| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 243086 | Applied Energy | 2013 | 7 Pages |
•Innovative amino acid (AA) and AA-complex based solid sorbents were developed for CO2 capture.•Complexed AA had improved AA water solubility and higher CO2 adsorption capacity.•The factors affecting CO2 adsorption properties were investigated.•AA sorbents could eliminate corrosion concerns and retain AA’s unique properties.
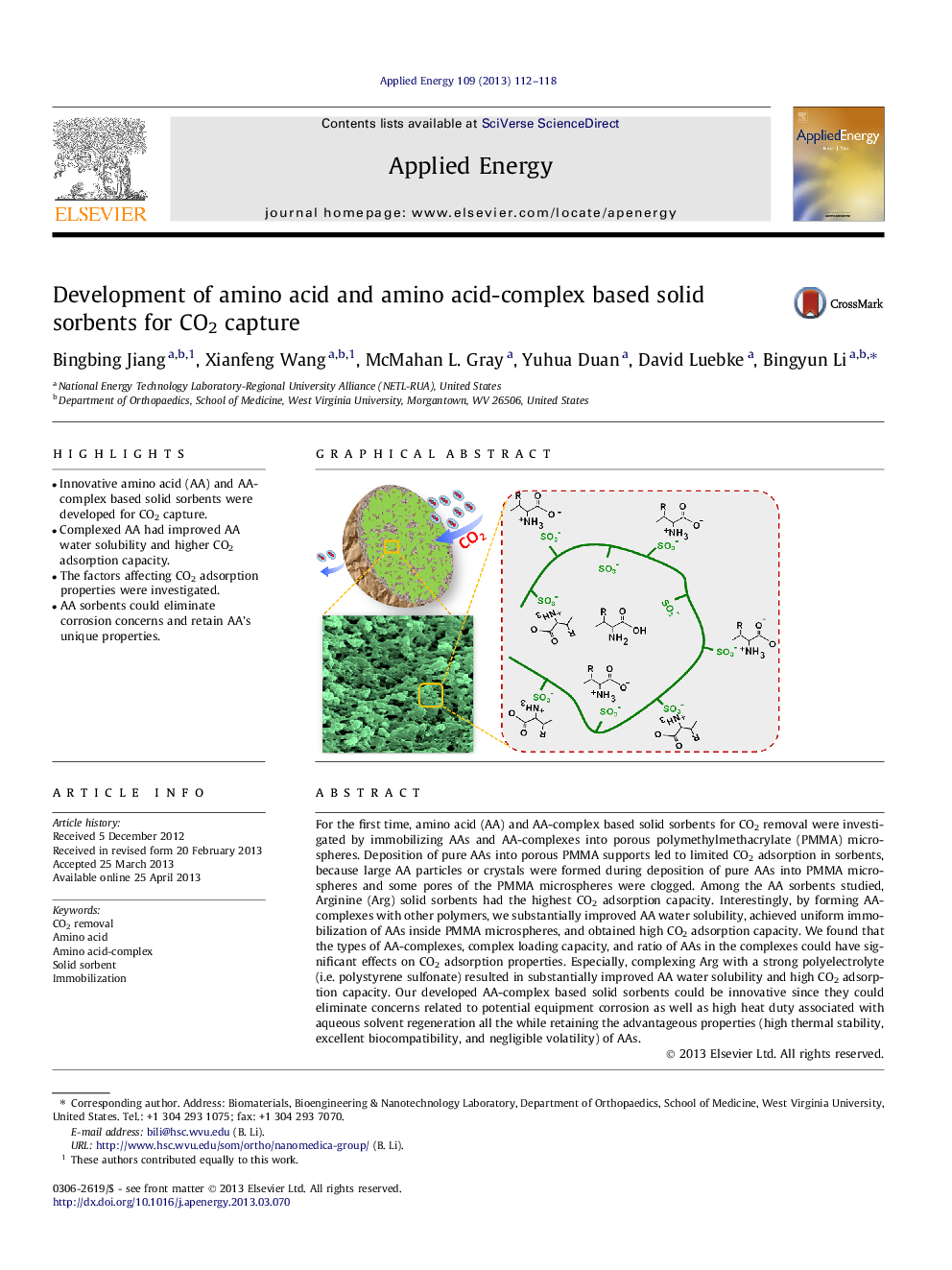
For the first time, amino acid (AA) and AA-complex based solid sorbents for CO2 removal were investigated by immobilizing AAs and AA-complexes into porous polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) microspheres. Deposition of pure AAs into porous PMMA supports led to limited CO2 adsorption in sorbents, because large AA particles or crystals were formed during deposition of pure AAs into PMMA microspheres and some pores of the PMMA microspheres were clogged. Among the AA sorbents studied, Arginine (Arg) solid sorbents had the highest CO2 adsorption capacity. Interestingly, by forming AA-complexes with other polymers, we substantially improved AA water solubility, achieved uniform immobilization of AAs inside PMMA microspheres, and obtained high CO2 adsorption capacity. We found that the types of AA-complexes, complex loading capacity, and ratio of AAs in the complexes could have significant effects on CO2 adsorption properties. Especially, complexing Arg with a strong polyelectrolyte (i.e. polystyrene sulfonate) resulted in substantially improved AA water solubility and high CO2 adsorption capacity. Our developed AA-complex based solid sorbents could be innovative since they could eliminate concerns related to potential equipment corrosion as well as high heat duty associated with aqueous solvent regeneration all the while retaining the advantageous properties (high thermal stability, excellent biocompatibility, and negligible volatility) of AAs.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide