| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4982442 | Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects | 2017 | 9 Pages |
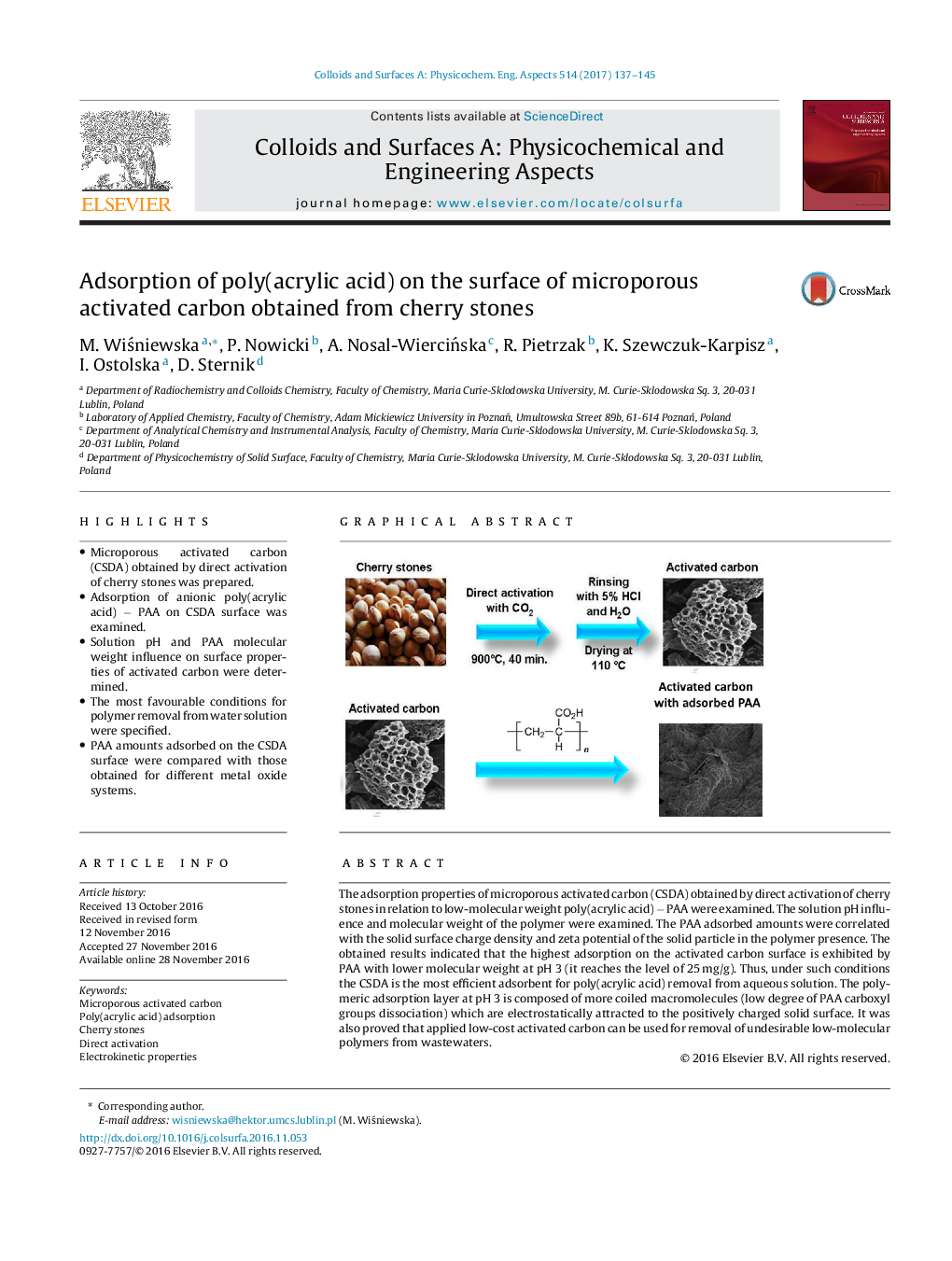
â¢Microporous activated carbon (CSDA) obtained by direct activation of cherry stones was prepared.â¢Adsorption of anionic poly(acrylic acid) â PAA on CSDA surface was examined.â¢Solution pH and PAA molecular weight influence on surface properties of activated carbon were determined.â¢The most favourable conditions for polymer removal from water solution were specified.â¢PAA amounts adsorbed on the CSDA surface were compared with those obtained for different metal oxide systems.
The adsorption properties of microporous activated carbon (CSDA) obtained by direct activation of cherry stones in relation to low-molecular weight poly(acrylic acid) â PAA were examined. The solution pH influence and molecular weight of the polymer were examined. The PAA adsorbed amounts were correlated with the solid surface charge density and zeta potential of the solid particle in the polymer presence. The obtained results indicated that the highest adsorption on the activated carbon surface is exhibited by PAA with lower molecular weight at pH 3 (it reaches the level of 25Â mg/g). Thus, under such conditions the CSDA is the most efficient adsorbent for poly(acrylic acid) removal from aqueous solution. The polymeric adsorption layer at pH 3 is composed of more coiled macromolecules (low degree of PAA carboxyl groups dissociation) which are electrostatically attracted to the positively charged solid surface. It was also proved that applied low-cost activated carbon can be used for removal of undesirable low-molecular polymers from wastewaters.
Graphical abstractDownload high-res image (200KB)Download full-size image