| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4985442 | Journal of Colloid and Interface Science | 2017 | 8 Pages |
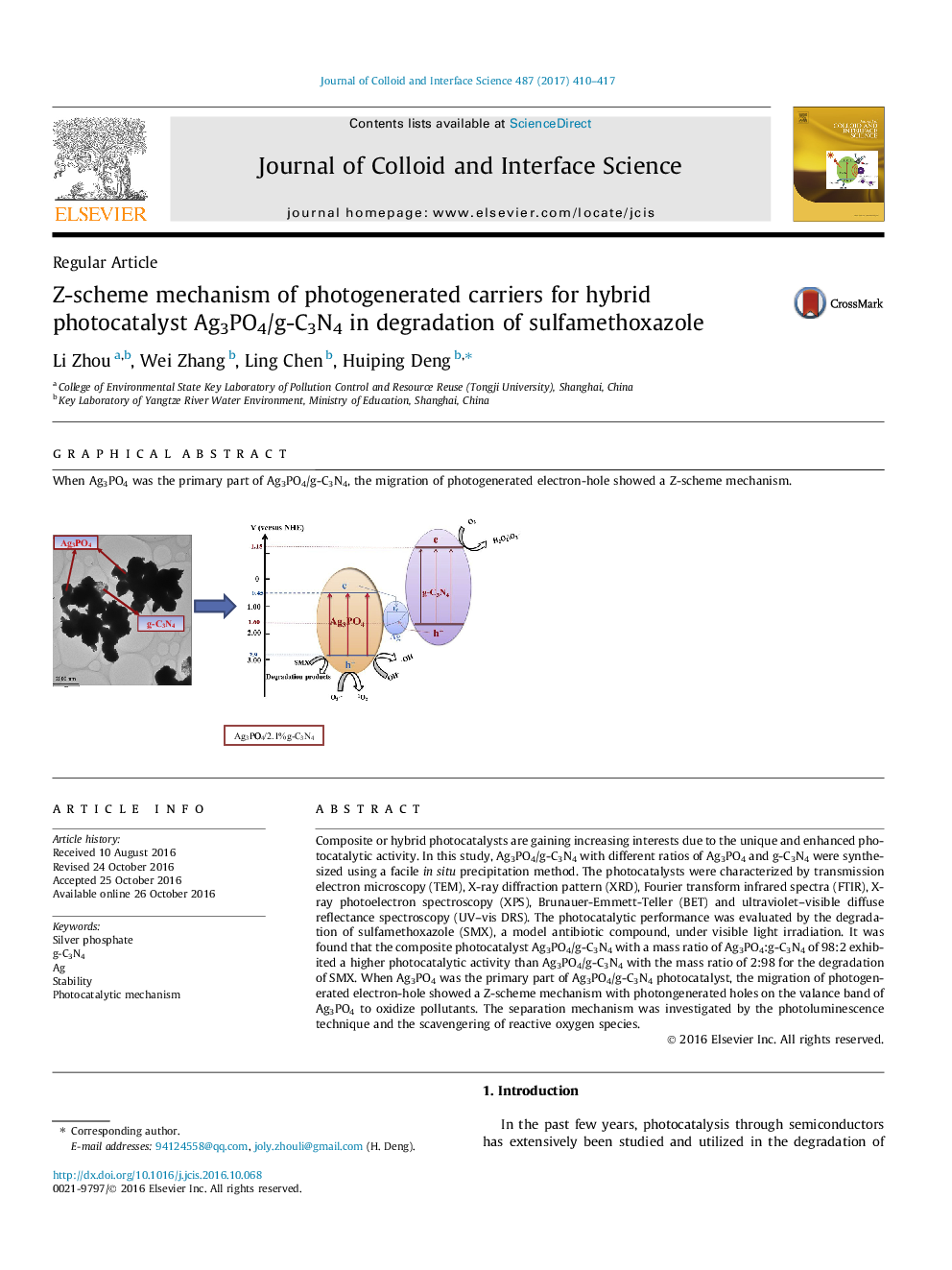
Composite or hybrid photocatalysts are gaining increasing interests due to the unique and enhanced photocatalytic activity. In this study, Ag3PO4/g-C3N4 with different ratios of Ag3PO4 and g-C3N4 were synthesized using a facile in situ precipitation method. The photocatalysts were characterized by transmission electron microscopy (TEM), X-ray diffraction pattern (XRD), Fourier transform infrared spectra (FTIR), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET) and ultraviolet-visible diffuse reflectance spectroscopy (UV-vis DRS). The photocatalytic performance was evaluated by the degradation of sulfamethoxazole (SMX), a model antibiotic compound, under visible light irradiation. It was found that the composite photocatalyst Ag3PO4/g-C3N4 with a mass ratio of Ag3PO4:g-C3N4 of 98:2 exhibited a higher photocatalytic activity than Ag3PO4/g-C3N4 with the mass ratio of 2:98 for the degradation of SMX. When Ag3PO4 was the primary part of Ag3PO4/g-C3N4 photocatalyst, the migration of photogenerated electron-hole showed a Z-scheme mechanism with photongenerated holes on the valance band of Ag3PO4 to oxidize pollutants. The separation mechanism was investigated by the photoluminescence technique and the scavengering of reactive oxygen species.
Graphical abstractWhen Ag3PO4 was the primary part of Ag3PO4/g-C3N4, the migration of photogenerated electron-hole showed a Z-scheme mechanism.Download high-res image (145KB)Download full-size image