| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4985139 | Journal of Colloid and Interface Science | 2017 | 7 Pages |
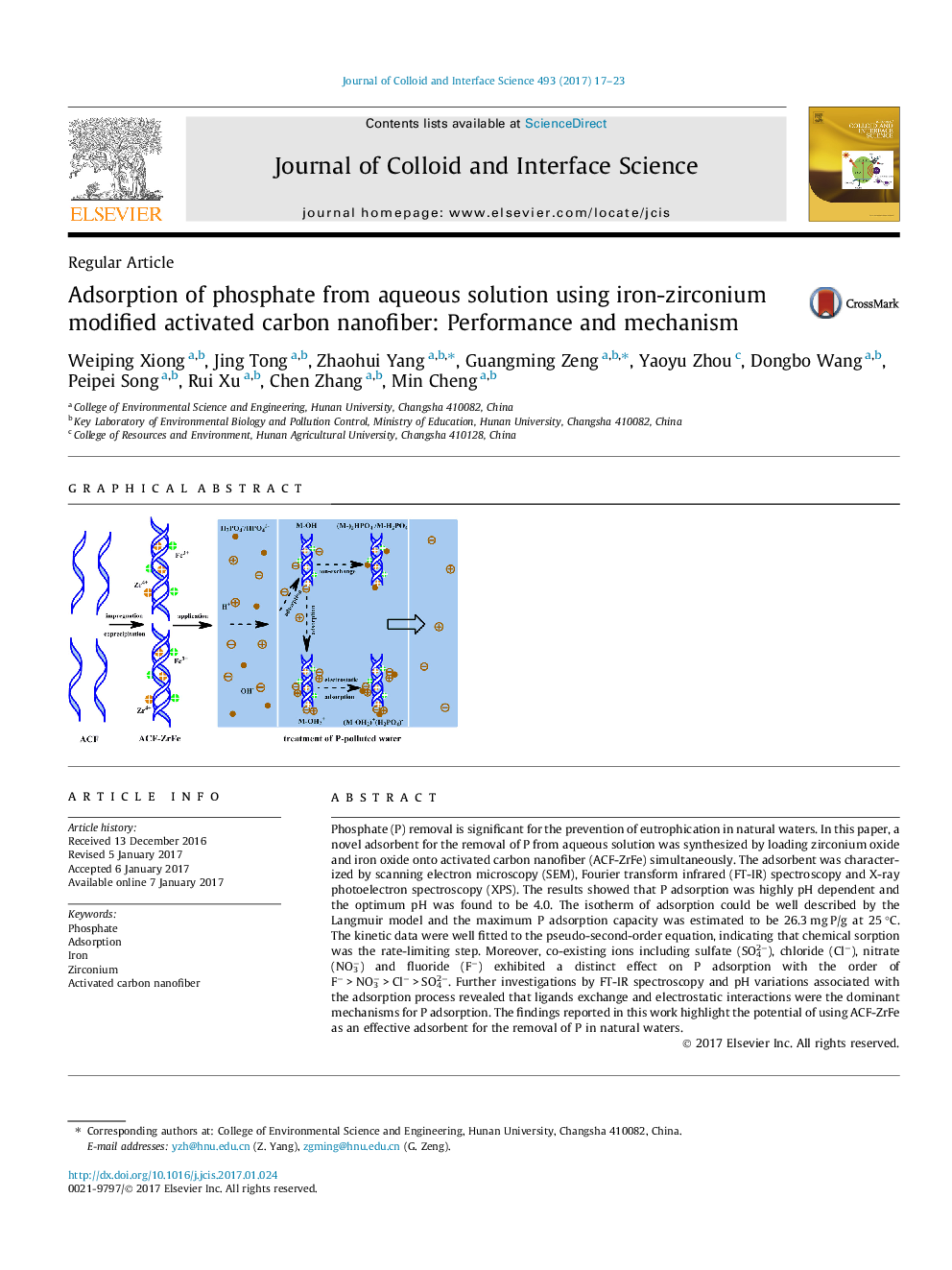
Phosphate (P) removal is significant for the prevention of eutrophication in natural waters. In this paper, a novel adsorbent for the removal of P from aqueous solution was synthesized by loading zirconium oxide and iron oxide onto activated carbon nanofiber (ACF-ZrFe) simultaneously. The adsorbent was characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The results showed that P adsorption was highly pH dependent and the optimum pH was found to be 4.0. The isotherm of adsorption could be well described by the Langmuir model and the maximum P adsorption capacity was estimated to be 26.3 mg P/g at 25 °C. The kinetic data were well fitted to the pseudo-second-order equation, indicating that chemical sorption was the rate-limiting step. Moreover, co-existing ions including sulfate (SO42â), chloride (Clâ), nitrate (NO3â) and fluoride (Fâ) exhibited a distinct effect on P adsorption with the order of Fâ > NO3â > Clâ > SO42â. Further investigations by FT-IR spectroscopy and pH variations associated with the adsorption process revealed that ligands exchange and electrostatic interactions were the dominant mechanisms for P adsorption. The findings reported in this work highlight the potential of using ACF-ZrFe as an effective adsorbent for the removal of P in natural waters.
Graphical abstractDownload high-res image (104KB)Download full-size image