| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1405541 | Journal of Molecular Structure | 2014 | 10 Pages |
•Ionization energy of the molecule is determined.•Appearance energies of main fragment ions are determined for the first time.•The mechanism of the dissociation procedure is studied.•Ring forming and H shift are found in the dissociation of parent ion.
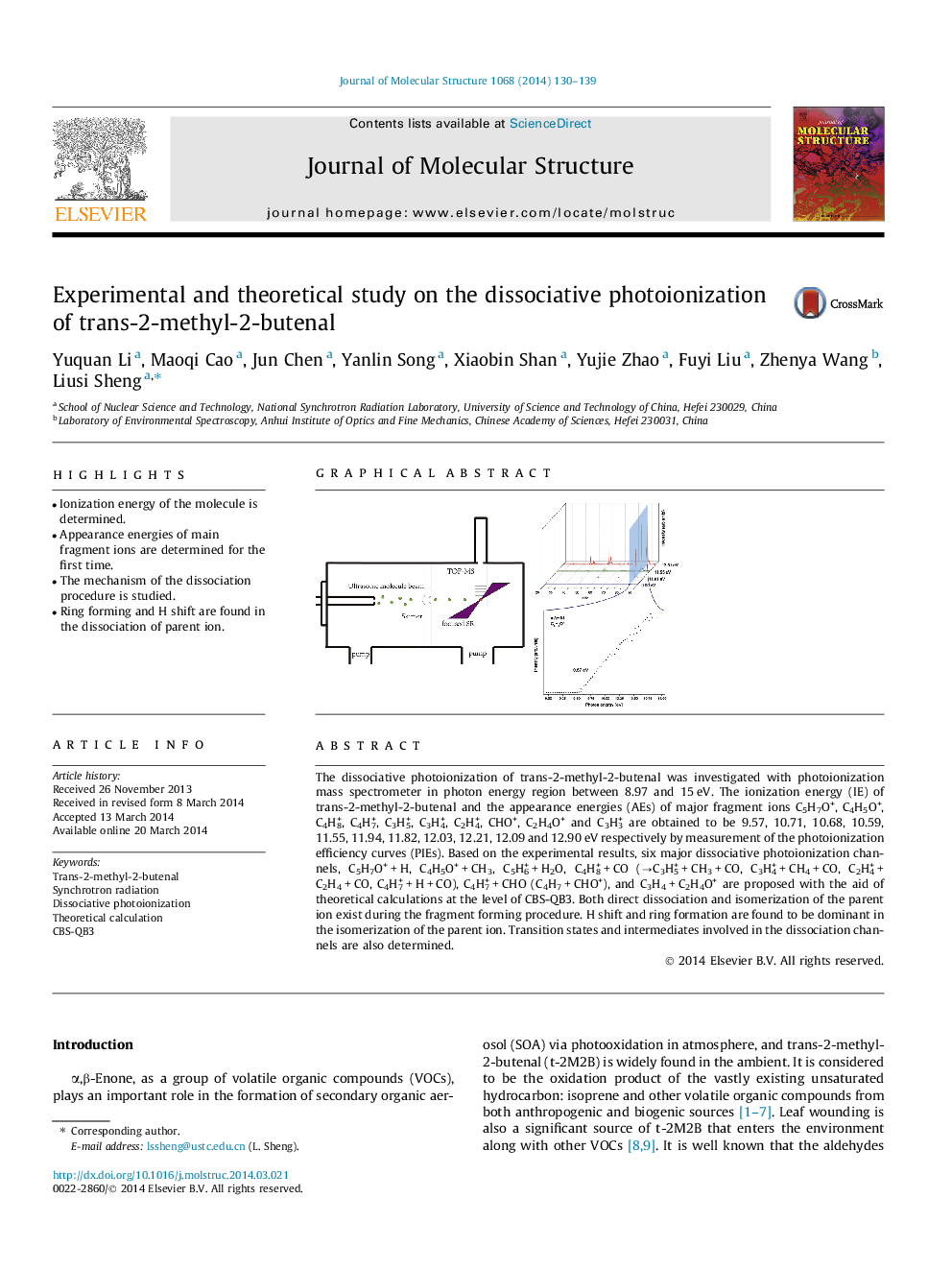
The dissociative photoionization of trans-2-methyl-2-butenal was investigated with photoionization mass spectrometer in photon energy region between 8.97 and 15 eV. The ionization energy (IE) of trans-2-methyl-2-butenal and the appearance energies (AEs) of major fragment ions C5H7O+, C4H5O+, C4H8+, C4H7+, C3H5+, C3H4+, C2H4+, CHO+, C2H4O+ and C3H3+ are obtained to be 9.57, 10.71, 10.68, 10.59, 11.55, 11.94, 11.82, 12.03, 12.21, 12.09 and 12.90 eV respectively by measurement of the photoionization efficiency curves (PIEs). Based on the experimental results, six major dissociative photoionization channels, C5H7O+ + H, C4H5O+ + CH3, C5H6+ + H2O, C4H8+ + CO (→C3H5+ + CH3 + CO, C3H4+ + CH4 + CO, C2H4+ + C2H4 + CO, C4H7+ + H + CO), C4H7+ + CHO (C4H7 + CHO+), and C3H4 + C2H4O+ are proposed with the aid of theoretical calculations at the level of CBS-QB3. Both direct dissociation and isomerization of the parent ion exist during the fragment forming procedure. H shift and ring formation are found to be dominant in the isomerization of the parent ion. Transition states and intermediates involved in the dissociation channels are also determined.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide