| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5130734 | Analytica Chimica Acta | 2017 | 7 Pages |
â¢We designed a new electrochemical immunoassay for human IgG1.â¢Metal sulfide quantum dot-doped bovine serum albumin as the signal-generation tag.â¢Antibody-functionalized magnetic beads as the sensing probes.â¢Acid-treated quantum dots for square-wave anodic stripping voltammetric measurement.
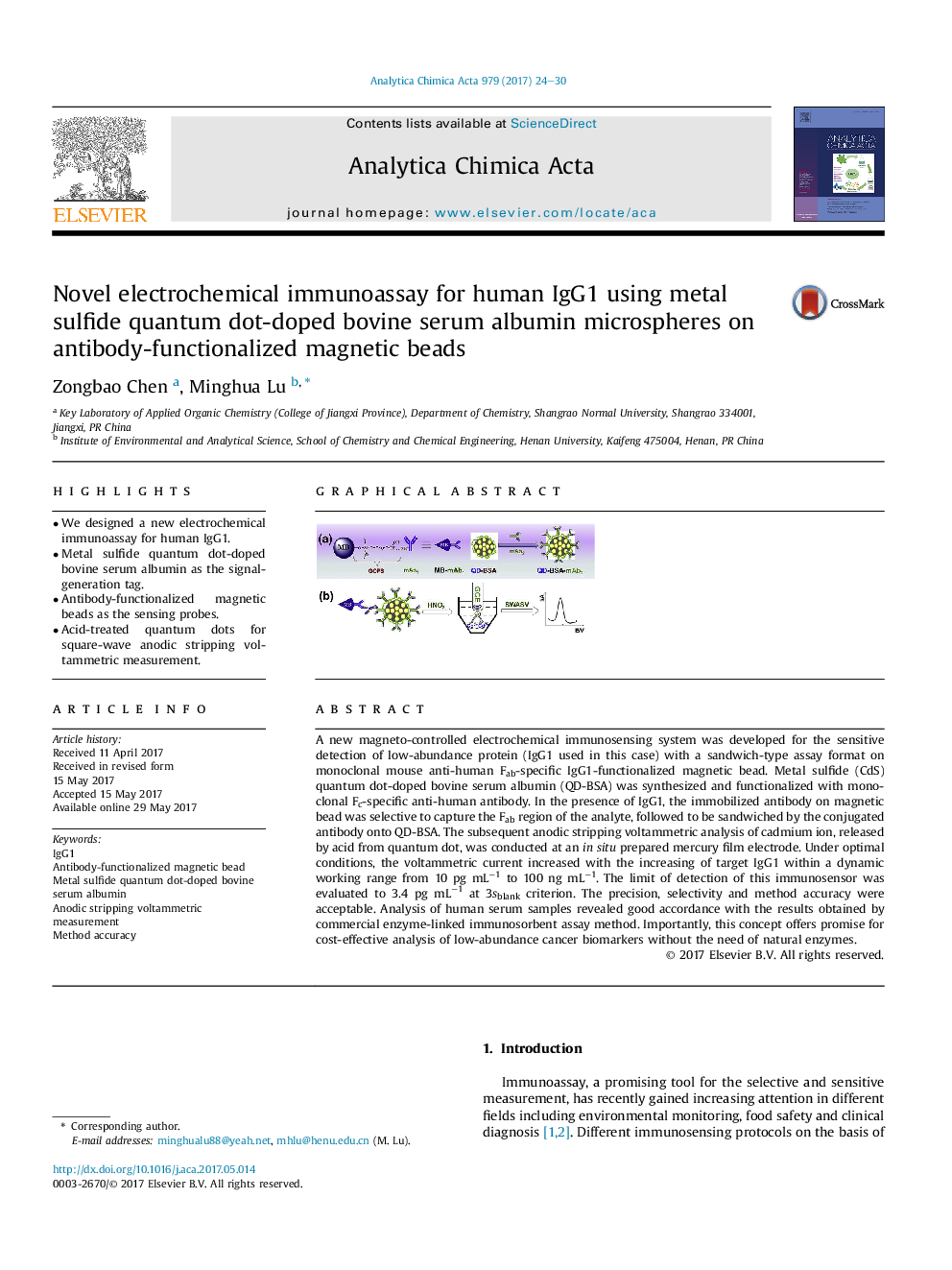
A new magneto-controlled electrochemical immunosensing system was developed for the sensitive detection of low-abundance protein (IgG1 used in this case) with a sandwich-type assay format on monoclonal mouse anti-human Fab-specific IgG1-functionalized magnetic bead. Metal sulfide (CdS) quantum dot-doped bovine serum albumin (QD-BSA) was synthesized and functionalized with monoclonal Fc-specific anti-human antibody. In the presence of IgG1, the immobilized antibody on magnetic bead was selective to capture the Fab region of the analyte, followed to be sandwiched by the conjugated antibody onto QD-BSA. The subsequent anodic stripping voltammetric analysis of cadmium ion, released by acid from quantum dot, was conducted at an in situ prepared mercury film electrode. Under optimal conditions, the voltammetric current increased with the increasing of target IgG1 within a dynamic working range from 10 pg mLâ1 to 100 ng mLâ1. The limit of detection of this immunosensor was evaluated to 3.4 pg mLâ1 at 3sblank criterion. The precision, selectivity and method accuracy were acceptable. Analysis of human serum samples revealed good accordance with the results obtained by commercial enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay method. Importantly, this concept offers promise for cost-effective analysis of low-abundance cancer biomarkers without the need of natural enzymes.
Graphical abstractDownload high-res image (405KB)Download full-size image