| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 440746 | Computer-Aided Design | 2014 | 8 Pages |
•Function-based morphing (FBM) method for patient-specific proximal femur was proposed.•FBM morphs the patient-specific model based on the biomechanical functions.•Detailed algorithms for a robust morphing are presented in this paper.•FBM provides a systematical way to analyze biomechanical responses of a specific bone.
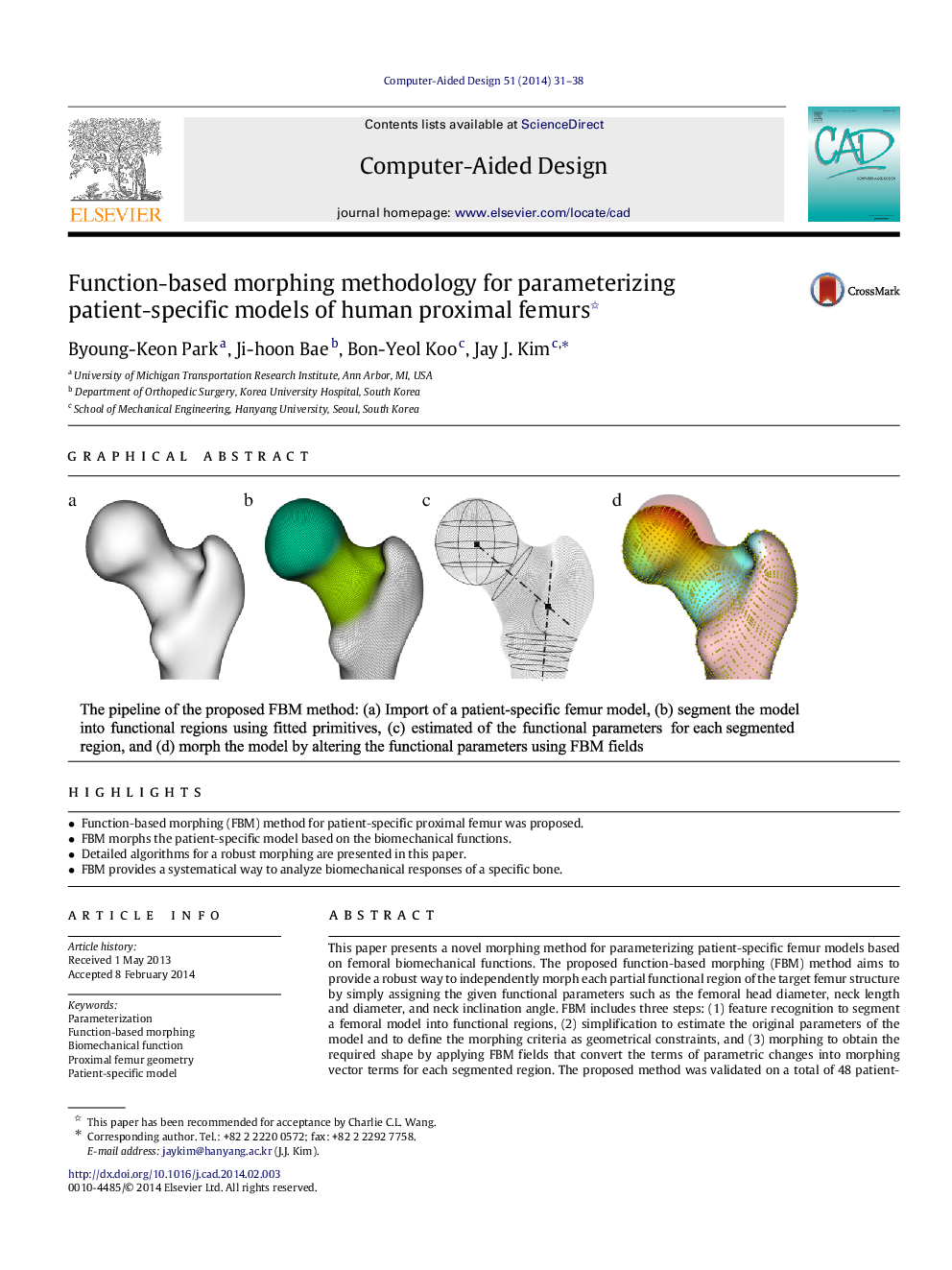
This paper presents a novel morphing method for parameterizing patient-specific femur models based on femoral biomechanical functions. The proposed function-based morphing (FBM) method aims to provide a robust way to independently morph each partial functional region of the target femur structure by simply assigning the given functional parameters such as the femoral head diameter, neck length and diameter, and neck inclination angle. FBM includes three steps: (1) feature recognition to segment a femoral model into functional regions, (2) simplification to estimate the original parameters of the model and to define the morphing criteria as geometrical constraints, and (3) morphing to obtain the required shape by applying FBM fields that convert the terms of parametric changes into morphing vector terms for each segmented region. The proposed method was validated on a total of 48 patient-specific femur models. These models were parameterized and morphed without unexpected parametric changes, and the averaged error between the required parameters and the re-estimated parameters after morphing was 3.47%. Our observations indicate that the variation models developed in this study can be used as fundamentals for various functional sensitivity analyses for predicting changes in biomechanical responses due to the morphological changes of a subject-specific femur structure.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide