| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5131142 | Analytica Chimica Acta | 2017 | 12 Pages |
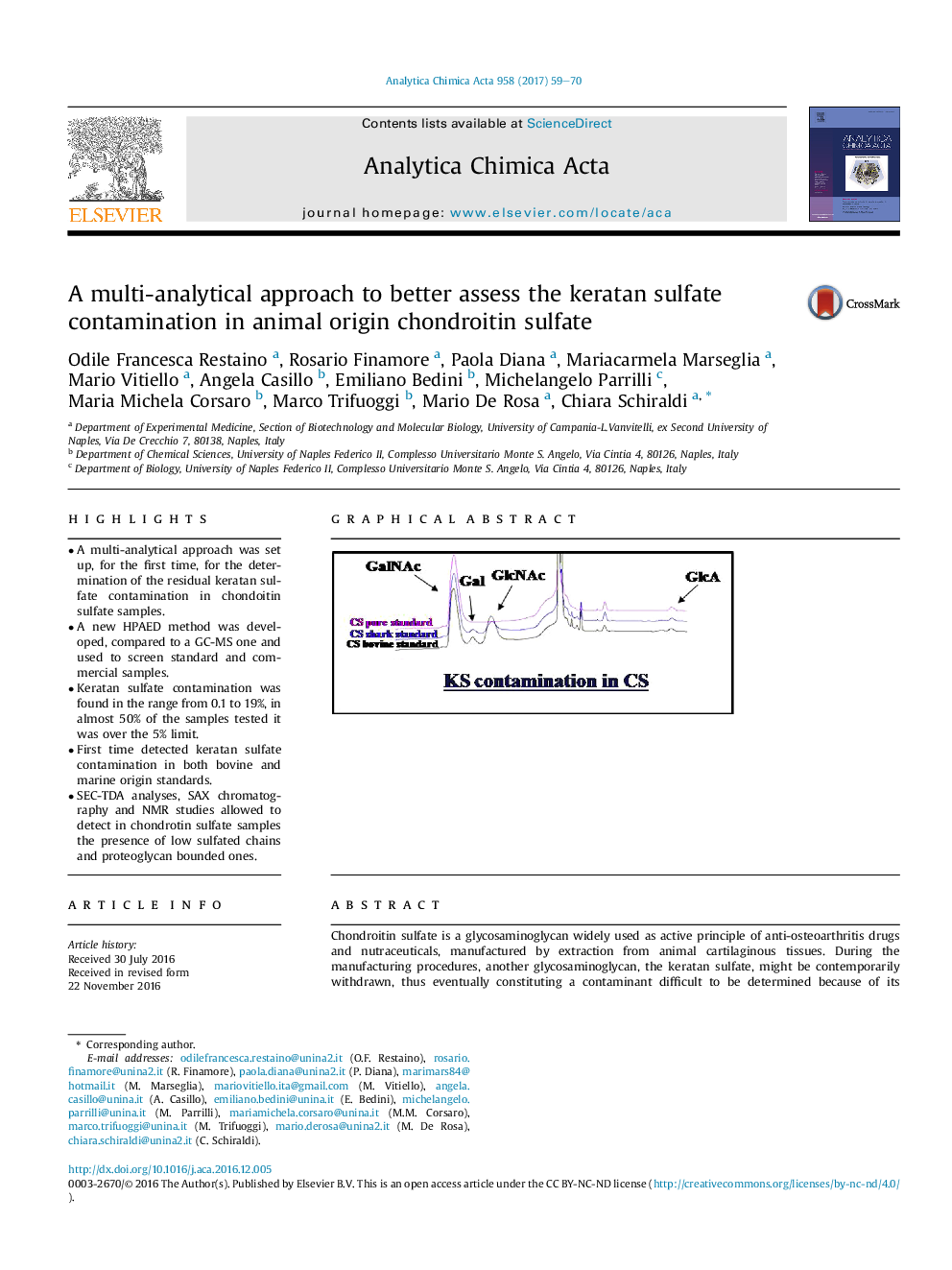
â¢A multi-analytical approach was set up, for the first time, for the determination of the residual keratan sulfate contamination in chondoitin sulfate samples.â¢A new HPAED method was developed, compared to a GC-MS one and used to screen standard and commercial samples.â¢Keratan sulfate contamination was found in the range from 0.1 to 19%, in almost 50% of the samples tested it was over the 5% limit.â¢First time detected keratan sulfate contamination in both bovine and marine origin standards.â¢SEC-TDA analyses, SAX chromatography and NMR studies allowed to detect in chondrotin sulfate samples the presence of low sulfated chains and proteoglycan bounded ones.
Chondroitin sulfate is a glycosaminoglycan widely used as active principle of anti-osteoarthritis drugs and nutraceuticals, manufactured by extraction from animal cartilaginous tissues. During the manufacturing procedures, another glycosaminoglycan, the keratan sulfate, might be contemporarily withdrawn, thus eventually constituting a contaminant difficult to be determined because of its structural similarity. Considering the strict regulatory rules on the pureness of pharmaceutical grade chondrotin sulfate there is an urgent need and interest to determine the residual keratan sulfate with specific, sensitive and reliable methods. To pursue this aim, in this paper, for the first time, we set up a multi-analytical and preparative approach based on: i) a newly developed method by high performance anion-exchange chromatography with pulsed amperometric detection, ii) gas chromatography-mass spectrometry analyses, iii) size exclusion chromatography analyses coupled with triple detector array module and on iv) strong anion exchange chromatography separation. Varied KS percentages, in the range from 0.1 to 19.0% (w/w), were determined in seven pharmacopeia and commercial standards and nine commercial samples of different animal origin and manufacturers. Strong anion exchange chromatography profiles of the samples showed three or four different peaks. These peaks analyzed by high performance anion-exchange with pulsed amperometric detection and size exclusion chromatography with triple detector array, ion chromatography and by mono- or two-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance revealed a heterogeneous composition of both glycosaminoglycans in terms of sulfation grade and molecular weight. High molecular weight species (>100Â KDa) were also present in the samples that counted for chains still partially linked to a proteoglycan core.
Graphical abstractDownload high-res image (192KB)Download full-size image