| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 591565 | Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects | 2016 | 10 Pages |
•A facile approach to prepare monodisperse polymeric nanoparticles was proposed.•The in situ neutralization between surfactant SDS and initiator was adjusted to control the volume of micelle or primary particles.•The effect of polymerization parameters on particle size distribution was investigated.
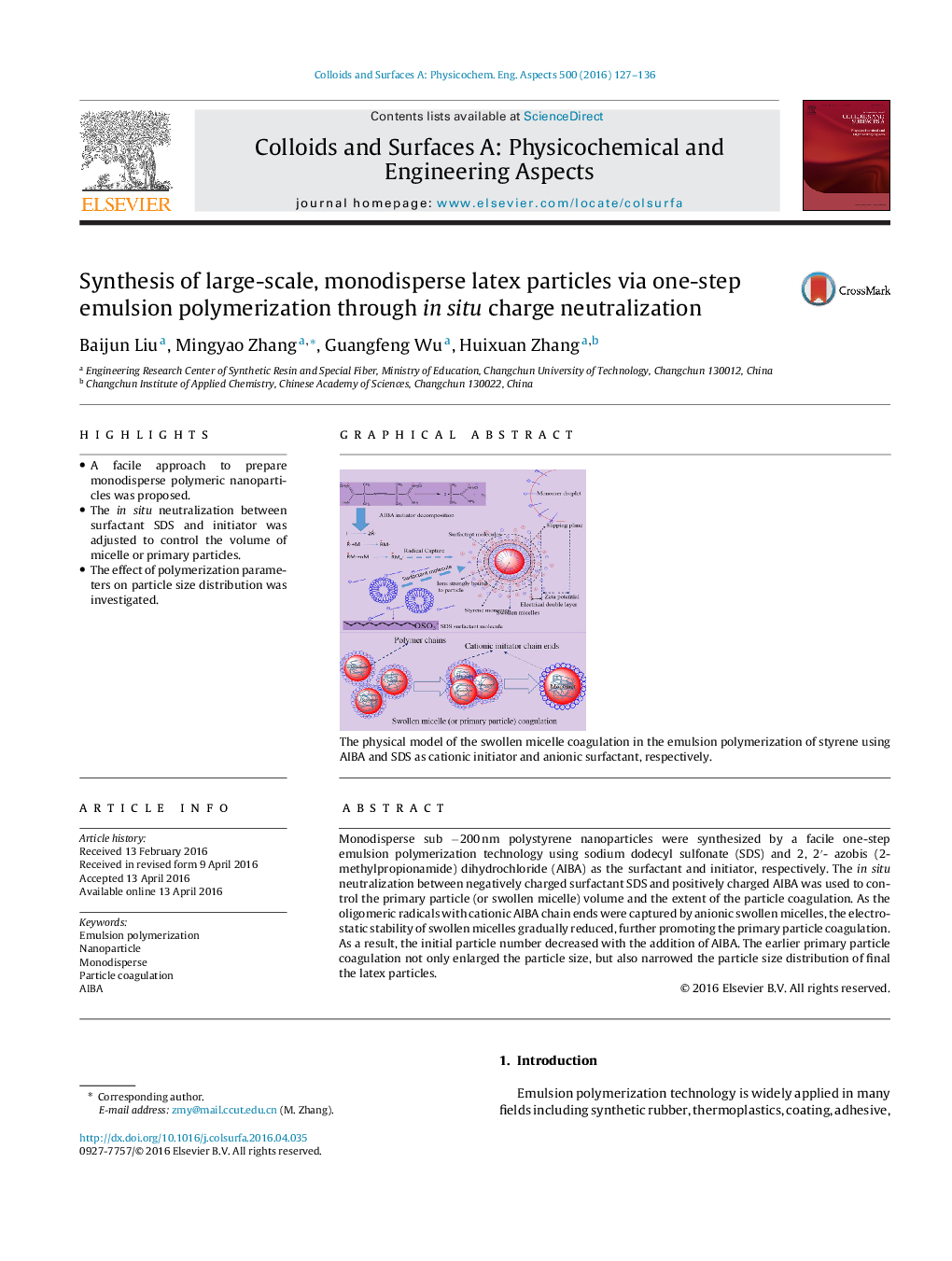
Monodisperse sub −200 nm polystyrene nanoparticles were synthesized by a facile one-step emulsion polymerization technology using sodium dodecyl sulfonate (SDS) and 2, 2′- azobis (2-methylpropionamide) dihydrochloride (AIBA) as the surfactant and initiator, respectively. The in situ neutralization between negatively charged surfactant SDS and positively charged AIBA was used to control the primary particle (or swollen micelle) volume and the extent of the particle coagulation. As the oligomeric radicals with cationic AIBA chain ends were captured by anionic swollen micelles, the electrostatic stability of swollen micelles gradually reduced, further promoting the primary particle coagulation. As a result, the initial particle number decreased with the addition of AIBA. The earlier primary particle coagulation not only enlarged the particle size, but also narrowed the particle size distribution of final the latex particles.
Graphical abstractThe physical model of the swollen micelle coagulation in the emulsion polymerization of styrene using AIBA and SDS as cationic initiator and anionic surfactant, respectively.Figure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide