| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5131321 | Analytica Chimica Acta | 2016 | 7 Pages |
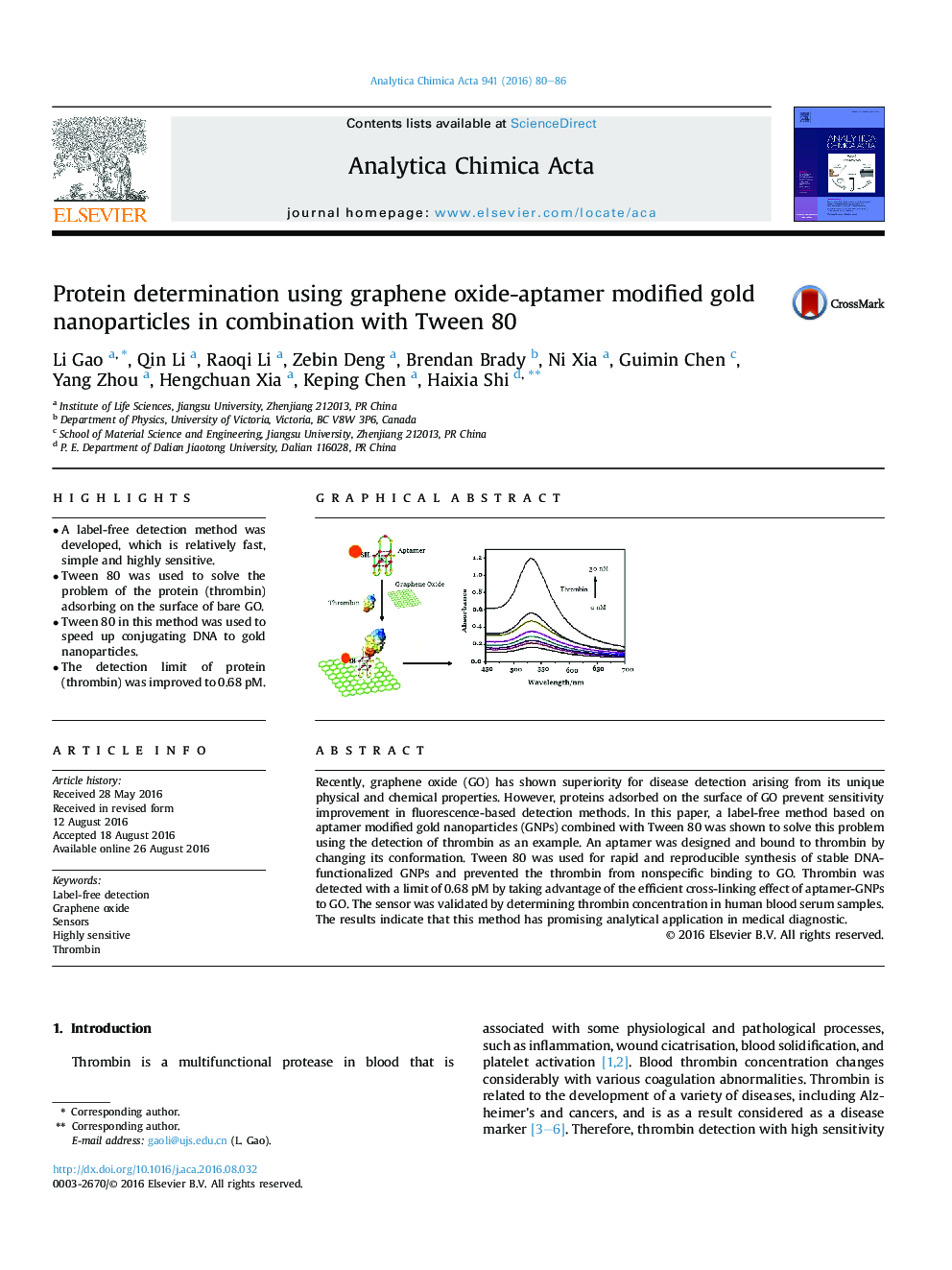
â¢A label-free detection method was developed, which is relatively fast, simple and highly sensitive.â¢Tween 80 was used to solve the problem of the protein (thrombin) adsorbing on the surface of bare GO.â¢Tween 80 in this method was used to speed up conjugating DNA to gold nanoparticles.â¢The detection limit of protein (thrombin) was improved to 0.68 pM.
Recently, graphene oxide (GO) has shown superiority for disease detection arising from its unique physical and chemical properties. However, proteins adsorbed on the surface of GO prevent sensitivity improvement in fluorescence-based detection methods. In this paper, a label-free method based on aptamer modified gold nanoparticles (GNPs) combined with Tween 80 was shown to solve this problem using the detection of thrombin as an example. An aptamer was designed and bound to thrombin by changing its conformation. Tween 80 was used for rapid and reproducible synthesis of stable DNA-functionalized GNPs and prevented the thrombin from nonspecific binding to GO. Thrombin was detected with a limit of 0.68 pM by taking advantage of the efficient cross-linking effect of aptamer-GNPs to GO. The sensor was validated by determining thrombin concentration in human blood serum samples. The results indicate that this method has promising analytical application in medical diagnostic.
Graphical abstractDownload high-res image (198KB)Download full-size image