| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 242487 | Applied Energy | 2015 | 10 Pages |
•Chemical reduction route was adopted for graphene preparation.•Electrochemical measurements were carried out in 6 M KOH.•Better electrochemical properties obtained for graphene than graphene oxide.•A high specific capacitance of 284.3 F/g was observed for SR1:10.
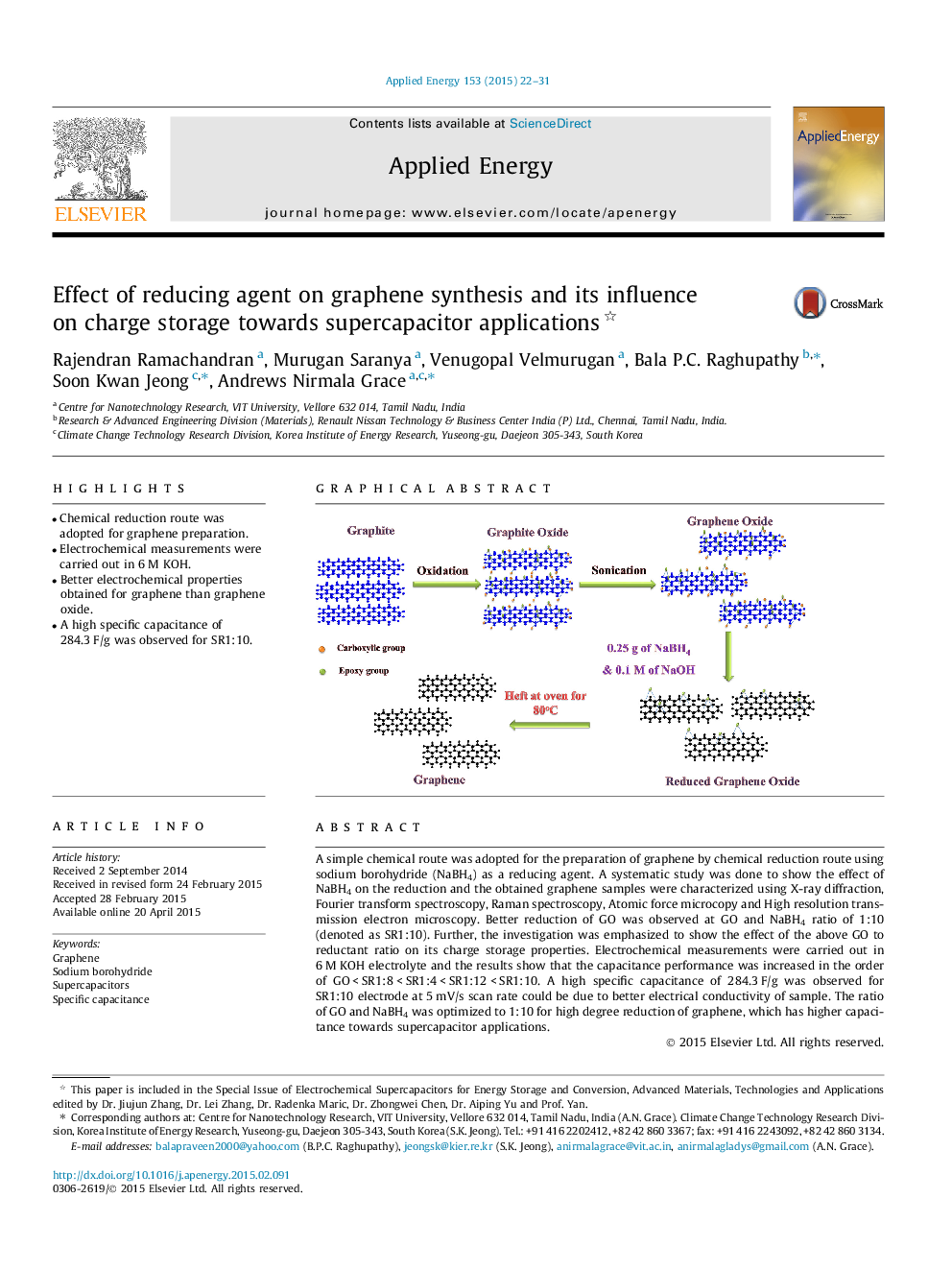
A simple chemical route was adopted for the preparation of graphene by chemical reduction route using sodium borohydride (NaBH4) as a reducing agent. A systematic study was done to show the effect of NaBH4 on the reduction and the obtained graphene samples were characterized using X-ray diffraction, Fourier transform spectroscopy, Raman spectroscopy, Atomic force microcopy and High resolution transmission electron microscopy. Better reduction of GO was observed at GO and NaBH4 ratio of 1:10 (denoted as SR1:10). Further, the investigation was emphasized to show the effect of the above GO to reductant ratio on its charge storage properties. Electrochemical measurements were carried out in 6 M KOH electrolyte and the results show that the capacitance performance was increased in the order of GO < SR1:8 < SR1:4 < SR1:12 < SR1:10. A high specific capacitance of 284.3 F/g was observed for SR1:10 electrode at 5 mV/s scan rate could be due to better electrical conductivity of sample. The ratio of GO and NaBH4 was optimized to 1:10 for high degree reduction of graphene, which has higher capacitance towards supercapacitor applications.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide