| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5131223 | Analytica Chimica Acta | 2016 | 8 Pages |
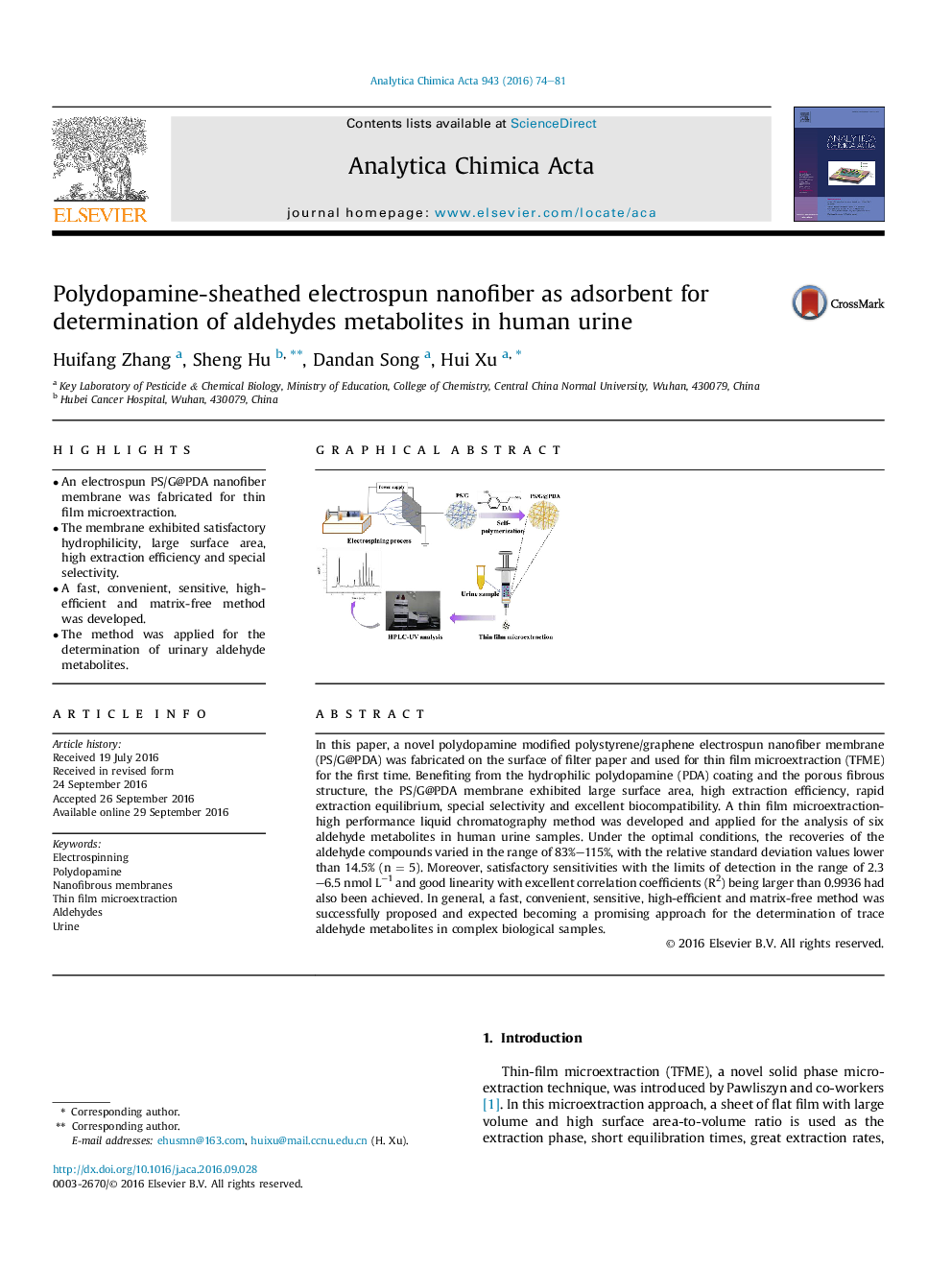
â¢An electrospun PS/G@PDA nanofiber membrane was fabricated for thin film microextraction.â¢The membrane exhibited satisfactory hydrophilicity, large surface area, high extraction efficiency and special selectivity.â¢A fast, convenient, sensitive, high-efficient and matrix-free method was developed.â¢The method was applied for the determination of urinary aldehyde metabolites.
In this paper, a novel polydopamine modified polystyrene/graphene electrospun nanofiber membrane (PS/G@PDA) was fabricated on the surface of filter paper and used for thin film microextraction (TFME) for the first time. Benefiting from the hydrophilic polydopamine (PDA) coating and the porous fibrous structure, the PS/G@PDA membrane exhibited large surface area, high extraction efficiency, rapid extraction equilibrium, special selectivity and excellent biocompatibility. A thin film microextraction-high performance liquid chromatography method was developed and applied for the analysis of six aldehyde metabolites in human urine samples. Under the optimal conditions, the recoveries of the aldehyde compounds varied in the range of 83%-115%, with the relative standard deviation values lower than 14.5% (n = 5). Moreover, satisfactory sensitivities with the limits of detection in the range of 2.3-6.5 nmol Lâ1 and good linearity with excellent correlation coefficients (R2) being larger than 0.9936 had also been achieved. In general, a fast, convenient, sensitive, high-efficient and matrix-free method was successfully proposed and expected becoming a promising approach for the determination of trace aldehyde metabolites in complex biological samples.
Graphical abstractDownload high-res image (156KB)Download full-size image