| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4982523 | Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects | 2017 | 7 Pages |
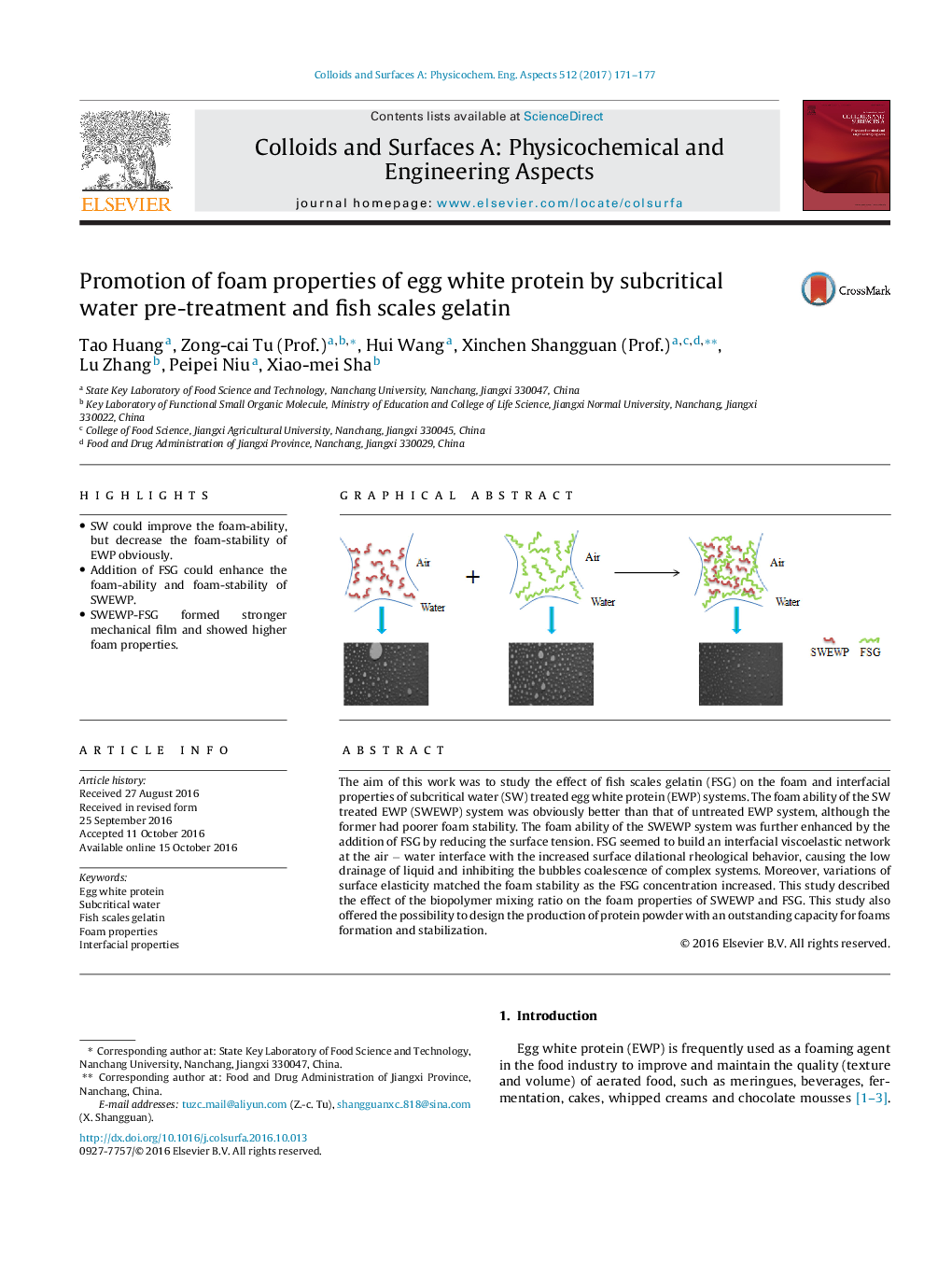
â¢SW could improve the foam-ability, but decrease the foam-stability of EWP obviously.â¢Addition of FSG could enhance the foam-ability and foam-stability of SWEWP.â¢SWEWP-FSG formed stronger mechanical film and showed higher foam properties.
The aim of this work was to study the effect of fish scales gelatin (FSG) on the foam and interfacial properties of subcritical water (SW) treated egg white protein (EWP) systems. The foam ability of the SW treated EWP (SWEWP) system was obviously better than that of untreated EWP system, although the former had poorer foam stability. The foam ability of the SWEWP system was further enhanced by the addition of FSG by reducing the surface tension. FSG seemed to build an interfacial viscoelastic network at the air â water interface with the increased surface dilational rheological behavior, causing the low drainage of liquid and inhibiting the bubbles coalescence of complex systems. Moreover, variations of surface elasticity matched the foam stability as the FSG concentration increased. This study described the effect of the biopolymer mixing ratio on the foam properties of SWEWP and FSG. This study also offered the possibility to design the production of protein powder with an outstanding capacity for foams formation and stabilization.
Graphical abstractDownload high-res image (157KB)Download full-size image