| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1482559 | Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids | 2010 | 5 Pages |
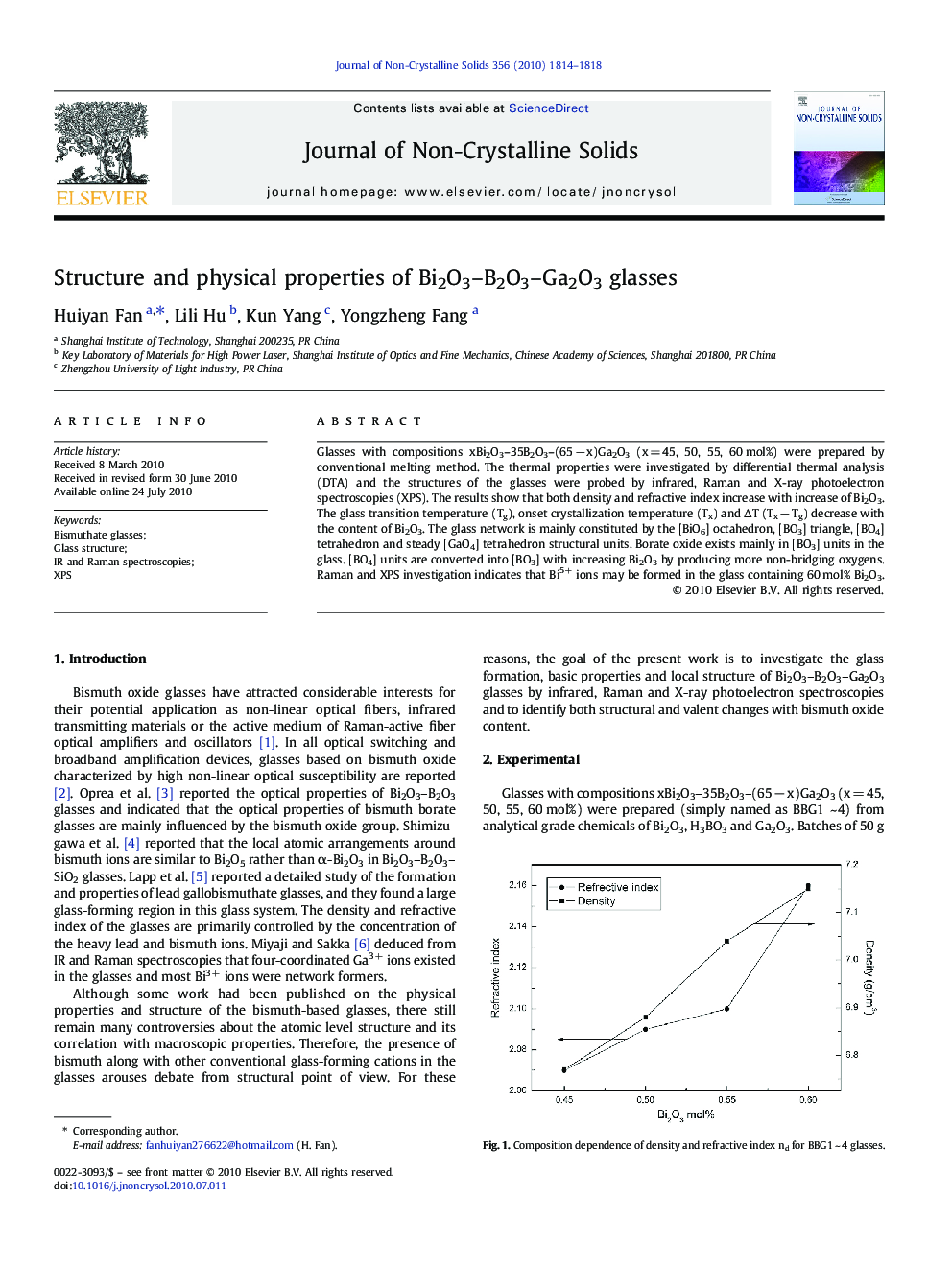
Glasses with compositions xBi2O3–35B2O3–(65 − x)Ga2O3 (x = 45, 50, 55, 60 mol%) were prepared by conventional melting method. The thermal properties were investigated by differential thermal analysis (DTA) and the structures of the glasses were probed by infrared, Raman and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopies (XPS). The results show that both density and refractive index increase with increase of Bi2O3. The glass transition temperature (Tg), onset crystallization temperature (Tx) and ΔT (Tx − Tg) decrease with the content of Bi2O3. The glass network is mainly constituted by the [BiO6] octahedron, [BO3] triangle, [BO4] tetrahedron and steady [GaO4] tetrahedron structural units. Borate oxide exists mainly in [BO3] units in the glass. [BO4] units are converted into [BO3] with increasing Bi2O3 by producing more non-bridging oxygens. Raman and XPS investigation indicates that Bi5+ ions may be formed in the glass containing 60 mol% Bi2O3.