| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1405635 | Journal of Molecular Structure | 2014 | 6 Pages |
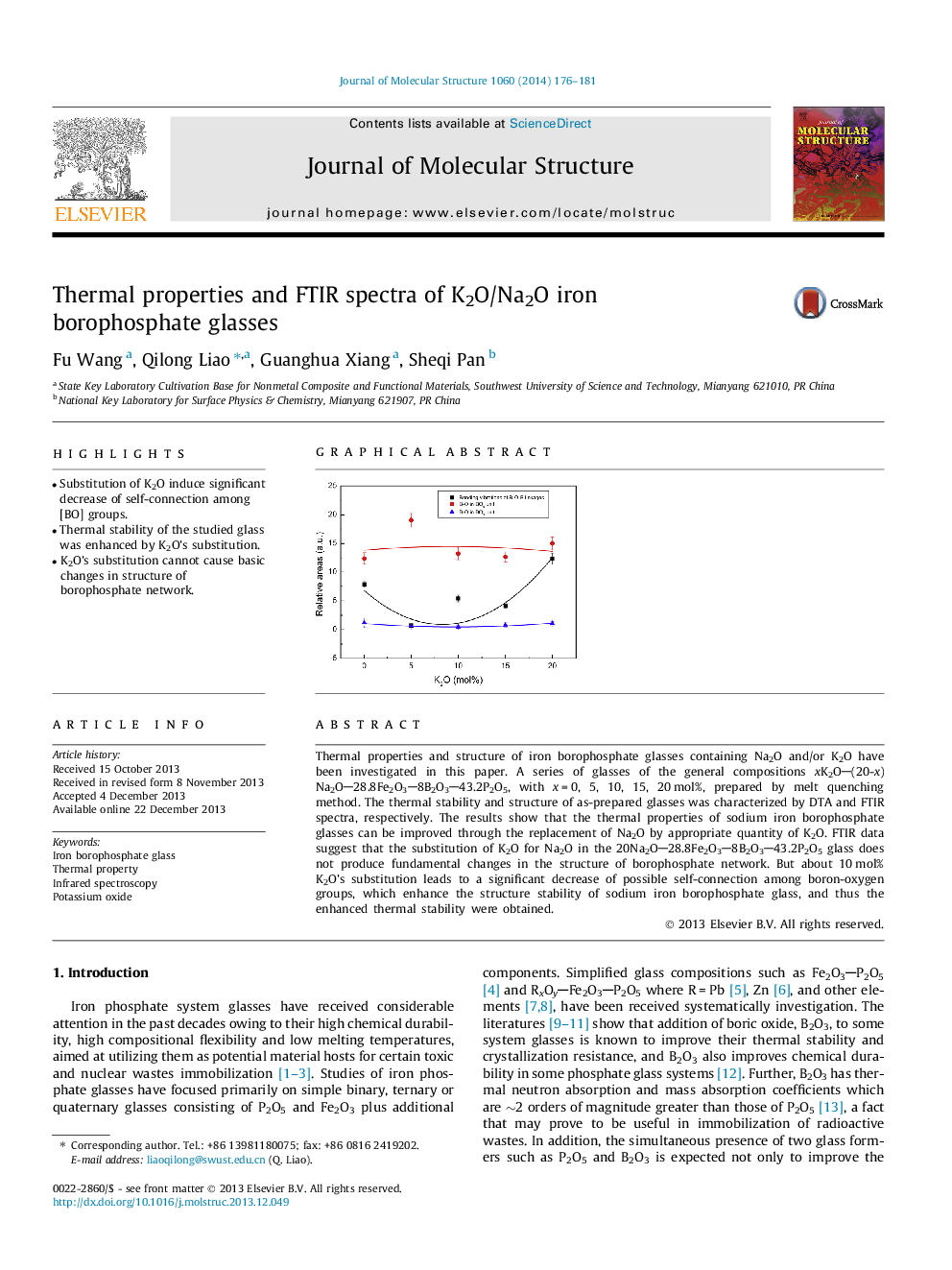
•Substitution of K2O induce significant decrease of self-connection among [BO] groups.•Thermal stability of the studied glass was enhanced by K2O’s substitution.•K2O’s substitution cannot cause basic changes in structure of borophosphate network.
Thermal properties and structure of iron borophosphate glasses containing Na2O and/or K2O have been investigated in this paper. A series of glasses of the general compositions xK2O(20-x)Na2O28.8Fe2O38B2O343.2P2O5, with x = 0, 5, 10, 15, 20 mol%, prepared by melt quenching method. The thermal stability and structure of as-prepared glasses was characterized by DTA and FTIR spectra, respectively. The results show that the thermal properties of sodium iron borophosphate glasses can be improved through the replacement of Na2O by appropriate quantity of K2O. FTIR data suggest that the substitution of K2O for Na2O in the 20Na2O28.8Fe2O38B2O343.2P2O5 glass does not produce fundamental changes in the structure of borophosphate network. But about 10 mol% K2O’s substitution leads to a significant decrease of possible self-connection among boron-oxygen groups, which enhance the structure stability of sodium iron borophosphate glass, and thus the enhanced thermal stability were obtained.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide