| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 145244 | Chemical Engineering Journal | 2016 | 7 Pages |
•Co-doped α-FeOOH was prepared via a simple co-precipitation method.•By varying molar ratios of Co:Fe, the composition can be freely manipulated.•The obtained samples show strikingly high sulfur capacity at room temperature.•The increased surface area and defects contribute to the improved activity.
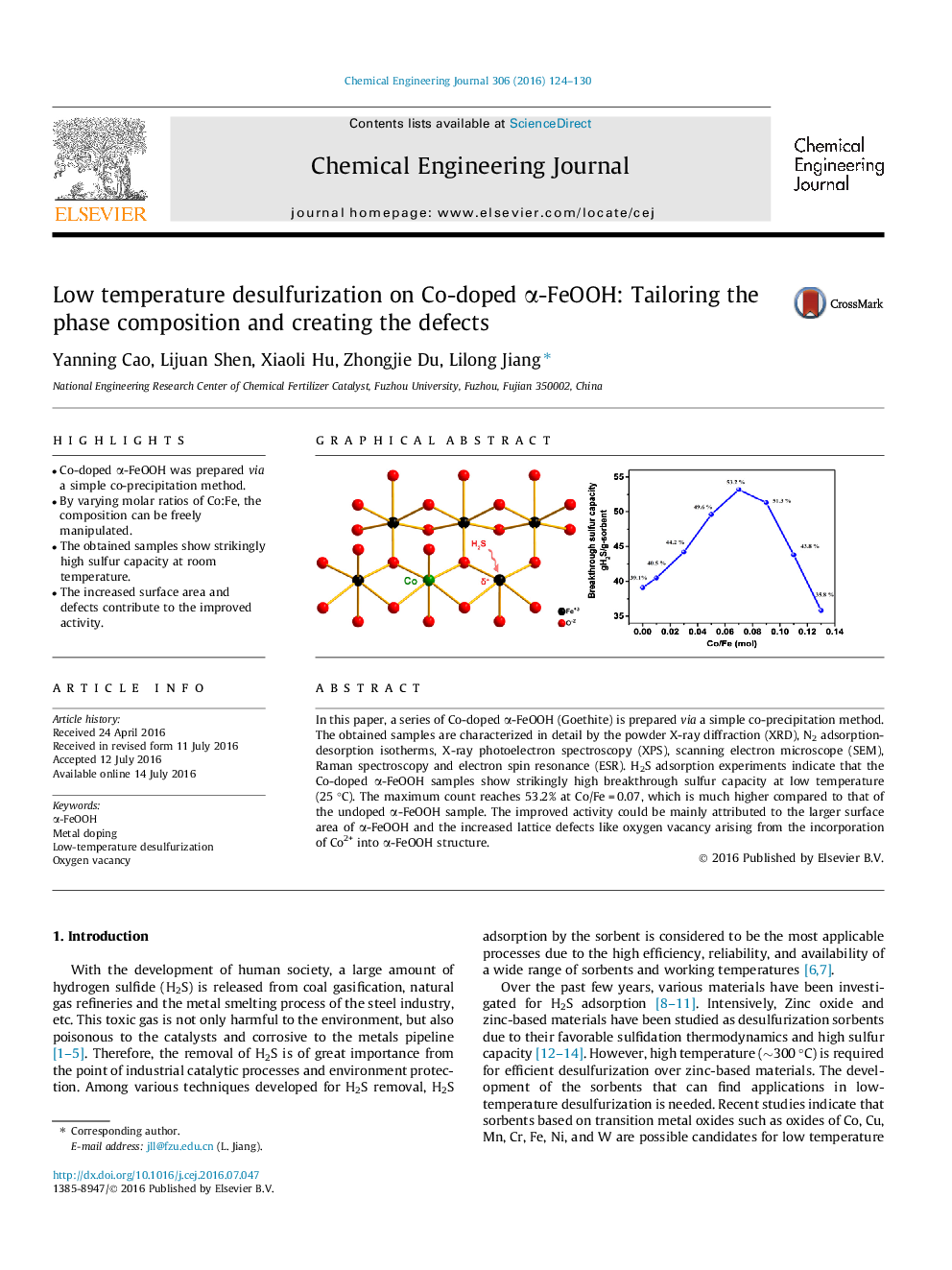
In this paper, a series of Co-doped α-FeOOH (Goethite) is prepared via a simple co-precipitation method. The obtained samples are characterized in detail by the powder X-ray diffraction (XRD), N2 adsorption-desorption isotherms, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), scanning electron microscope (SEM), Raman spectroscopy and electron spin resonance (ESR). H2S adsorption experiments indicate that the Co-doped α-FeOOH samples show strikingly high breakthrough sulfur capacity at low temperature (25 °C). The maximum count reaches 53.2% at Co/Fe = 0.07, which is much higher compared to that of the undoped α-FeOOH sample. The improved activity could be mainly attributed to the larger surface area of α-FeOOH and the increased lattice defects like oxygen vacancy arising from the incorporation of Co2+ into α-FeOOH structure.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide