| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 591450 | Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects | 2016 | 7 Pages |
•Why nitrobenzene droplet has a high spontaneous motility?•Micelle formation is unrelated to the spontaneous droplet motion.•Contribution ratio among iodic ions to ion associate reaction with cationic surfactant.•Temporal change of droplet contact angle during running motion.
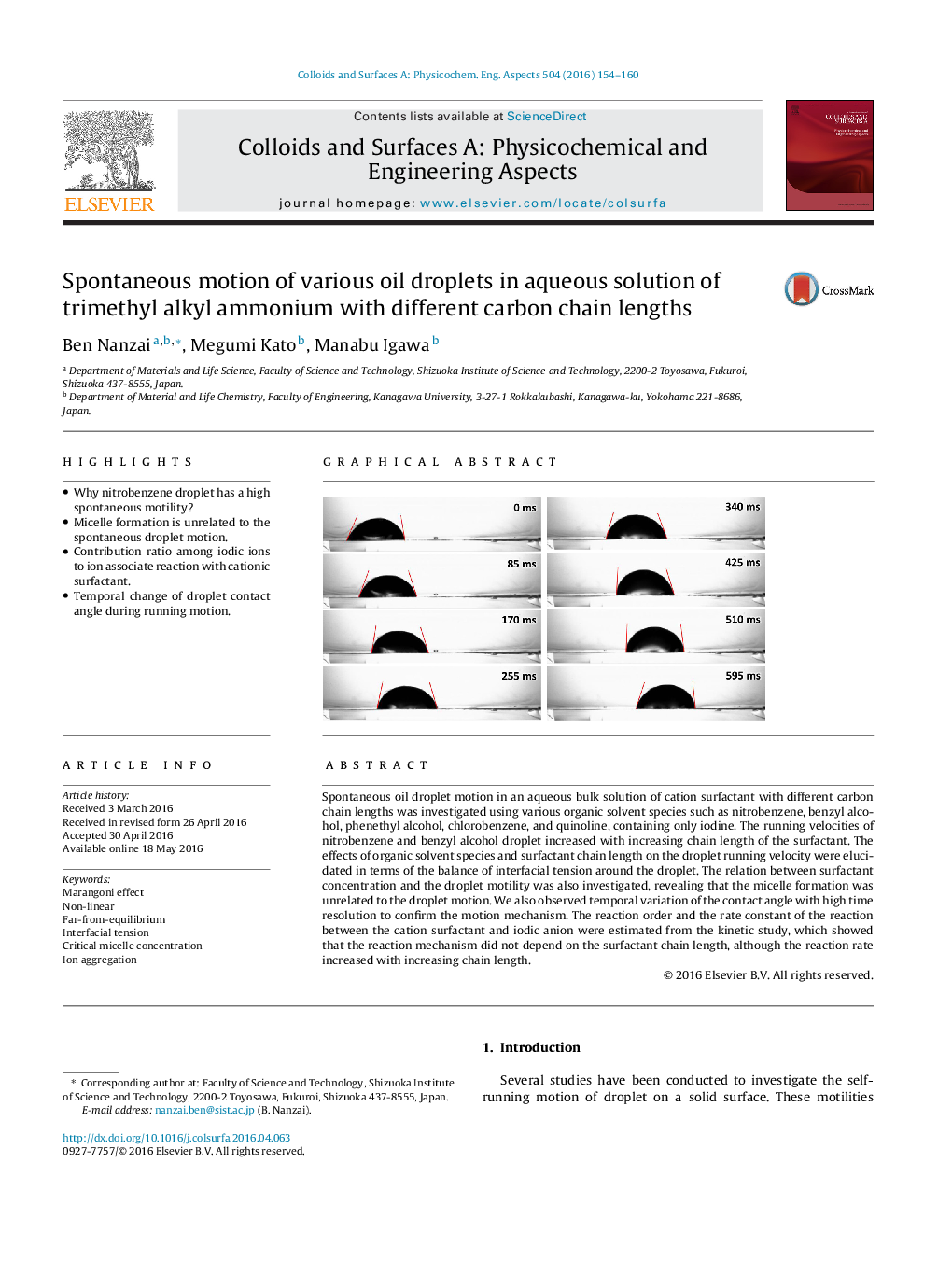
Spontaneous oil droplet motion in an aqueous bulk solution of cation surfactant with different carbon chain lengths was investigated using various organic solvent species such as nitrobenzene, benzyl alcohol, phenethyl alcohol, chlorobenzene, and quinoline, containing only iodine. The running velocities of nitrobenzene and benzyl alcohol droplet increased with increasing chain length of the surfactant. The effects of organic solvent species and surfactant chain length on the droplet running velocity were elucidated in terms of the balance of interfacial tension around the droplet. The relation between surfactant concentration and the droplet motility was also investigated, revealing that the micelle formation was unrelated to the droplet motion. We also observed temporal variation of the contact angle with high time resolution to confirm the motion mechanism. The reaction order and the rate constant of the reaction between the cation surfactant and iodic anion were estimated from the kinetic study, which showed that the reaction mechanism did not depend on the surfactant chain length, although the reaction rate increased with increasing chain length.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide