| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 591462 | Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects | 2016 | 7 Pages |
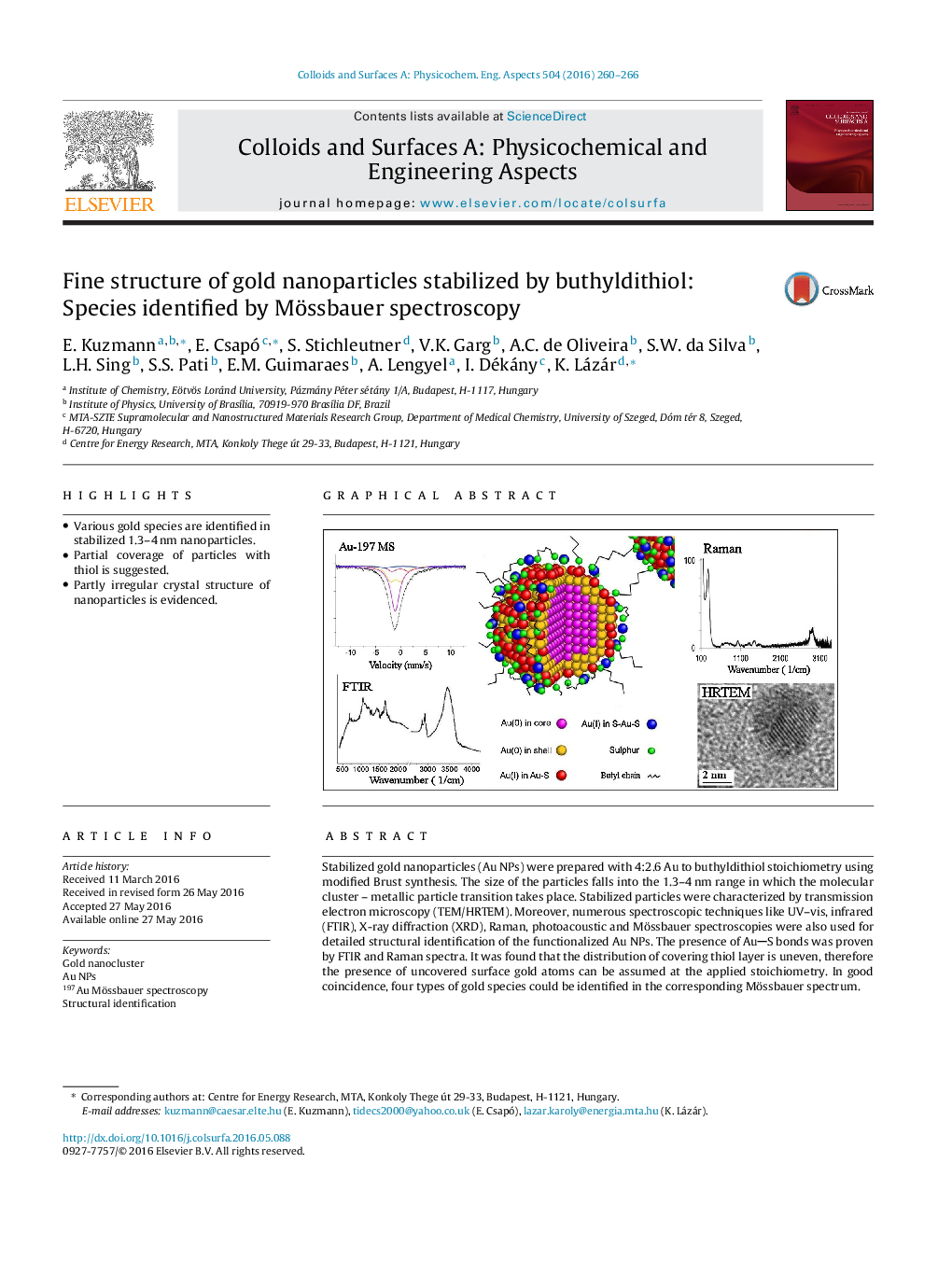
•Various gold species are identified in stabilized 1.3–4 nm nanoparticles.•Partial coverage of particles with thiol is suggested.•Partly irregular crystal structure of nanoparticles is evidenced.
Stabilized gold nanoparticles (Au NPs) were prepared with 4:2.6 Au to buthyldithiol stoichiometry using modified Brust synthesis. The size of the particles falls into the 1.3–4 nm range in which the molecular cluster – metallic particle transition takes place. Stabilized particles were characterized by transmission electron microscopy (TEM/HRTEM). Moreover, numerous spectroscopic techniques like UV–vis, infrared (FTIR), X-ray diffraction (XRD), Raman, photoacoustic and Mössbauer spectroscopies were also used for detailed structural identification of the functionalized Au NPs. The presence of AuS bonds was proven by FTIR and Raman spectra. It was found that the distribution of covering thiol layer is uneven, therefore the presence of uncovered surface gold atoms can be assumed at the applied stoichiometry. In good coincidence, four types of gold species could be identified in the corresponding Mössbauer spectrum. They can be attributed to metallic gold in the core, to bare gold in the surface layer, to surface gold atoms attached to thiol, and finally, to gold atoms pulled out from the particle, located in SAuS bridges.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide