| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1405411 | Journal of Molecular Structure | 2015 | 7 Pages |
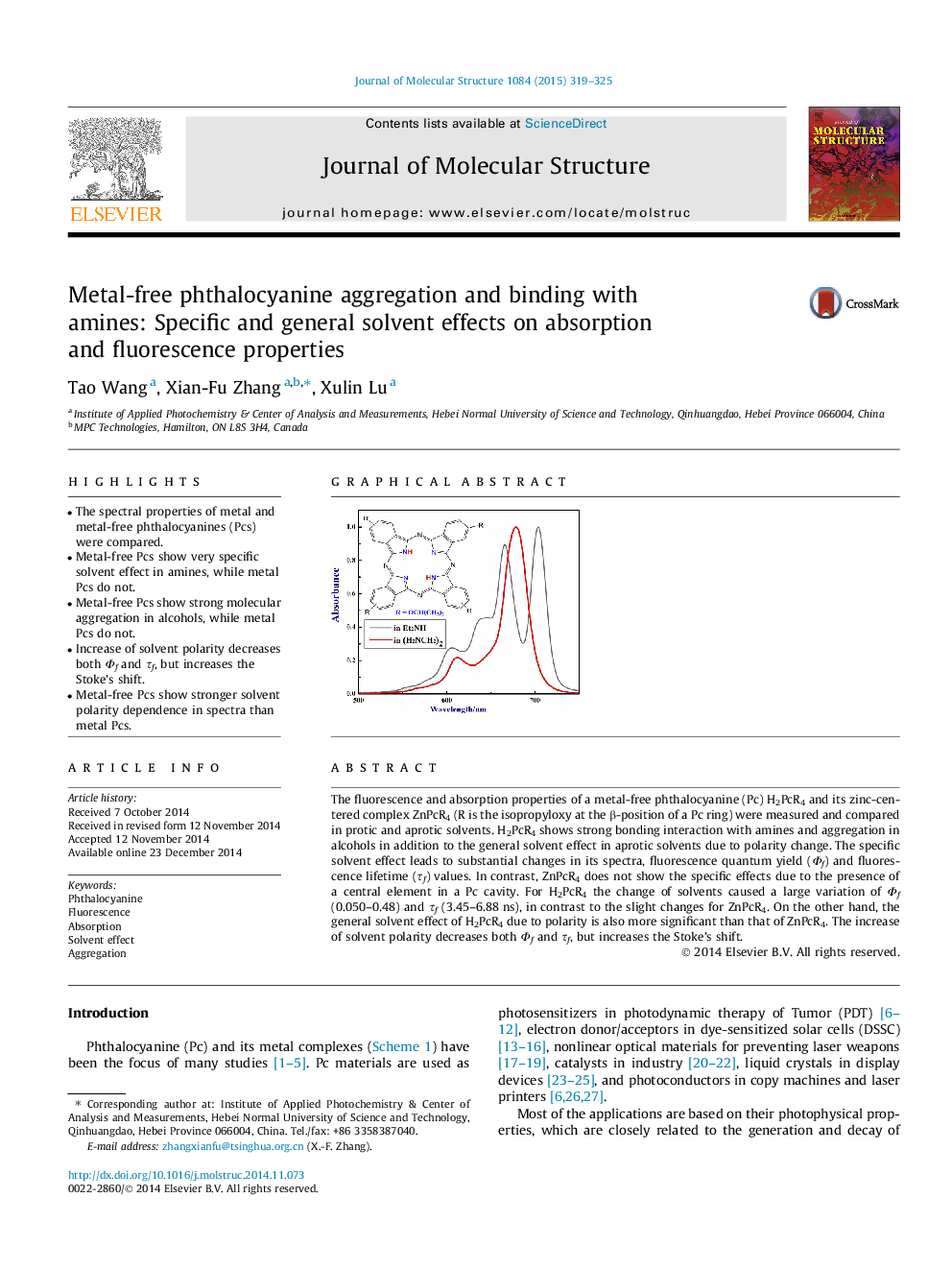
•The spectral properties of metal and metal-free phthalocyanines (Pcs) were compared.•Metal-free Pcs show very specific solvent effect in amines, while metal Pcs do not.•Metal-free Pcs show strong molecular aggregation in alcohols, while metal Pcs do not.•Increase of solvent polarity decreases both Φf and τf, but increases the Stoke’s shift.•Metal-free Pcs show stronger solvent polarity dependence in spectra than metal Pcs.
The fluorescence and absorption properties of a metal-free phthalocyanine (Pc) H2PcR4 and its zinc-centered complex ZnPcR4 (R is the isopropyloxy at the β-position of a Pc ring) were measured and compared in protic and aprotic solvents. H2PcR4 shows strong bonding interaction with amines and aggregation in alcohols in addition to the general solvent effect in aprotic solvents due to polarity change. The specific solvent effect leads to substantial changes in its spectra, fluorescence quantum yield (Φf) and fluorescence lifetime (τf) values. In contrast, ZnPcR4 does not show the specific effects due to the presence of a central element in a Pc cavity. For H2PcR4 the change of solvents caused a large variation of Φf (0.050–0.48) and τf (3.45–6.88 ns), in contrast to the slight changes for ZnPcR4. On the other hand, the general solvent effect of H2PcR4 due to polarity is also more significant than that of ZnPcR4. The increase of solvent polarity decreases both Φf and τf, but increases the Stoke’s shift.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide