| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 591456 | Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects | 2016 | 9 Pages |
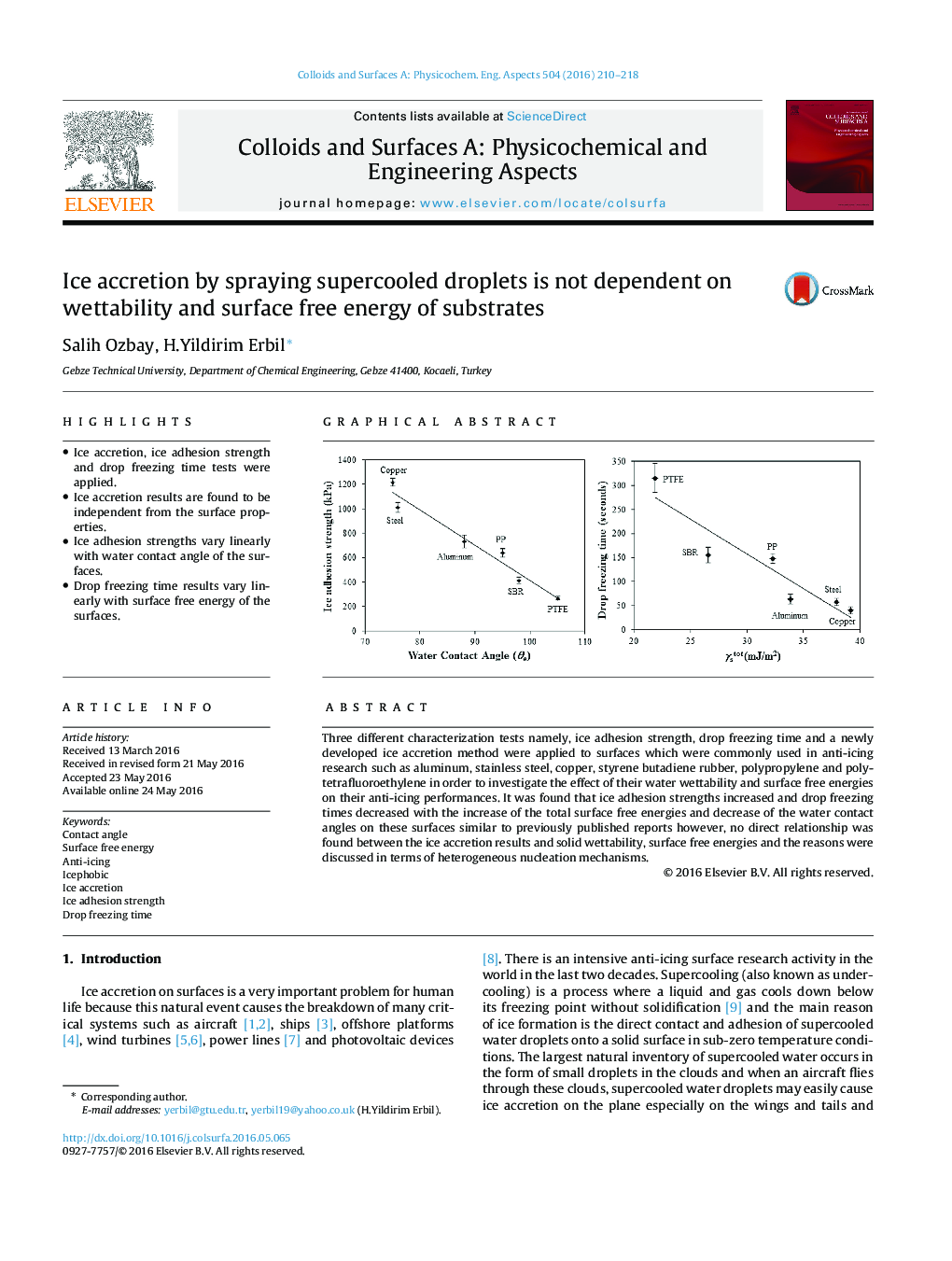
•Ice accretion, ice adhesion strength and drop freezing time tests were applied.•Ice accretion results are found to be independent from the surface properties.•Ice adhesion strengths vary linearly with water contact angle of the surfaces.•Drop freezing time results vary linearly with surface free energy of the surfaces.
Three different characterization tests namely, ice adhesion strength, drop freezing time and a newly developed ice accretion method were applied to surfaces which were commonly used in anti-icing research such as aluminum, stainless steel, copper, styrene butadiene rubber, polypropylene and polytetrafluoroethylene in order to investigate the effect of their water wettability and surface free energies on their anti-icing performances. It was found that ice adhesion strengths increased and drop freezing times decreased with the increase of the total surface free energies and decrease of the water contact angles on these surfaces similar to previously published reports however, no direct relationship was found between the ice accretion results and solid wettability, surface free energies and the reasons were discussed in terms of heterogeneous nucleation mechanisms.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide