| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 145235 | Chemical Engineering Journal | 2016 | 8 Pages |
•Dmin was used as a performance indicator for UV reactor configuration optimization.•Dmin proved to be a qualified alternative to RED for UV reactor optimal design.•Reactor with a well-mixed flow dispersed by lamp array had the best performance.•Disinfection capability of the optimally designed UV reactor was elevated by 47−100%.
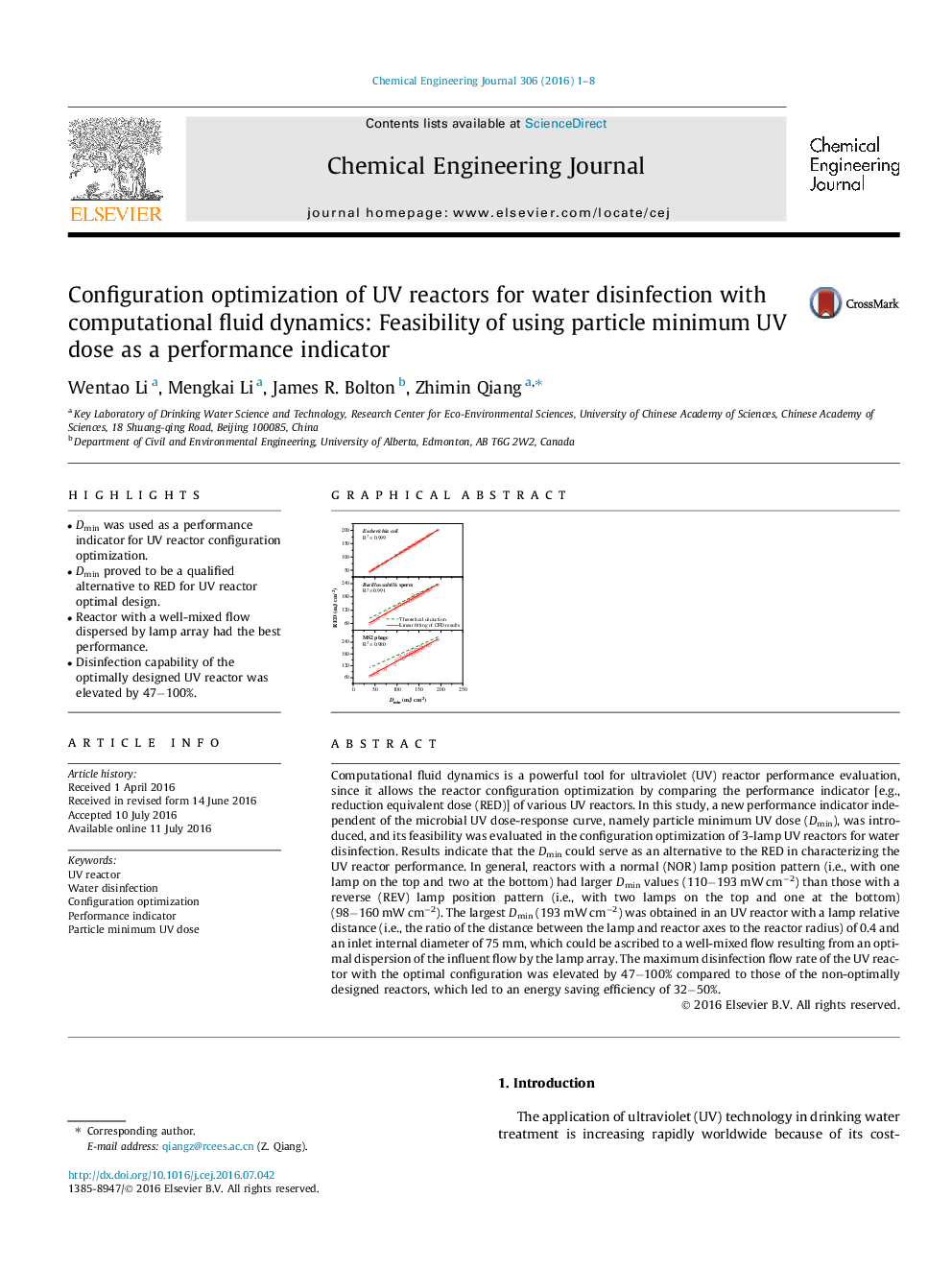
Computational fluid dynamics is a powerful tool for ultraviolet (UV) reactor performance evaluation, since it allows the reactor configuration optimization by comparing the performance indicator [e.g., reduction equivalent dose (RED)] of various UV reactors. In this study, a new performance indicator independent of the microbial UV dose-response curve, namely particle minimum UV dose (Dmin), was introduced, and its feasibility was evaluated in the configuration optimization of 3-lamp UV reactors for water disinfection. Results indicate that the Dmin could serve as an alternative to the RED in characterizing the UV reactor performance. In general, reactors with a normal (NOR) lamp position pattern (i.e., with one lamp on the top and two at the bottom) had larger Dmin values (110−193 mW cm−2) than those with a reverse (REV) lamp position pattern (i.e., with two lamps on the top and one at the bottom) (98−160 mW cm−2). The largest Dmin (193 mW cm−2) was obtained in an UV reactor with a lamp relative distance (i.e., the ratio of the distance between the lamp and reactor axes to the reactor radius) of 0.4 and an inlet internal diameter of 75 mm, which could be ascribed to a well-mixed flow resulting from an optimal dispersion of the influent flow by the lamp array. The maximum disinfection flow rate of the UV reactor with the optimal configuration was elevated by 47−100% compared to those of the non-optimally designed reactors, which led to an energy saving efficiency of 32−50%.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide