| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4984298 | Journal of Colloid and Interface Science | 2018 | 7 Pages |
â¢AgBr@Bi2WO6/WO3 exhibited greatly enhanced photocatalytic activity.â¢The AgBr@Bi2WO6/WO3 composite is a novel ternary system.â¢The increased photocatalytic activity of the double Z-scheme system was discussed in detail.
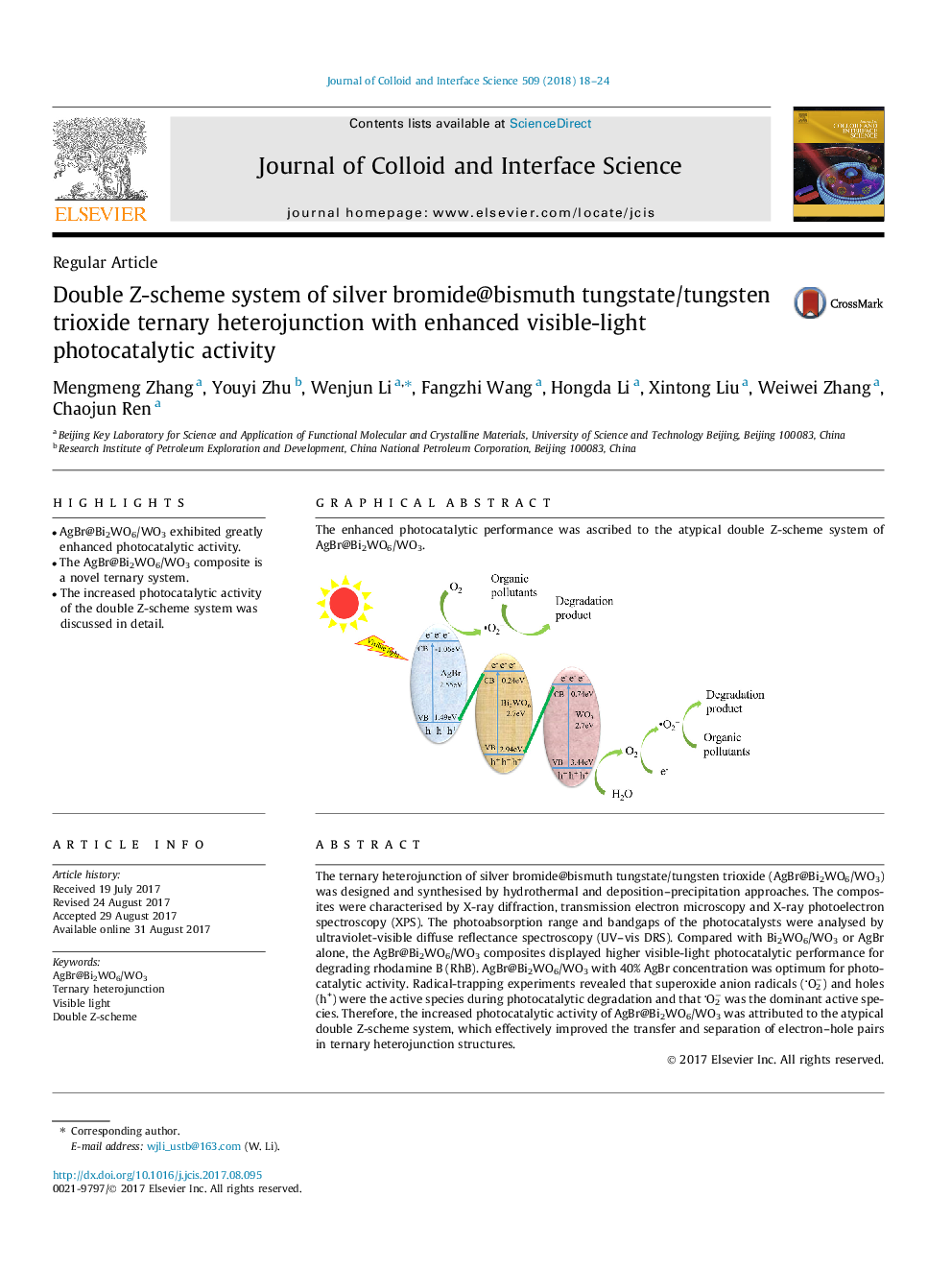
The ternary heterojunction of silver bromide@bismuth tungstate/tungsten trioxide (AgBr@Bi2WO6/WO3) was designed and synthesised by hydrothermal and deposition-precipitation approaches. The composites were characterised by X-ray diffraction, transmission electron microscopy and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The photoabsorption range and bandgaps of the photocatalysts were analysed by ultraviolet-visible diffuse reflectance spectroscopy (UV-vis DRS). Compared with Bi2WO6/WO3 or AgBr alone, the AgBr@Bi2WO6/WO3 composites displayed higher visible-light photocatalytic performance for degrading rhodamine B (RhB). AgBr@Bi2WO6/WO3 with 40% AgBr concentration was optimum for photocatalytic activity. Radical-trapping experiments revealed that superoxide anion radicals (O2â) and holes (h+) were the active species during photocatalytic degradation and that O2â was the dominant active species. Therefore, the increased photocatalytic activity of AgBr@Bi2WO6/WO3 was attributed to the atypical double Z-scheme system, which effectively improved the transfer and separation of electron-hole pairs in ternary heterojunction structures.
Graphical abstractThe enhanced photocatalytic performance was ascribed to the atypical double Z-scheme system of AgBr@Bi2WO6/WO3.Download high-res image (74KB)Download full-size image