| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4360831 | Cell Host & Microbe | 2015 | 12 Pages |
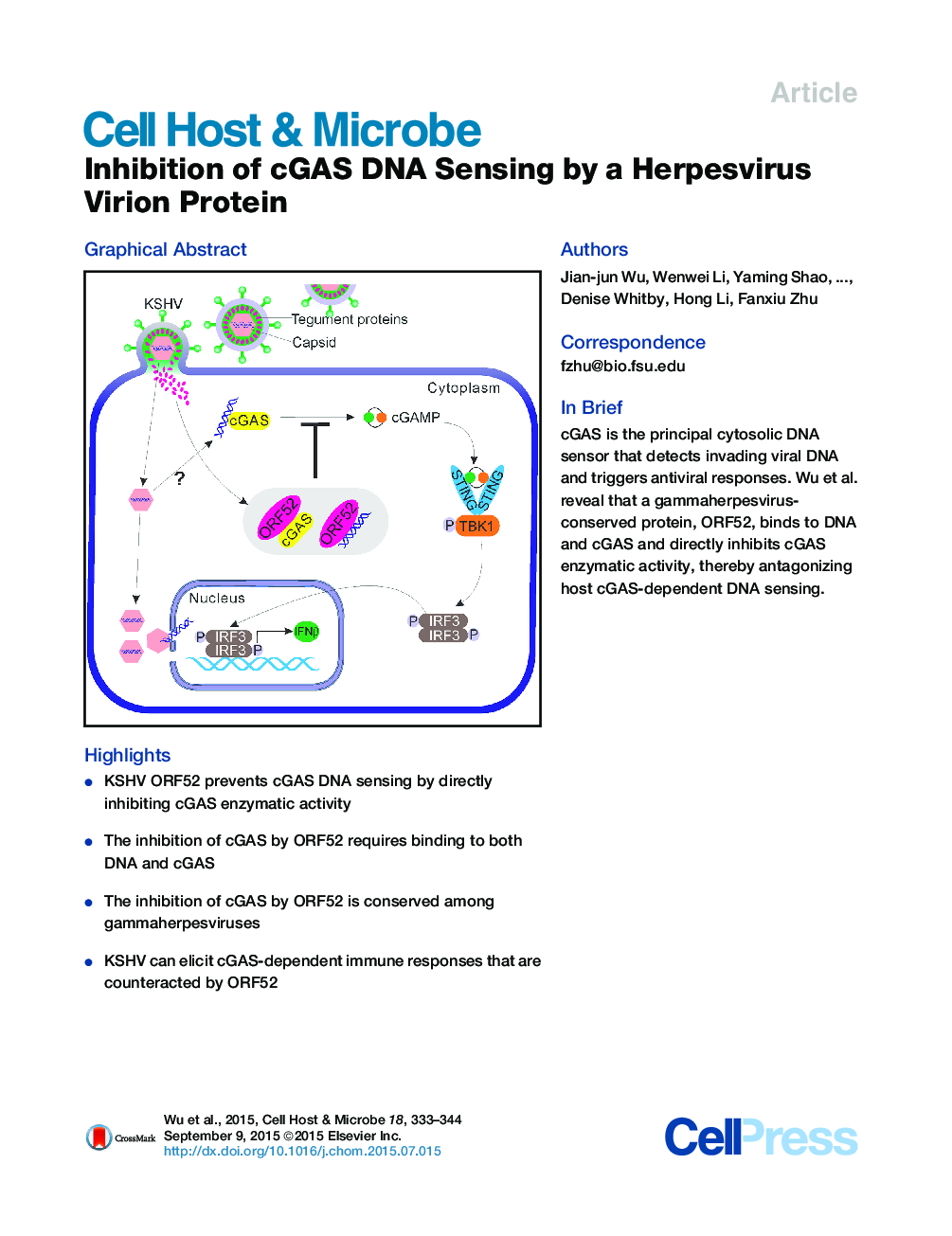
•KSHV ORF52 prevents cGAS DNA sensing by directly inhibiting cGAS enzymatic activity•The inhibition of cGAS by ORF52 requires binding to both DNA and cGAS•The inhibition of cGAS by ORF52 is conserved among gammaherpesviruses•KSHV can elicit cGAS-dependent immune responses that are counteracted by ORF52
SummaryInvading viral DNA can be recognized by the host cytosolic DNA sensor, cyclic GMP-AMP (cGAMP) synthase (cGAS), resulting in production of the second messenger cGAMP, which directs the adaptor protein STING to stimulate production of type I interferons (IFNs). Although several DNA viruses are sensed by cGAS, viral strategies targeting cGAS are virtually unknown. We report here that Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) ORF52, an abundant gammaherpesvirus-specific tegument protein, subverts cytosolic DNA sensing by directly inhibiting cGAS enzymatic activity through a mechanism involving both cGAS binding and DNA binding. Moreover, ORF52 homologs in other gammaherpesviruses also inhibit cGAS activity and similarly bind cGAS and DNA, suggesting conserved inhibitory mechanisms. Furthermore, KSHV infection evokes cGAS-dependent responses that can limit the infection, and an ORF52 null mutant exhibits increased cGAS signaling. Our findings reveal a mechanism through which gammaherpesviruses antagonize host cGAS DNA sensing.
Graphical AbstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload high-quality image (213 K)Download as PowerPoint slide