| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4985452 | Journal of Colloid and Interface Science | 2017 | 11 Pages |
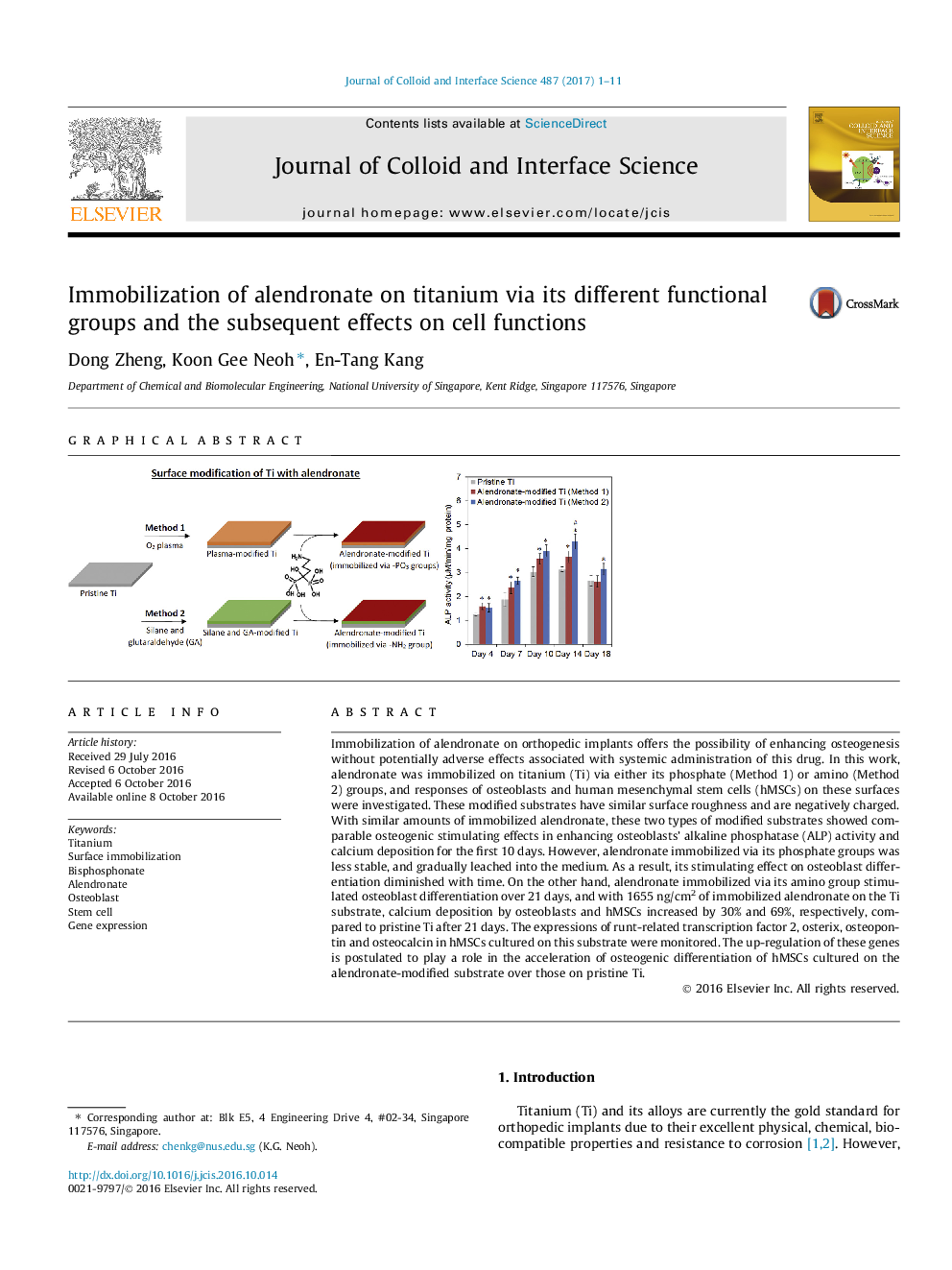
Immobilization of alendronate on orthopedic implants offers the possibility of enhancing osteogenesis without potentially adverse effects associated with systemic administration of this drug. In this work, alendronate was immobilized on titanium (Ti) via either its phosphate (Method 1) or amino (Method 2) groups, and responses of osteoblasts and human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs) on these surfaces were investigated. These modified substrates have similar surface roughness and are negatively charged. With similar amounts of immobilized alendronate, these two types of modified substrates showed comparable osteogenic stimulating effects in enhancing osteoblasts' alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity and calcium deposition for the first 10Â days. However, alendronate immobilized via its phosphate groups was less stable, and gradually leached into the medium. As a result, its stimulating effect on osteoblast differentiation diminished with time. On the other hand, alendronate immobilized via its amino group stimulated osteoblast differentiation over 21Â days, and with 1655Â ng/cm2 of immobilized alendronate on the Ti substrate, calcium deposition by osteoblasts and hMSCs increased by 30% and 69%, respectively, compared to pristine Ti after 21Â days. The expressions of runt-related transcription factor 2, osterix, osteopontin and osteocalcin in hMSCs cultured on this substrate were monitored. The up-regulation of these genes is postulated to play a role in the acceleration of osteogenic differentiation of hMSCs cultured on the alendronate-modified substrate over those on pristine Ti.
Graphical abstractDownload high-res image (88KB)Download full-size image