| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 591614 | Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects | 2016 | 11 Pages |
•Electrical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) tests were carried out to study the complexation process.•Gum Arabic and chitosan in bulk solution were considered.•Parameters from a fractional-order Randles circuit were used as indicators of coacervation changes.•The EIS was compared with that obtained via traditional ζ-potential measurements
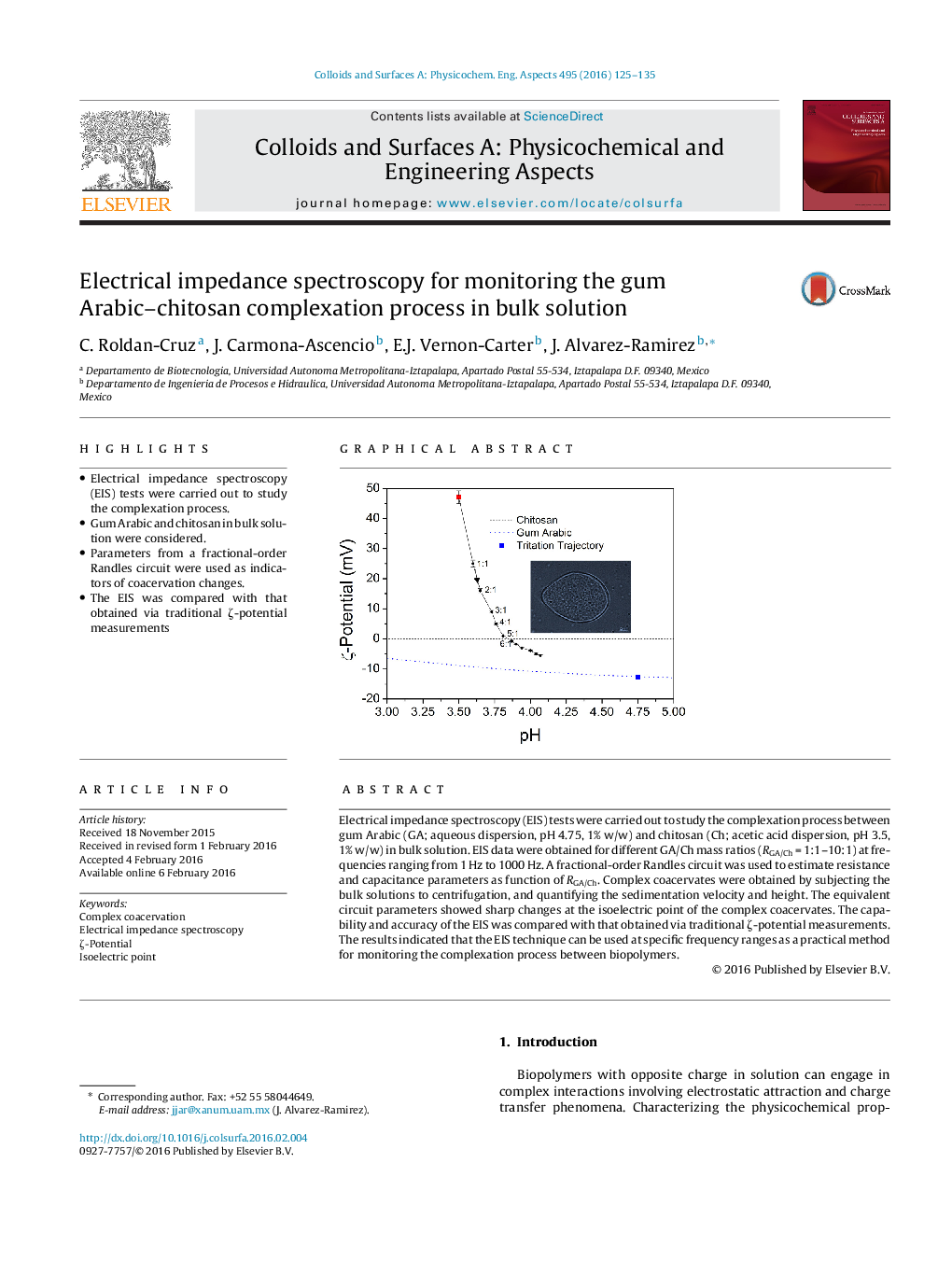
Electrical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) tests were carried out to study the complexation process between gum Arabic (GA; aqueous dispersion, pH 4.75, 1% w/w) and chitosan (Ch; acetic acid dispersion, pH 3.5, 1% w/w) in bulk solution. EIS data were obtained for different GA/Ch mass ratios (RGA/Ch = 1:1–10:1) at frequencies ranging from 1 Hz to 1000 Hz. A fractional-order Randles circuit was used to estimate resistance and capacitance parameters as function of RGA/Ch. Complex coacervates were obtained by subjecting the bulk solutions to centrifugation, and quantifying the sedimentation velocity and height. The equivalent circuit parameters showed sharp changes at the isoelectric point of the complex coacervates. The capability and accuracy of the EIS was compared with that obtained via traditional ζ-potential measurements. The results indicated that the EIS technique can be used at specific frequency ranges as a practical method for monitoring the complexation process between biopolymers.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide