| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5131093 | Analytica Chimica Acta | 2017 | 7 Pages |
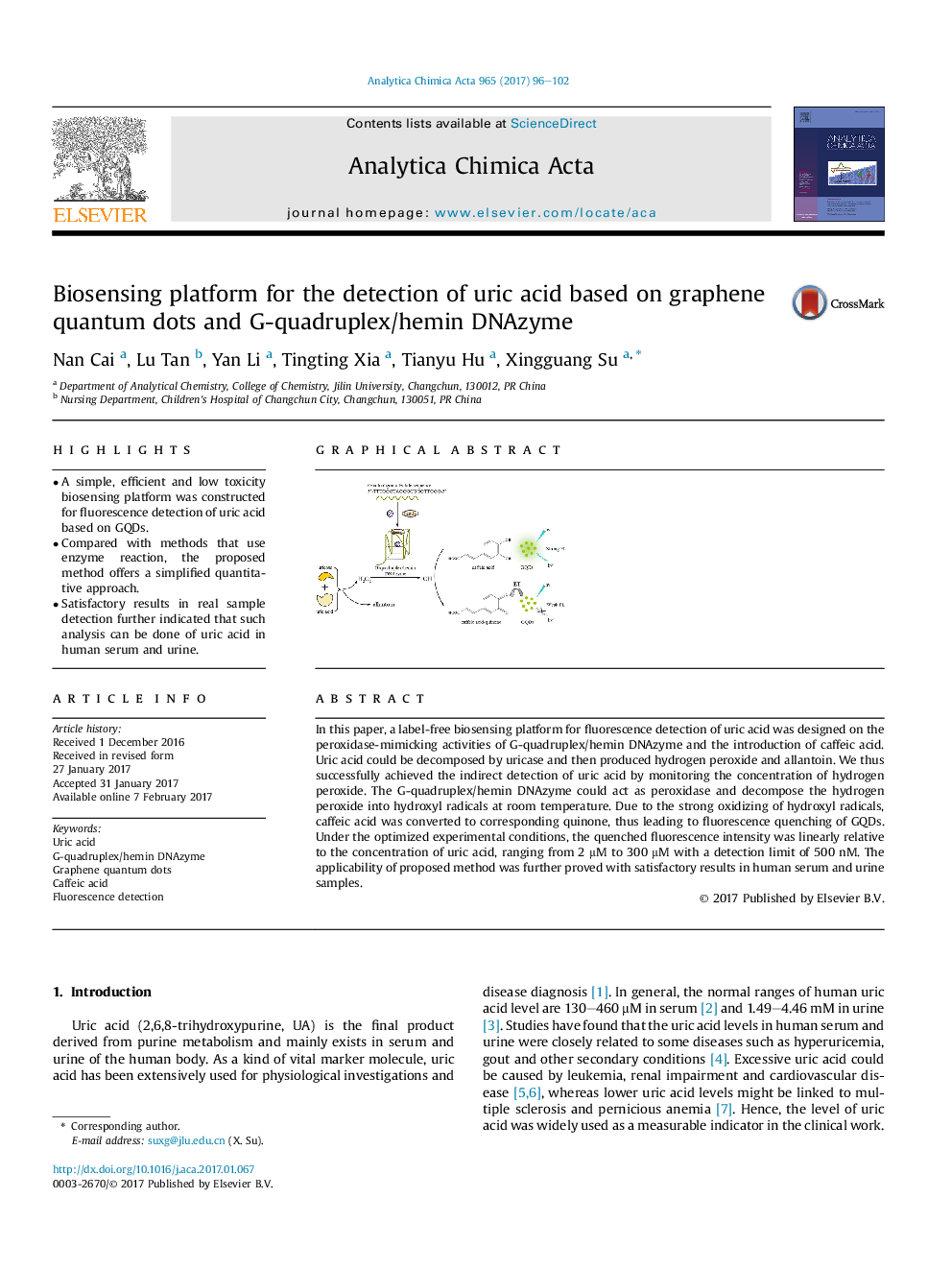
â¢A simple, efficient and low toxicity biosensing platform was constructed for fluorescence detection of uric acid based on GQDs.â¢Compared with methods that use enzyme reaction, the proposed method offers a simplified quantitative approach.â¢Satisfactory results in real sample detection further indicated that such analysis can be done of uric acid in human serum and urine.
In this paper, a label-free biosensing platform for fluorescence detection of uric acid was designed on the peroxidase-mimicking activities of G-quadruplex/hemin DNAzyme and the introduction of caffeic acid. Uric acid could be decomposed by uricase and then produced hydrogen peroxide and allantoin. We thus successfully achieved the indirect detection of uric acid by monitoring the concentration of hydrogen peroxide. The G-quadruplex/hemin DNAzyme could act as peroxidase and decompose the hydrogen peroxide into hydroxyl radicals at room temperature. Due to the strong oxidizing of hydroxyl radicals, caffeic acid was converted to corresponding quinone, thus leading to fluorescence quenching of GQDs. Under the optimized experimental conditions, the quenched fluorescence intensity was linearly relative to the concentration of uric acid, ranging from 2 μM to 300 μM with a detection limit of 500 nM. The applicability of proposed method was further proved with satisfactory results in human serum and urine samples.
Graphical abstractDownload high-res image (145KB)Download full-size image