| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1405491 | Journal of Molecular Structure | 2014 | 7 Pages |
•TL studies on PbO–Al2O3–SiO2: Dy3+ glasses exposed to γ-rays have been carried out.•Glow curves exhibited dosimetric peak at about 180 °C and high temperature peak at 300 °C.•TL light output increased with increasing Al2O3 content and also γ-ray dose.•Results were analyzed within a framework of induced structural changes.
Thermoluminescence (TL) studies on PbO–Al2O3–SiO2: Dy3+ glasses mixed with varying concentrations (5–10 mol%) of Al2O3 exposed to γ-rays of dose, 0–5.0 kGy, have been carried out. The glow curves of these glasses have exhibited a dosimetric peak at about 180 °C and a high temperature peak at about 300 °C. The TL light output has been observed to increase with increasing Al2O3 and also with the γ-ray dose. Results of these studies (coupled with data on optical absorption, and IR spectroscopy) have been analyzed within a framework of induced structural changes in the glass network. Probable mechanisms responsible for TL emission have been identified and discussed. The dose response of these glass samples exhibited linear behavior within the dose range of 1.0–3.0 kGy and beyond that it exhibited near saturation.
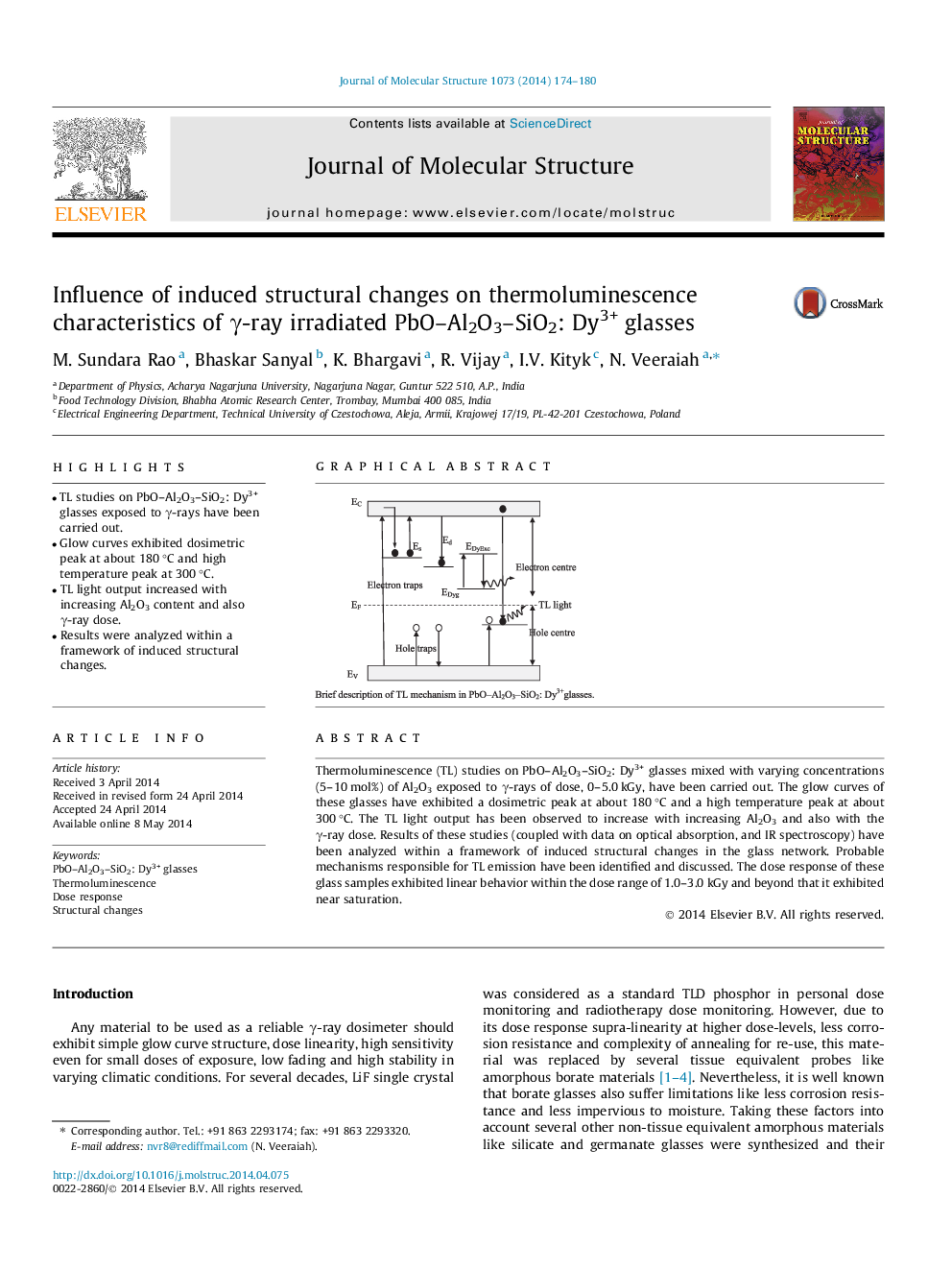
Graphical abstractBrief description of TL mechanism in PbO–Al2O3–SiO2: Dy3+ glasses.Figure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide