| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5130904 | Analytica Chimica Acta | 2017 | 9 Pages |
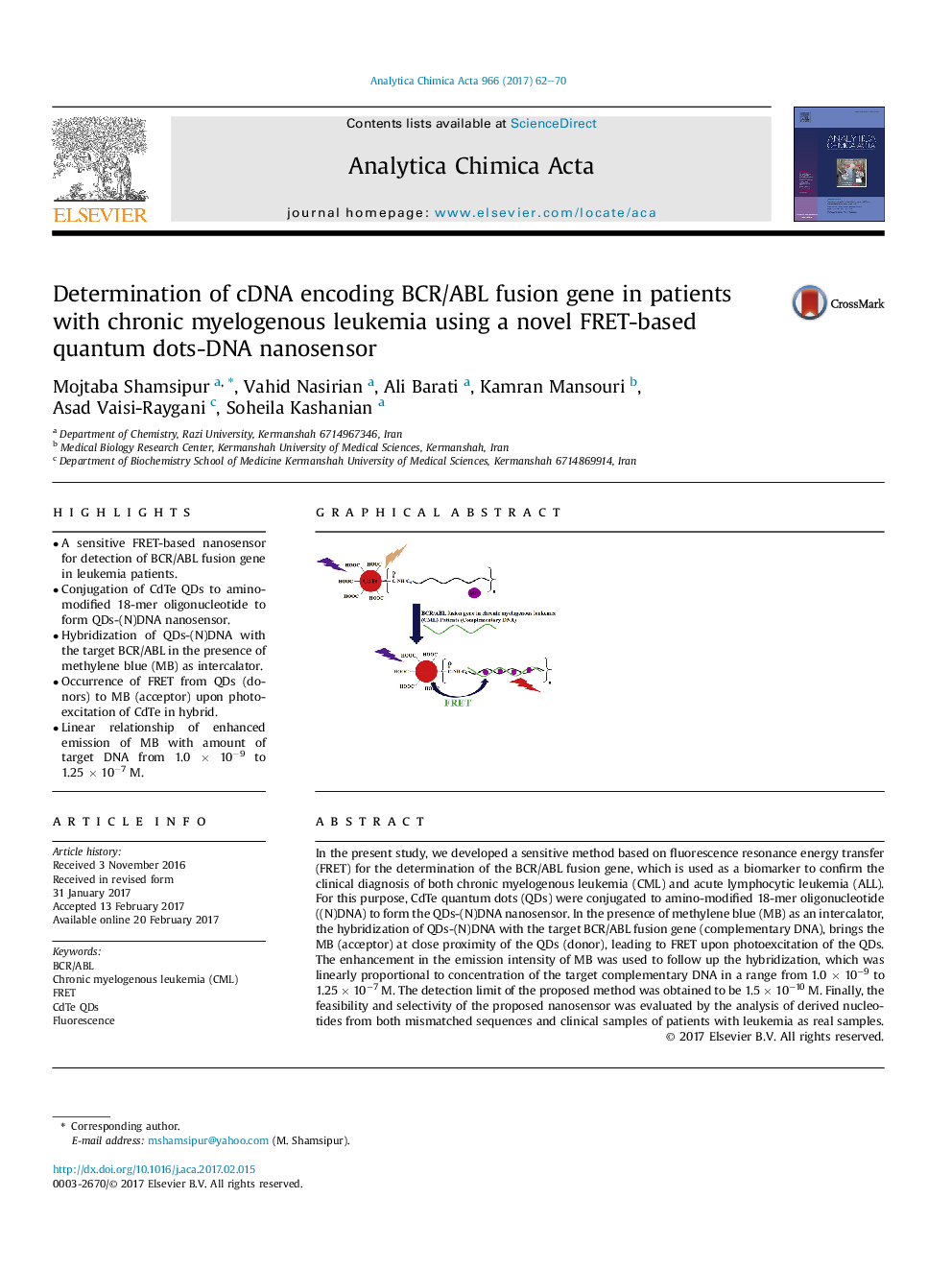
â¢A sensitive FRET-based nanosensor for detection of BCR/ABL fusion gene in leukemia patients.â¢Conjugation of CdTe QDs to amino-modified 18-mer oligonucleotide to form QDs-(N)DNA nanosensor.â¢Hybridization of QDs-(N)DNA with the target BCR/ABL in the presence of methylene blue (MB) as intercalator.â¢Occurrence of FRET from QDs (donors) to MB (acceptor) upon photoexcitation of CdTe in hybrid.â¢Linear relationship of enhanced emission of MB with amount of target DNA from 1.0 Ã 10â9 to 1.25 Ã 10â7 M.
In the present study, we developed a sensitive method based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) for the determination of the BCR/ABL fusion gene, which is used as a biomarker to confirm the clinical diagnosis of both chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) and acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL). For this purpose, CdTe quantum dots (QDs) were conjugated to amino-modified 18-mer oligonucleotide ((N)DNA) to form the QDs-(N)DNA nanosensor. In the presence of methylene blue (MB) as an intercalator, the hybridization of QDs-(N)DNA with the target BCR/ABL fusion gene (complementary DNA), brings the MB (acceptor) at close proximity of the QDs (donor), leading to FRET upon photoexcitation of the QDs. The enhancement in the emission intensity of MB was used to follow up the hybridization, which was linearly proportional to concentration of the target complementary DNA in a range from 1.0Â ÃÂ 10â9 to 1.25Â ÃÂ 10â7Â M. The detection limit of the proposed method was obtained to be 1.5Â ÃÂ 10â10Â M. Finally, the feasibility and selectivity of the proposed nanosensor was evaluated by the analysis of derived nucleotides from both mismatched sequences and clinical samples of patients with leukemia as real samples.
Graphical abstractDownload high-res image (152KB)Download full-size image