| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 591448 | Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects | 2016 | 8 Pages |
•Cosolvent effect on the micellization of amino sulfonate (C12AS) with cationic surfactant.•The change in the conformation of C12AS.•An abnormal dependence of component’s fraction in mixed micelle on cosolvent.•Electrostatic interaction between two surfactants.•Molecular and thermodynamic mechanisms are presented.
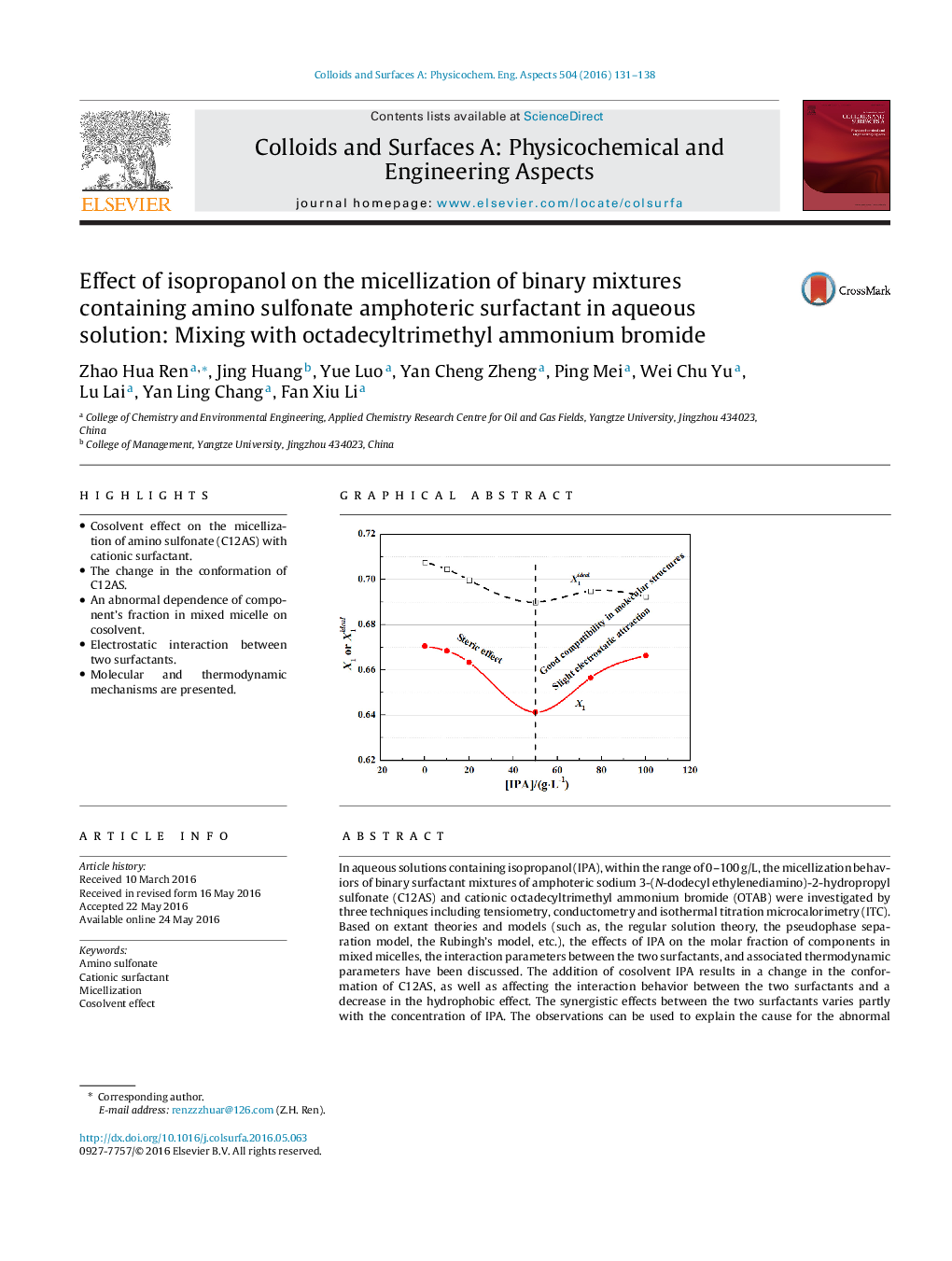
In aqueous solutions containing isopropanol (IPA), within the range of 0–100 g/L, the micellization behaviors of binary surfactant mixtures of amphoteric sodium 3-(N-dodecyl ethylenediamino)-2-hydropropyl sulfonate (C12AS) and cationic octadecyltrimethyl ammonium bromide (OTAB) were investigated by three techniques including tensiometry, conductometry and isothermal titration microcalorimetry (ITC). Based on extant theories and models (such as, the regular solution theory, the pseudophase separation model, the Rubingh’s model, etc.), the effects of IPA on the molar fraction of components in mixed micelles, the interaction parameters between the two surfactants, and associated thermodynamic parameters have been discussed. The addition of cosolvent IPA results in a change in the conformation of C12AS, as well as affecting the interaction behavior between the two surfactants and a decrease in the hydrophobic effect. The synergistic effects between the two surfactants varies partly with the concentration of IPA. The observations can be used to explain the cause for the abnormal dependence of the molar fraction of components in mixed micelles and the interaction parameters on the concentration of the cosolvent IPA. Thermodynamic parameters further show the effect of IPA on the entropy-driven process of micellization.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide