| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 242613 | Applied Energy | 2015 | 10 Pages |
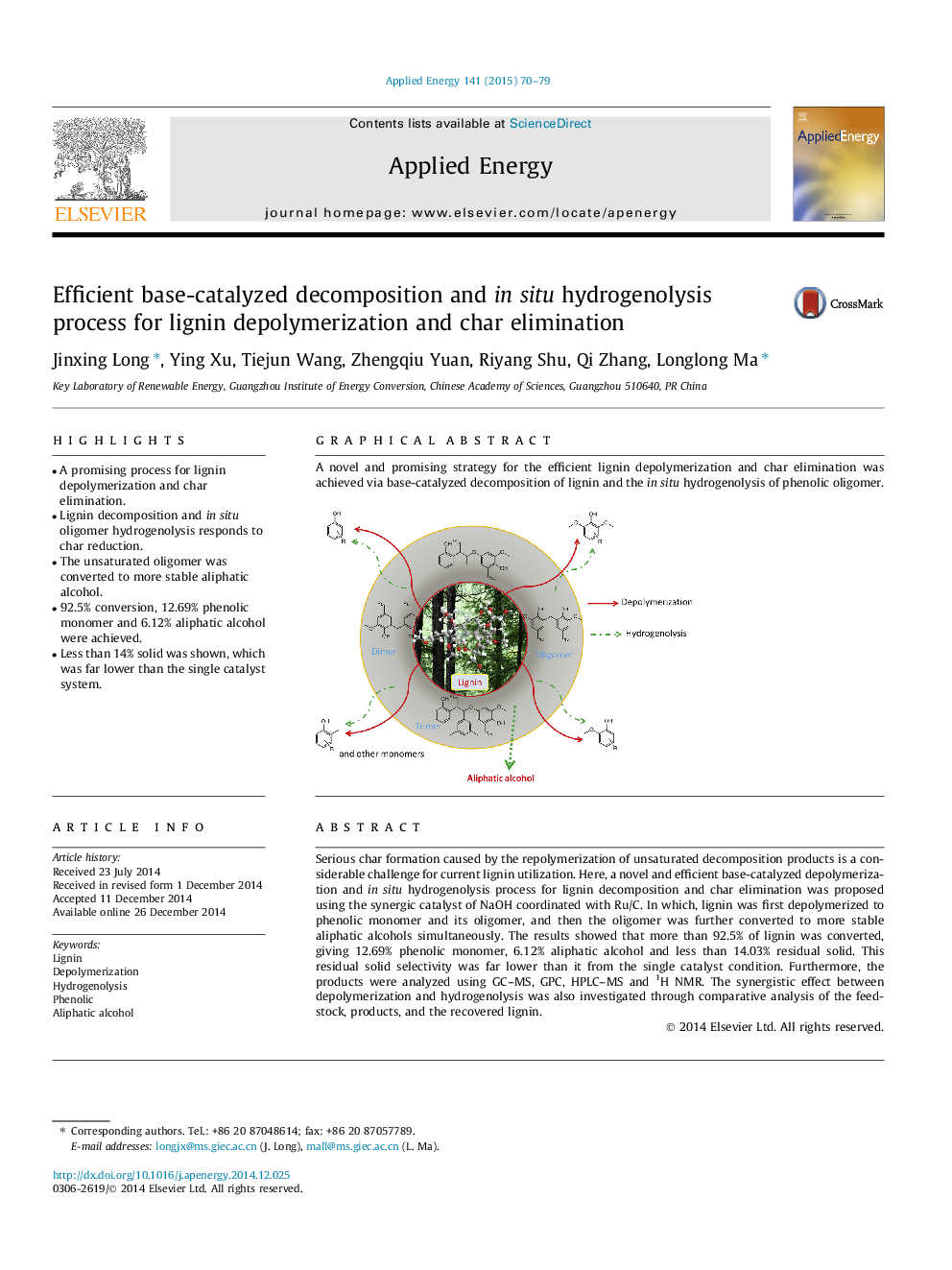
•A promising process for lignin depolymerization and char elimination.•Lignin decomposition and in situ oligomer hydrogenolysis responds to char reduction.•The unsaturated oligomer was converted to more stable aliphatic alcohol.•92.5% conversion, 12.69% phenolic monomer and 6.12% aliphatic alcohol were achieved.•Less than 14% solid was shown, which was far lower than the single catalyst system.
Serious char formation caused by the repolymerization of unsaturated decomposition products is a considerable challenge for current lignin utilization. Here, a novel and efficient base-catalyzed depolymerization and in situ hydrogenolysis process for lignin decomposition and char elimination was proposed using the synergic catalyst of NaOH coordinated with Ru/C. In which, lignin was first depolymerized to phenolic monomer and its oligomer, and then the oligomer was further converted to more stable aliphatic alcohols simultaneously. The results showed that more than 92.5% of lignin was converted, giving 12.69% phenolic monomer, 6.12% aliphatic alcohol and less than 14.03% residual solid. This residual solid selectivity was far lower than it from the single catalyst condition. Furthermore, the products were analyzed using GC–MS, GPC, HPLC–MS and 1H NMR. The synergistic effect between depolymerization and hydrogenolysis was also investigated through comparative analysis of the feedstock, products, and the recovered lignin.
Graphical abstractA novel and promising strategy for the efficient lignin depolymerization and char elimination was achieved via base-catalyzed decomposition of lignin and the in situ hydrogenolysis of phenolic oligomer.Figure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide