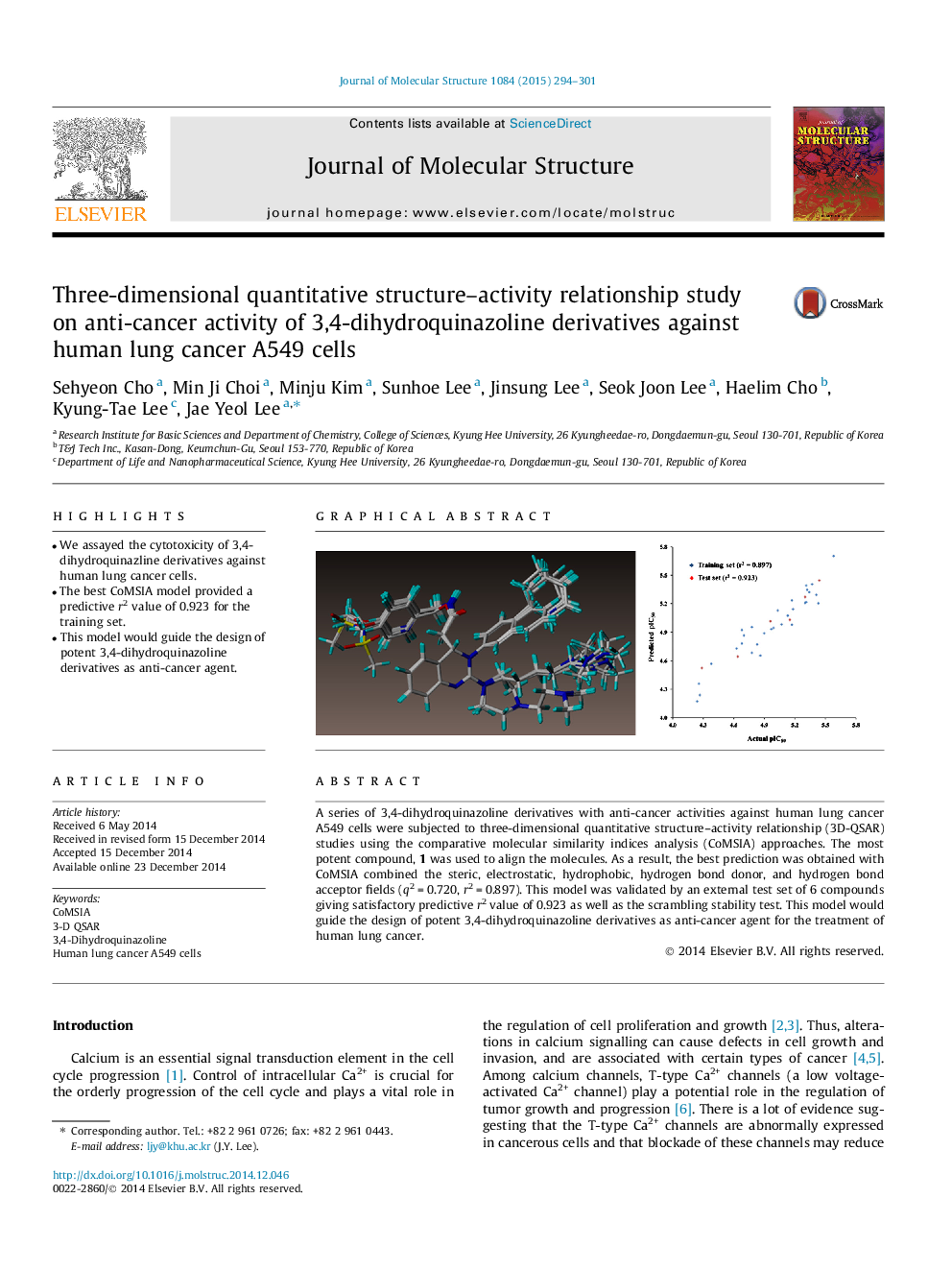
•We assayed the cytotoxicity of 3,4-dihydroquinazline derivatives against human lung cancer cells.•The best CoMSIA model provided a predictive r2 value of 0.923 for the training set.•This model would guide the design of potent 3,4-dihydroquinazoline derivatives as anti-cancer agent.
A series of 3,4-dihydroquinazoline derivatives with anti-cancer activities against human lung cancer A549 cells were subjected to three-dimensional quantitative structure–activity relationship (3D-QSAR) studies using the comparative molecular similarity indices analysis (CoMSIA) approaches. The most potent compound, 1 was used to align the molecules. As a result, the best prediction was obtained with CoMSIA combined the steric, electrostatic, hydrophobic, hydrogen bond donor, and hydrogen bond acceptor fields (q2 = 0.720, r2 = 0.897). This model was validated by an external test set of 6 compounds giving satisfactory predictive r2 value of 0.923 as well as the scrambling stability test. This model would guide the design of potent 3,4-dihydroquinazoline derivatives as anti-cancer agent for the treatment of human lung cancer.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide