| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2937536 | JACC: Basic to Translational Science | 2016 | 12 Pages |
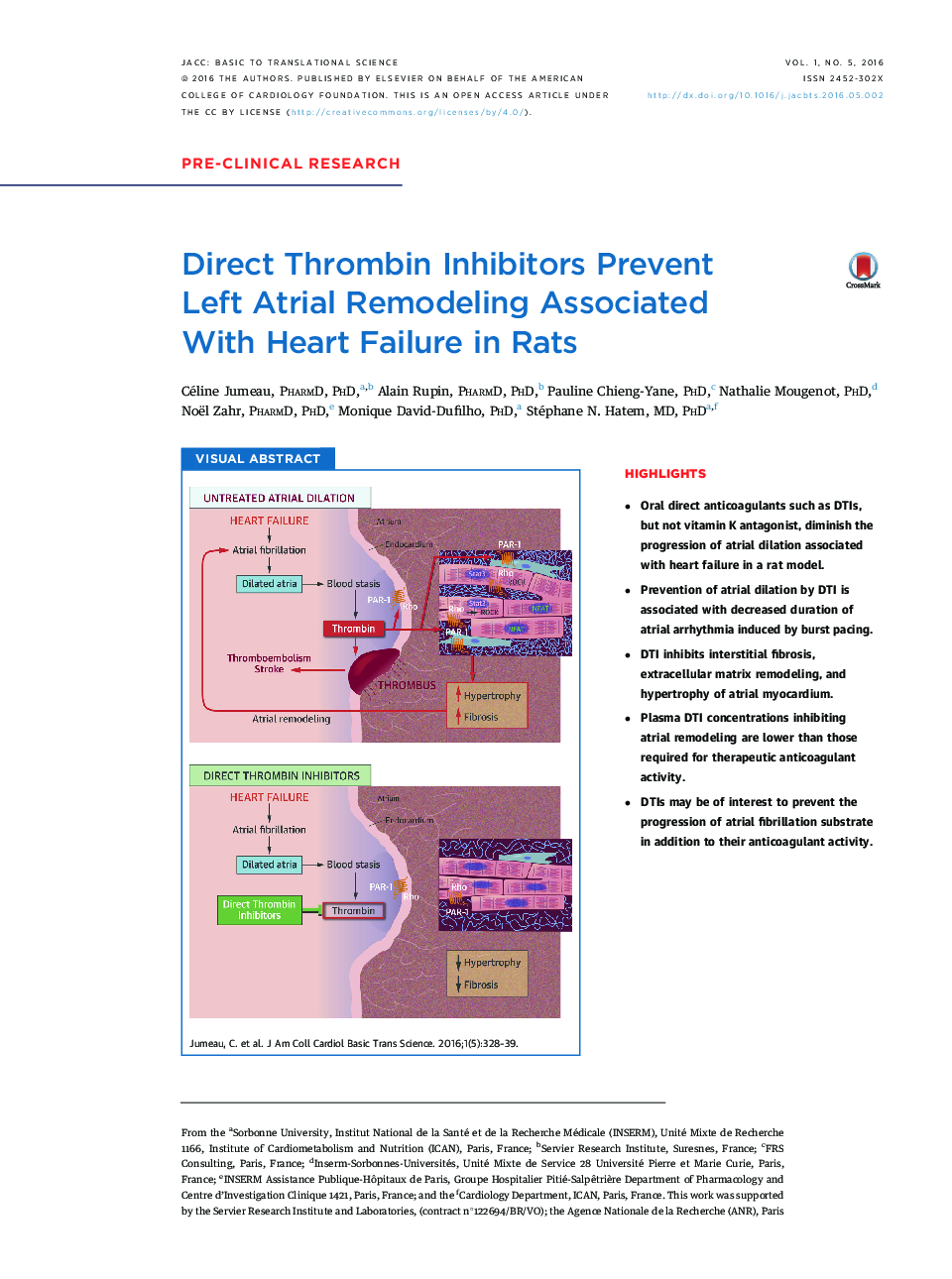
•Oral direct anticoagulants such as DTIs, but not vitamin K antagonist, diminish the progression of atrial dilation associated with heart failure in a rat model.•Prevention of atrial dilation by DTI is associated with decreased duration of atrial arrhythmia induced by burst pacing.•DTI inhibits interstitial fibrosis, extracellular matrix remodeling, and hypertrophy of atrial myocardium.•Plasma DTI concentrations inhibiting atrial remodeling are lower than those required for therapeutic anticoagulant activity.•DTIs may be of interest to prevent the progression of atrial fibrillation substrate in addition to their anticoagulant activity.
SummaryThe present study tested the hypothesis that thrombin participates in formation of left atrial remodeling and that direct oral anticoagulants, such as direct thrombin inhibitors (DTIs), can prevent its progression. In a rat model of heart failure associated with left atrial dilation, we found that chronic treatment with DTIs reduces the atrial remodeling and the duration of atrial fibrillation (AF) episodes induced by burst pacing by inhibiting myocardial hypertrophy and fibrosis. In addition to the prevention of thromboembolism complicating AF, DTIs may be of interest to slow down the progression of the arrhythmogenic substrate.
Visual AbstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload high-quality image (2411 K)Download as PowerPoint slide