| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4360923 | Cell Host & Microbe | 2016 | 12 Pages |
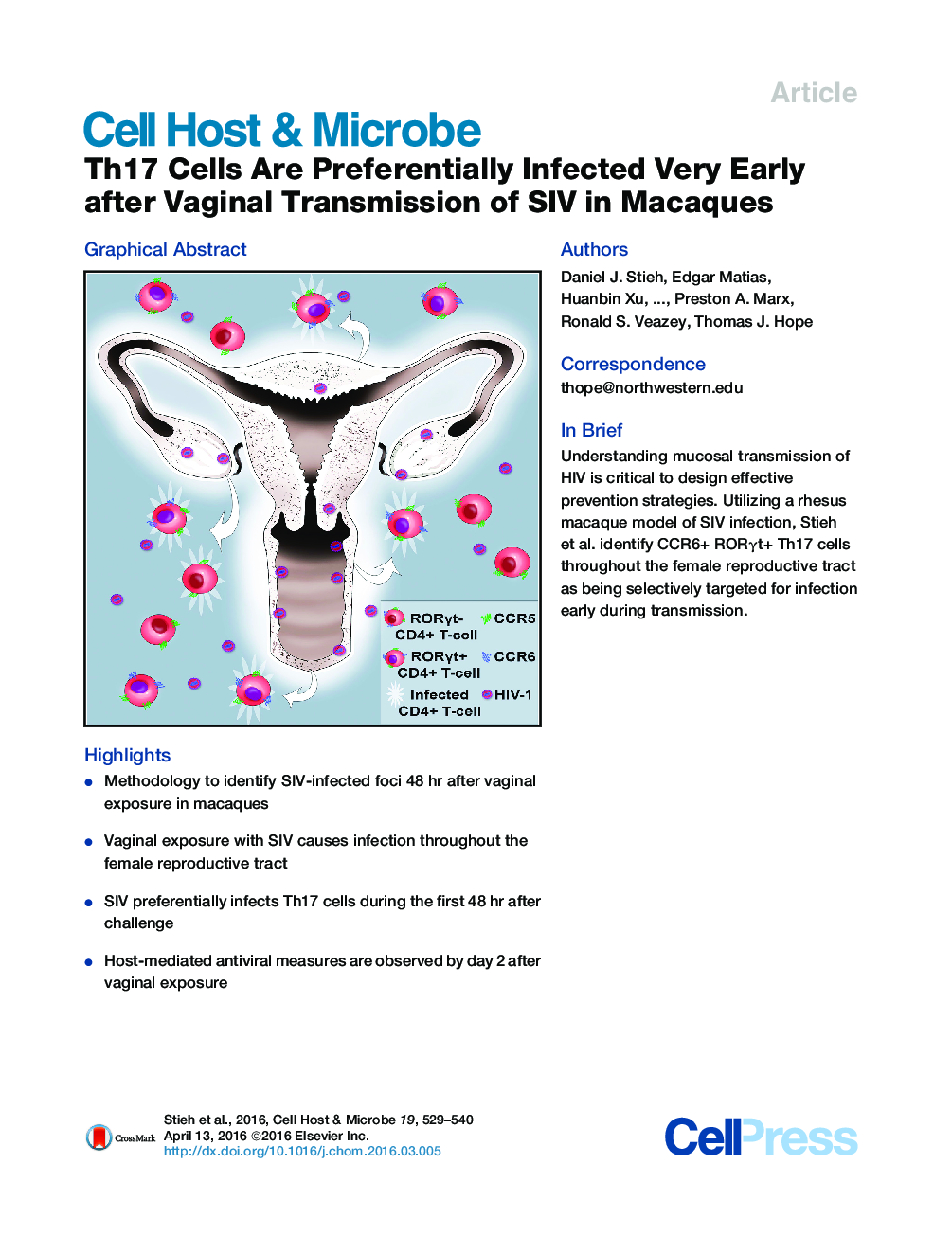
•Methodology to identify SIV-infected foci 48 hr after vaginal exposure in macaques•Vaginal exposure with SIV causes infection throughout the female reproductive tract•SIV preferentially infects Th17 cells during the first 48 hr after challenge•Host-mediated antiviral measures are observed by day 2 after vaginal exposure
SummaryThe difficulty in detecting rare infected cells immediately after mucosal HIV transmission has hindered our understanding of the initial cells targeted by the virus. Working with the macaque simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) vaginal challenge model, we developed methodology to identify discrete foci of SIV (mac239) infection 48 hr after vaginal inoculation. We find infectious foci throughout the reproductive tract, from labia to ovary. Phenotyping infected cells reveals that SIV has a significant bias for infection of CCR6+ CD4+ T cells. SIV-infected cells expressed the transcriptional regulator RORγt, confirming that the initial target cells are specifically of the Th17 lineage. Furthermore, we detect host responses to infection, as evidenced by apoptosis, cell lysis, and phagocytosis of infected cells. Thus, our analysis identifies Th17-lineage CCR6+ CD4+ T cells as primary targets of SIV during vaginal transmission. This opens new opportunities for interventions to protect these cells and prevent HIV transmission.
Graphical AbstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload high-quality image (302 K)Download as PowerPoint slide